
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of L1-L2. It splits a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. It also provides motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.

The pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle of the human chest. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor muscle.

Pectoralis minor muscle is a thin, triangular muscle, situated at the upper part of the chest, beneath the pectoralis major in the human body. It arises from ribs III-V; it inserts onto the coracoid process of the scapula. It is innervated by the medial pectoral nerve. Its function is to stabilise the scapula by holding it fast in position against the chest wall.
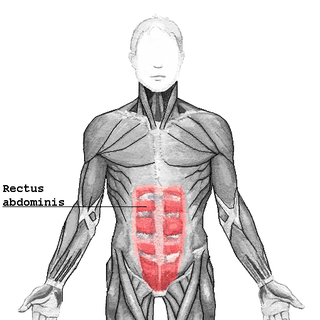
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly.
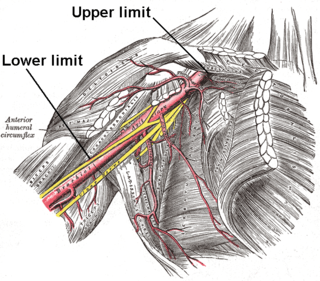
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule, it gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The subclavius is a small triangular muscle, placed between the clavicle and the first rib. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles, the subclavius muscle makes up the anterior axioappendicular muscles, also known as anterior wall of the axilla.

The thoracoacromial artery is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor.

The medial pectoral nerve is (typically) a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1. It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor muscle, and the lower half of the pectoralis major muscle. It runs along the inferior border of the pectoralis minor muscle.

The lateral pectoral nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7.
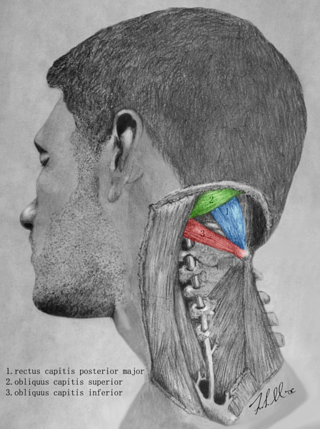
The suboccipital triangle is a region of the neck bounded by the following three muscles of the suboccipital group of muscles:

The pectoral fascia is a thin lamina, covering the surface of the pectoralis major, and sending numerous prolongations between its fasciculi: it is attached, in the middle line, to the front of the sternum; above, to the clavicle; laterally and below it is continuous with the fascia of the shoulder, axilla, and thorax.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.

The clavipectoral triangle is an anatomical region found in humans and other animals. It is bordered by the following structures:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

















