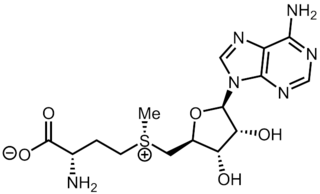
S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952.
In enzymology, a cobalt-factor II C20-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a magnesium protoporphyrin IX methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a precorrin-2 C20-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, precorrin-3B C17-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a precorrin-4 C11-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
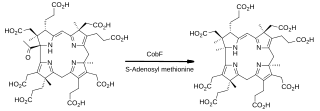
In enzymology, precorrin-6A synthase (deacetylating) (EC 2.1.1.152) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a precorrin-6Y C5,15-methyltransferase (decarboxylating) (EC 2.1.1.132) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Caffeine synthase is a methyltransferase enzyme involved in the caffeine biosynthesis pathway. It is expressed in tea species, coffee species, and cocoa species. The enzyme catalyses the following reactions:

Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet.
Radical SAM is a designation for a superfamily of enzymes that use a [4Fe-4S]+ cluster to reductively cleave S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to generate a radical, usually a 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical (5'-dAdo), as a critical intermediate. These enzymes utilize this radical intermediate to perform diverse transformations, often to functionalize unactivated C-H bonds. Radical SAM enzymes are involved in cofactor biosynthesis, enzyme activation, peptide modification, post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications, metalloprotein cluster formation, tRNA modification, lipid metabolism, biosynthesis of antibiotics and natural products etc. The vast majority of known radical SAM enzymes belong to the radical SAM superfamily, and have a cysteine-rich motif that matches or resembles CxxxCxxC. rSAMs comprise the largest superfamily of metal-containing enzymes.
5-hydroxyfuranocoumarin 5-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:5-hydroxyfurocoumarin 5-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
8-hydroxyfuranocoumarin 8-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:8-hydroxyfurocoumarin 8-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase, uroporphyrinogen methyltransferase, uroporphyrinogen-III methyltransferase, adenosylmethionine-uroporphyrinogen III methyltransferase, S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent uroporphyrinogen III methylase, uroporphyrinogen-III methylase, SirA, CysG, CobA, uroporphyrin-III C-methyltransferase, S-adenosyl-L-methionine:uroporphyrin-III C-methyltransferase) is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Demethylmenaquinone methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:demethylmenaquinone methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cobalt-precorrin-5B (C1)-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.195), cobalt-precorrin-6A synthase, CbiD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:cobalt-precorrin-5B (C1)-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
tRNA (cytidine56-2'-O)-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tRNA (cytidine56-2'-O)-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavanone 4'-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:2,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavanone 4'-O-methyltransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cobalt-precorrin 5A hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.12), CbiG (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name cobalt-precorrin 5A acylhydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction









