
The Serranidae are a large family of fishes belonging to the order Perciformes. The family contains about 450 species in 65 genera, including the sea basses and the groupers. Although many species are small, in some cases less than 10 cm (3.9 in), the giant grouper is one of the largest bony fishes in the world, growing to 2.7 m in length and 400 kg (880 lb) in weight. Representatives of this group live in tropical and subtropical seas worldwide.

A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.

Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral.

Groupers are fish of any of a number of genera in the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae, in the order Perciformes.

Amphiprion akindynos, the Barrier Reef anemonefish, is a species of anemonefish that is principally found in the Great Barrier Reef of Australia, but also in nearby locations in the Western Pacific. The species name 'akindynos' is Greek, meaning 'safe' or 'without danger' in reference to the safety afforded amongst the tentacles of its host anemone. Like all anemonefishes it forms a symbiotic mutualism with sea anemones and is unaffected by the stinging tentacles of the host anemone. It is a sequential hermaphrodite with a strict size-based dominance hierarchy: the female is largest, the breeding male is second largest, and the male non-breeders get progressively smaller as the hierarchy descends. They exhibit protandry, meaning the breeding male will change to female if the sole breeding female dies, with the largest non-breeder becomes the breeding male. The fish's natural diet includes zooplankton.

The ring-tailed cardinalfish is a widespread fish species in the family Apogonidae found in the Red Sea and off East Africa to Papua New Guinea, north to Japan, and south to Australia.

The potato grouper, also called the potato cod or potato bass, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution.

The golden grouper, also known as the pink grouper or Powell's grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the eastern Indian Ocean and Western Pacific Ocean.

Ostorhinchus cyanosoma, commonly known as the yellow-striped cardinalfish, goldenstriped cardinalfish, or the orange-lined cardinalfish, is a species of marine fish in the cardinalfish family of order Perciformes. It is native to the Indo-West Pacific.
Ceratomyxa is a genus of myxozoan.
Anilocra pomacentri is a species of marine isopod in the family Cymothoidae. It is found off the coast of eastern Australia and is an external parasite of the yellowback puller, a species of damselfish. The presence of the parasite on a fish causes a significant slowing of the growth rate and an increased mortality.
Ceratomyxa brayi is a species of myxosporean parasites that infect gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Cephalopholis boenak.
Ceratomyxa gleesoni is a myxosporean parasite that infects gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Plectropomus leopardus.
Ceratomyxa hooperi is a myxosporean parasite that infects gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Epinephelus quoyanus.
Ceratomyxa nolani is a myxosporean parasite that infects gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Epinephelus quoyanus.
Ceratomyxa whippsi is a myxosporean parasite that infects gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Cephalopholis boenak.
Ceratomyxa yokoyamai is a myxosporean parasite that infects gall-bladders of serranid fishes from the Great Barrier Reef. It was first found on Epinephelus maculatus.
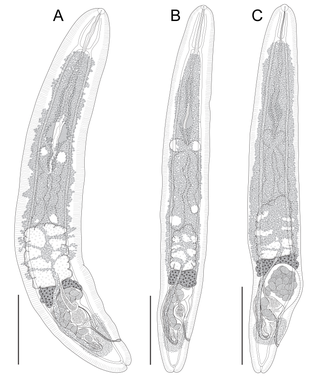
Aporocotylidae is a family of trematodes within the order Diplostomida, which contains species commonly known as fish blood flukes. It contains more than 40 genera, the largest being Cardicola. Species in this family parasite fish in both fresh and marine water.
Pseudorhabdosynochus youngi is species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the blacktip grouper, Epinephelus fasciatus. It was described in 2009.
Ceratomyxa auratae is a species of myxozoan parasite that infects the gall bladder of the gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata. It was discovered in an aquaculture facility in southern Portugal.










