
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.
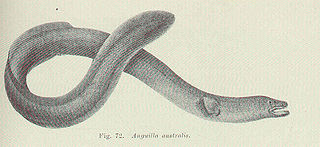
The short-finned eel, also known as the shortfin eel, is one of the 15 species of eel in the family Anguillidae. It is native to the lakes, dams and coastal rivers of south-eastern Australia, New Zealand, and much of the South Pacific, including New Caledonia, Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, Tahiti, and Fiji.

The New Zealand blue cod is a temperate marine fish of the family Pinguipedidae. It is also known by its Māori names, rāwaru, pākirikiri and patutuki, and by its other names in English, Boston blue cod, New Zealand cod or sand perch.

The New Zealand pea crab, is a species of small, parasitic crab that lives most commonly inside New Zealand green-lipped mussels. Adult females are about the size and shape of a pea, while adult males are smaller and flatter. Adult New Zealand pea crabs are completely reliant on their host mussel for shelter and food, which it steals from the mussel's gills. The New Zealand pea crab is found throughout New Zealand and can infect up to 70% of natural populations. These crabs are of concern to green-lipped mussel aquaculture because they reduce the size and growth of mussels, although infected mussels can be harvested and consumed.

The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is the only family in the monotypic subclass Branchiura and the order Arguloida, although a second family, Dipteropeltidae, has been proposed. Although they are thought to be primitive forms, they have no fossil record.

The orange wrasse is a species of wrasse native to the Pacific Ocean from Australia to New Zealand and the Kermadec Islands. It is found in inshore waters at depths from 10 to 50 metres. It can reach a length of 17 centimetres (6.7 in) SL. It can also be found in the aquarium trade.

The New Zealand longfin eel, also known as ōrea, is a species of freshwater eel that is endemic to New Zealand. It is the largest freshwater eel in New Zealand and the only endemic species – the other eels found in New Zealand are the native shortfin eel, also found in Australia, and the naturally introduced Australian longfin eel. Longfin eels are long-lived, migrating to the Pacific Ocean near Tonga to breed at the end of their lives. They are good climbers as juveniles and so are found in streams and lakes a long way inland. An important traditional food source for Māori, who name them ōrea, longfin eel numbers are declining and they are classified as endangered, but over one hundred tonnes are still commercially fished each year.
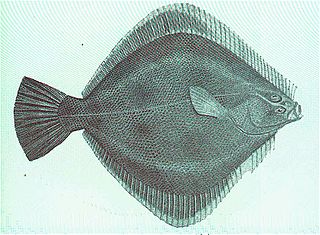
The New Zealand sand flounder is a righteye flounder of the genus Rhombosolea, found around New Zealand in shallow waters down to depths of 100 m.
Paracalliope is a genus of amphipod crustaceans that live in Australasia. They include the most common freshwater amphipods in New Zealand, where they are particularly frequent in slow-flowing reaches of rivers. They shelter among weed beds and are important prey items for fish such as the New Zealand smelt, Retropinna retropinna, which are in turn important prey for the freshwater eels Anguilla australis and Anguilla dieffenbachii. Paracalliope acts as an intermediate host for the nematode Hedruris spinigera, which can thus reach their primary host, the eel.

The bluefin gurnard or Pacific red gurnard is a species of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. Its Māori names are kumukumu and pūwahaiau. It is found in the western Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean, being common around Australia and New Zealand at depths down to 200 metres (660 ft). The fish is one of the most important commercial fish species in New Zealand.

Poecilostomatoida is a suborder of copepods. Although it was previously considered a separate order.
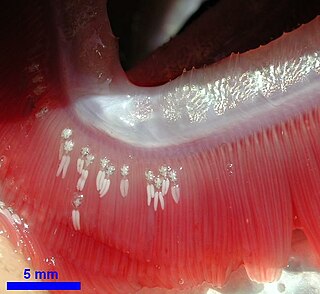
Ergasilidae is a widespread family of copepods and comprises many species. The type genus is Ergasilus. With a few doubtful exceptions all ergasilids are parasitic on fishes.

Acartia clausi is a species of marine copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. This species was previously thought to have a worldwide distribution but recent research has restricted its range to coastal regions of the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean as far north as Iceland, the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea, with specimens from other regions assigned to different species.
Acartia teclae is a species of copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. This species was discovered when specimens previously identified as Acartia clausi were examined and found to belong to a separate species. This species appears to have a similar range to, and occupies similar brackish estuarine habitats as, Acartia lefevreae but differs in the absence of spines on the dorsal part of the posterior body segment (metasome).
Acartia ensifera is a species of marine copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. This is a slender copepod, around 0.8–0.9 mm (0.031–0.035 in) in length, with distinctively long caudal rami. It is found around the coasts of New Zealand.
Acartia simplex is a species of marine copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. It is found in the waters near Australia and New Zealand.
Acartia jilletti is a species of marine copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. This species has a total length of up to 1 mm. It is very similar to Acartia ensifera but the female can be distinguished by the shorter caudal rami and the male by the relative length of spines on the fifth pair of legs. This species has been recorded from scattered locations around the coast of New Zealand.
Acartia tranteri is a species of marine copepod belonging to the family Acartiidae. This Australian species is related to the New Zealand species A. ensifera, A. jilletti and A. simplex but can be distinguished by the lack of any ventral prominence posterior to the genital opening in the female and the presence of posterior spines on the metasome of the male. It is found off the southern coast of Australia.
The Tasman Front is a relatively warm water east-flowing surface current and thermal boundary that separates the Coral Sea to the north and the Tasman Sea to the south.
Ergasilus curticrus is a freshwater parasitic copepod named in 2015. Described from the Orinoco river basin, it was found solely to be hosted by individuals of the Characiform fish species Bryconops giacopinii. Of those located in South America, it is one of only five species in its genus to be found outside of Brazil.













