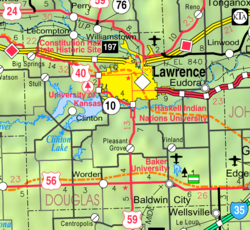
Douglas County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kansas. Its county seat and most populous city is Lawrence. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 118,785, making it the fifth-most populous county in Kansas. The county was named after Stephen Douglas, a U.S. Senator from Illinois and advocate for the popular sovereignty choice in the Kansas slavery debate.

Lawrence is a city in and the county seat of Douglas County, Kansas, United States, and the sixth-largest city in the state. It is in the northeastern sector of the state, astride Interstate 70, between the Kansas and Wakarusa Rivers. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 94,934. Lawrence is a college town and the home to both the University of Kansas and Haskell Indian Nations University.

Lecompton is a city in Douglas County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 588. Lecompton was the de jure territorial capital of Kansas from 1855 to 1861, and the Douglas County seat from 1855 to 1858. Anti-slavery Lawrence became the de facto capital during the latter part of this period, when the county seat was moved there. This time period was known as Bleeding Kansas, due to the violence perpetrated by the pro-slavery, and to a lesser extent the anti-slavery, factions in the eastern part of the state. Lecompton was a hotbed of pro-slavery sentiment during the mid-1800s.

The Lecompton Constitution (1858) was the second of four proposed constitutions for the state of Kansas. Named for the city of Lecompton where it was drafted, it was strongly pro-slavery. It never went into effect.

Clinton Lake is a reservoir on the southwestern edge of Lawrence, Kansas. The lake was created by the construction of the Clinton Dam, and the 35 square miles (91 km2) of land and water is maintained by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.

Stull is an unincorporated community in Douglas County, Kansas, United States. Founded in 1857, the settlement was initially known as Deer Creek until it was renamed after its only postmaster, Sylvester Stull. As of 2018, only a handful of structures remain in the area.

Richland is currently a ghost town in southeastern Shawnee County, Kansas, United States.

Big Springs is an unincorporated community in northwest Douglas County, Kansas, United States.

Prairie City is a ghost town in southeast Douglas County, Kansas, United States, near present-day Baldwin City.
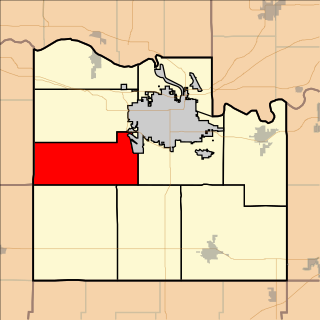
Clinton Township is a township in Douglas County, Kansas, USA. As of the 2000 census, its population was 531. It took its name from Clinton, Illinois.

Wakarusa Township is a township in Douglas County, Kansas, USA. As of the 2010 census, its population was 2,318. It was named for the Wakarusa River which flows through Douglas County from Wabaunsee County to the Kansas River near Eudora.

Lecompton Constitution Hall, also known as Constitution Hall, is a building in Lecompton, Kansas, that played an important role in the long-running Bleeding Kansas crisis over slavery in Kansas. It is operated by the Kansas Historical Society as Constitution Hall State Historic Site.

Williamstown is an unincorporated community in southeastern Jefferson County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the community and nearby areas was 96. It is located south of the junction of US-24 and US-59 highways.

Lone Star is an unincorporated community in Douglas County, Kansas, United States. It is located 7 miles (11 km) southwest of Lawrence.

John Henry Kagi, also spelled John Henri Kagi, was an American attorney, abolitionist, and second in command to John Brown in Brown's failed raid on Harper's Ferry. He bore the title of "Secretary of War" in Brown's "provisional government." At age 24, Kagi was killed during the raid. He had previously been active in fighting on the abolitionist side in 1856 in "Bleeding Kansas". He was considered an excellent debater and speaker.

U.S. Route 59 (US-59) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from the Mexico–US border in Laredo, Texas, as a continuation of Mexican Federal Highway 85D north to the Lancaster–Tolstoi Border Crossing on the Canada–US border, where it continues as Manitoba Highway 59. In the U.S. state of Kansas, US-59 is a main north–south highway that travels from Chetopa to Atchison.
Franklin is a ghost town in Douglas County, Kansas, United States. Established as a proslavery stronghold, the town played a key role in the "Bleeding Kansas" conflict that troubled the territory in the 1850s.
The Battle of Fort Titus occurred during conflicts in the Kansas Territory between abolitionist and pro-slavery militias prior to the American Civil War. The era is known as Bleeding Kansas.
Fort Titus was the fortress residence of pro-slavery advocate Henry T. Titus, built in Kansas in April 1856, during a period when forces aligned with Titus came into conflict with free-state settlers. The wider conflict, which emerged from a political and ideological debate over the legality of slavery in the proposed state of Kansas, became known as Bleeding Kansas.

Samuel Jefferson Jones was a pro-slavery settler who held the position of Douglas County sheriff in Kansas Territory from late 1855 until early 1857. He helped found the territorial capital of Lecompton and played a prominent role in the "Bleeding Kansas" conflict.