External links
| | This article about a philanthropic or charitable organization is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Cesvi (Italian, "cooperazione e sviluppo", cooperation and development) is an Italian humanitarian organization. Founded in 1985, it has about 30 offices all over the world.
Cesvi provides assistance in emergency situations (including famine and epidemics (especially malaria and dengue in the South East Asia, malaria and HIV/AIDS in Africa), helps refugees (e.g. North Uganda and DR Congo) and flood victims, supports reconstruction after disasters (earthquakes, tsunami), implements projects for sustainable development and environmental defence in poor countries.
The organization is sponsored by Italian private donors (34%), public donors (European Union, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Italy, United Nations agencies), foundations, companies, local authorities. Among its fields of expertise are the problems of food/nutrition, HIV/AIDS, health, refugees and IDPs, shelter, water and sanitation.
The Cesvi projects in Vietnam include education of mothers and schoolchildren, growth monitoring, training of health workers on community and clinical nutrition, scientific workshops for university professors and trainers, production and distribution of food and supplements for kindergartens, hospitals and families, microcredit support of integrated farming systems at the household level, clinical consultations, nutritional rehabilitation.

The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria is an international financing and partnership organization that aims to "attract, leverage and invest additional resources to end the epidemics of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria to support attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations". This multistakeholder international organization maintains its secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland. The organization began operations in January 2002. Microsoft founder Bill Gates was one of the first donors to provide seed money for the partnership. From January 2006 it has benefited from certain US Privileges, Exemptions, and Immunities under executive order 13395, which conferred International Organizations Immunities Act status on it.
The European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP) is a partnership between the European Union (EU), Norway, Switzerland and developing countries and other donors, as well as the pharmaceutical industry, to enable clinical trials and the development of new medicines and vaccines against HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria. The need for global action against these diseases in order to promote poverty reduction has been recognised by the United Nations, the G8, and the African Union, and the program envisioned the provision of €600 million for the period 2003–2007 in order to translate medical research results into clinical applications relevant to the needs of developing countries.
FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization based in North Carolina. FHI 360 operates in more than 70 countries and all U.S. states and territories. Established in 1971, the organization manages projects relating to family planning and reproductive health. In 1986 the organization began a worldwide response to HIV/AIDS. FHI 360's research and programs also address malaria, tuberculosis, and other infectious and chronic diseases and international agencies, governments, foundations, research institutions, and individual donors.
Diseases of poverty are diseases that are more prevalent in low-income populations. They include infectious diseases, as well as diseases related to malnutrition and poor health behaviour. Poverty is one of the major social determinants of health. The World Health Report (2002) states that diseases of poverty account for 45% of the disease burden in the countries with high poverty rate which are preventable or treatable with existing interventions. Diseases of poverty are often co-morbid and ubiquitous with malnutrition. Poverty increases the chances of having these diseases as the deprivation of shelter, safe drinking water, nutritious food, sanitation, and access to health services contributes towards poor health behaviour. At the same time, these diseases act as a barrier for economic growth to affected people and families caring for them which in turn results into increased poverty in the community. These diseases produced in part by poverty are in contrast to diseases of affluence, which are diseases thought to be a result of increasing wealth in a society.

PATH is an international, nonprofit global health organization. PATH is based in Seattle with 1,600 employees in more than 70 countries around the world. Its president and CEO is Nikolaj Gilbert, who is also the Managing Director and CEO of Foundations for Appropriate Technologies in Health (FATH), PATH's Swiss subsidiary. PATH focuses on six platforms: vaccines, drugs, diagnostics, devices, system, and service innovations.

The United States established diplomatic relations with Malawi in 1964 after Malawi gained independence from the United Kingdom. Malawi's transition from a one-party state to a multi-party democracy significantly strengthened the already cordial U.S. relationship with Malawi. Significant numbers of Malawians study in the United States. The United States has an active Peace Corps program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Health and Human Services, and an Agency for International Development (USAID) mission in Malawi. Both countries have a common history and English language, as they were part of the British Empire.

The diplomatic relationship between the United States of America and Zambia can be characterized as warm and cooperative. Relations are based on their shared experiences as British colonies, both before, after and during the struggle for independence. Several U.S. administrations cooperated closely with Zambia's first president, Kenneth Kaunda, in hopes of facilitating solutions to the conflicts in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. The United States works closely with the Zambian Government to defeat the HIV/AIDS pandemic that is ravaging Zambia, to promote economic growth and development, and to effect political reform needed to promote responsive and responsible government. The United States is also supporting the government's efforts to root out corruption. Zambia is a beneficiary of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). The U.S. Government provides a variety of technical assistance and other support that is managed by the Department of State, U.S. Agency for International Development, Millennium Challenge Account (MCA) Threshold Program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Treasury, Department of Defense, and Peace Corps. The majority of U.S. assistance is provided through the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), in support of the fight against HIV/AIDS.
The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program is responsible for collecting and disseminating accurate, nationally representative data on health and population in developing countries. The project is implemented by ICF International and is funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) with contributions from other donors such as UNICEF, UNFPA, WHO, and UNAIDS.
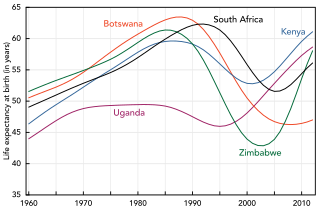
HIV/AIDS affects economic growth by reducing the availability of human capital. Without proper prevention, nutrition, health care and medicine that is available in developing countries, large numbers of people are developing AIDS.

Rwanda faces a generalized epidemic, with an HIV prevalence rate of 3.1 percent among adults ages 15 to 49. The prevalence rate has remained relatively stable, with an overall decline since the late 1990s, partly due to improved HIV surveillance methodology. In general, HIV prevalence is higher in urban areas than in rural areas, and women are at higher risk of HIV infection than men. Young women ages 15 to 24 are twice as likely to be infected with HIV as young men in the same age group. Populations at higher risk of HIV infection include people in prostitution and men attending clinics for sexually transmitted infections.
Cases of HIV/AIDS in Peru are considered to have reached the level of a concentrated epidemic.

Health problems have been a long-standing issue limiting development in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Volunteer Partnerships for West Africa (VPWA) is a volunteer-driven, non-profit NGO based in Ghana, which aims to promote better life opportunities for people in underprivileged communities through sustainable development initiatives. VPWA has pioneered several social innovations in the region, including micro leasing, the establishment of a Children and Youth Development Centre in the Eastern Region of Ghana, and campaigns such as Deworm Ghana, Green Ghana, Kick Malaria Out, and Street Library.
Starfish Greathearts Foundation is an international non-governmental organization formed in 2001 to help orphaned and vulnerable children in South Africa. Its mission is to help make a difference in the lives of such children via community-based projects working at grassroots level. This enables individual communities to develop their own solutions to fight the challenges they come across. As of January 2022, Starfish projects have reached more than 220,000 children in 110 communities across South Africa.</ref> Starfish Greathearts Foundation.

Jeannette Nyiramongi Kagame is the wife of Paul Kagame. She became the First Lady of Rwanda when her husband took office as President in 2000. Kagame is the founder and chairman of Imbuto Foundation, a non-profit organization whose mission is to support the development of a healthy, educated and prosperous society.
Global Health Initiatives (GHIs) are humanitarian initiatives that raise and disburse additional funds for infectious diseases – such as AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria – for immunizations and for strengthening health systems in developing countries. GHIs classify a type of global initiative, which is defined as an organized effort integrating the involvement of organizations, individuals, and stakeholders around the world to address a global issue.
People living with HIV/AIDS face increased challenges in maintaining proper nutrition. Despite developments in medical treatment, nutrition remains a key component in managing this condition. The challenges that those living with HIV/AIDS face can be the result of the viral infection itself or from the effects of anti-HIV therapy (HAART).

Health in Mozambique has a complex history, influenced by the social, economic, and political changes that the country has experienced. Before the Mozambican Civil War, healthcare was heavily influenced by the Portuguese. After the civil war, the conflict affected the country's health status and ability to provide services to its people, breeding the host of health challenges the country faces in present day.

Armenia was admitted into the United Nations on 2 March 1992, following its independence from the Soviet Union. In December 1992, the UN opened its first office in Yerevan. Since then, Armenia has signed and ratified several international treaties. There are 20 specialized agencies, programs, and funds operating in the country under the supervision of the UN Resident Coordinator. Armenia strengthened its relations with the UN by cooperating with various UN agencies and bodies such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the World Food Programme, and with the financial institutions of the UN. Armenia is a candidate to preside as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council in 2031.

The Catholic Medical Mission Board (CMMB) is an international, faith-based NGO, providing long-term, co-operative medical and development aid to communities affected by poverty and healthcare issues. It was established in 1912 and officially registered in 1928. CMMB is headquartered in New York City, USA, and currently has country offices in Haiti, Kenya, Peru, South Sudan, and Zambia.