
Salmon is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic and North Pacific basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, char, grayling, whitefish, lenok and taimen.

Fish farming or pisciculture involves commercial breeding of fish, most often for food, in fish tanks or artificial enclosures such as fish ponds. It is a particular type of aquaculture, which is the controlled cultivation and harvesting of aquatic animals such as fish, crustaceans, molluscs and so on, in natural or pseudo-natural environments. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement a species' natural numbers is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Worldwide, the most important fish species produced in fish farming are carp, catfish, salmon and tilapia.

Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.

Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

A salmon run is an annual fish migration event where many salmonid species, which are typically hatched in fresh water and live most of the adult life downstream in the ocean, swim back against the stream to the upper reaches of rivers to spawn on the gravel beds of small creeks. After spawning, all species of Pacific salmon and most Atlantic salmon die, and the salmon life cycle starts over again with the new generation of hatchlings.

Anisakis is a genus of parasitic nematodes that have life cycles involving fish and marine mammals. They are infective to humans and cause anisakiasis. People who produce immunoglobulin E in response to this parasite may subsequently have an allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis, after eating fish infected with Anisakis species.

Numedalslågen is a river located in the counties of Vestfold and Telemark and Viken in southeastern Norway. It is one of the longest rivers in Norway.
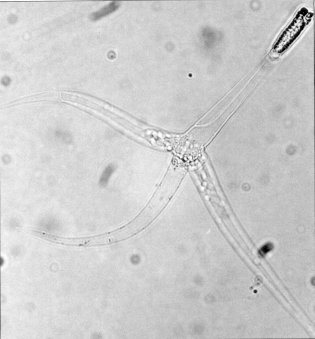
Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany in 1893, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe, the United States, South Africa, Canada and other countries from shipments of cultured and wild fish. In the 1980s, M. cerebralis was found to require a tubificid oligochaete to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules. This infects the cartilage and possibly the nervous tissue of salmonids, causing a potentially lethal infection in which the host develops a black tail, spinal deformities, and possibly more deformities in the anterior part of the fish.
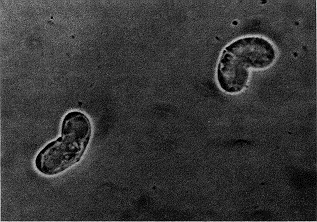
Ceratonova shasta is a myxosporean parasite that infects salmonid fish on the Pacific coast of North America. It was first observed at the Crystal Lake Hatchery, Shasta County, California, and has now been reported from Idaho, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia and Alaska.
Infectious salmon anemia (ISA) is a viral disease of Atlantic salmon caused by Salmon isavirus. It affects fish farms in Canada, Norway, Scotland and Chile, causing severe losses to infected farms. ISA has been a World Organisation for Animal Health notifiable disease since 1990. In the EU, it is classified as a non-exotic disease, and is monitored by the European Community Reference Laboratory for Fish Diseases.

The Driva river runs through Trøndelag and Møre og Romsdal counties in Norway. The headwaters lie in the Dovrefjell mountains in the south, from where it flows northward, downward through the Drivdalen valley in the municipality of Oppdal. When the river gets to the village of Oppdal, it turns westward and heads down the Sunndalen valley to the Sunndalsfjord at the village of Sunndalsøra in the municipality of Sunndal. Some of the other villages along the river include Grøa, Hoelsand, Lønset, and Vognillan. The Norwegian National Road 70 follows the river for most of its course.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.

Vefsna (Norwegian), also known as Vaapstenjeanoe (Southern Sami) or Vapstälven (Swedish), is the largest river in Nordland county, Norway. It is 163 kilometres (101 mi) long and drains a watershed of 4,122 square kilometres (1,592 sq mi). Its headwaters lie in the mountains of Børgefjell National Park at the lake Simskardvatnet. The river runs through the municipalities of Hattfjelldal, Grane, and Vefsn. The southern parts of the river are sometimes called the river Susna. The river flows north, not far from the Swedish border, and some of the minor tributaries come from Sweden. At the town of Mosjøen, the river discharges into the Vefsnfjord. The Laksforsen waterfall lies along its course.

The salmon louse is a species of copepod in the genus Lepeophtheirus. It is a sea louse, a parasite living mostly on salmon, particularly on Pacific and Atlantic salmon and sea trout, but is also sometimes found on the three-spined stickleback. It feeds on the mucus, skin and blood of the fish. Once detached, they can be blown by wind across the surface of the sea, like plankton. When they encounter a suitable marine fish host, they adhere themselves to the skin, fins, or gills of the fish, and feed on the mucus or skin. Sea lice only affect fish and are not harmful to humans.

Nanophyetus salmincola is a food-borne intestinal trematode parasite prevalent on the Pacific Northwest coast. The species may be the most common trematode endemic to the United States.

The aquaculture of salmonids is the farming and harvesting of salmonid fish under controlled conditions for both commercial and recreational purposes. Salmonids, along with carp and tilapia, are the three most important fish groups in aquaculture. The most commonly commercially farmed salmonid is the Atlantic salmon.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.

Diseases and parasites in salmon, trout and other salmon-like fishes of the family Salmonidae are also found in other fish species. The life cycle of many salmonids is anadromous, so such fish are exposed to parasites in fresh water, brackish water and saline water.

Batnfjordelva is a river in Gjemnes Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. It originates from the lake Botnvatnet and it flows to the east and later northeast until it empties into the Batnfjorden at the village of Batnfjordsøra. The river is 19.2 kilometres (11.9 mi) long and it has a catchment of 70 square kilometres (27 sq mi). The discharge rate at the mouth of the river is 4.61 cubic metres per second (163 cu ft/s).

The Monopisthocotylea are a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea.





















