| Rhomboid minor | |
|---|---|
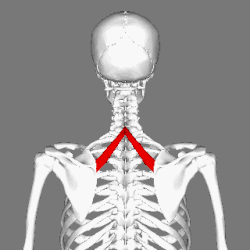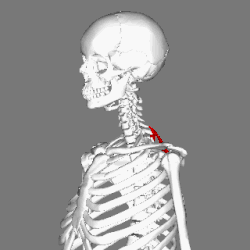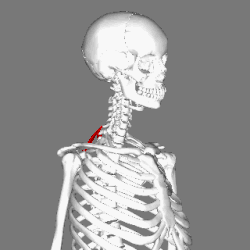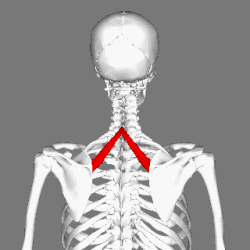
 Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column. (Rhomboid minor in red) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7-T1 |
| Insertion | Medial border of scapula, superior to the insertion of rhomboid major muscle |
| Artery | Deep branch of transverse cervical artery |
| Nerve | Dorsal scapular nerve (C4–5) |
| Actions | Retracts and rotates scapula, fixes scapula to thoracic wall |
| Antagonist | Serratus anterior |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rhomboideus minor |
| TA98 | A04.3.01.008 |
| TA2 | 2233 |
| FMA | 13380 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula to the vertebrae of the spinal column. [1] It arises from the nuchal ligament, the 7th cervical and 1st thoracic vertebrae and intervening supraspinous ligaments; it inserts onto the medial border of the scapula, and is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve. It acts together with the rhomboid major to keep the scapula pressed against the thoracic wall. [2]