
Amaryllis is the only genus in the subtribe Amaryllidinae. It is a small genus of flowering bulbs, with two species. The better known of the two, Amaryllis belladonna, is a native of the Western Cape region of South Africa, particularly the rocky southwest area between the Olifants River Valley and Knysna.

The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface.

The pied kingfisher is a species of water kingfisher widely distributed across Africa and Asia. Originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, it has five recognised subspecies. Its black and white plumage and crest, as well as its habit of hovering over clear lakes and rivers before diving for fish, make it distinctive. Males have a double band across the breast, while females have a single broken breast band. They are usually found in pairs or small family groups. When perched, they often bob their head and flick up their tail.

Freesia is a genus of herbaceous perennial flowering plants in the family Iridaceae, first described as a genus in 1866 by Christian Friedrich Ecklon (1886) and named after the German botanist and medical practitioner, Friedrich Freese (1795–1876). It is native to the eastern side of southern Africa, from Kenya south to South Africa, most species being found in Cape Provinces. Species of the former genus Anomatheca are now included in Freesia. The plants commonly known as "freesias", with fragrant funnel-shaped flowers, are cultivated hybrids of a number of Freesia species. Some other species are also grown as ornamental plants.
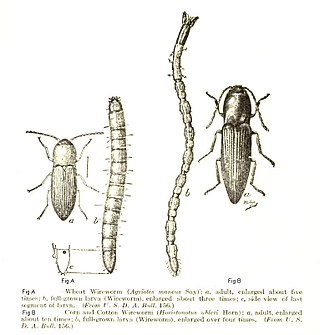
Elateridae or click beetles are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, spring beetles or skipjacks. This family was defined by William Elford Leach (1790–1836) in 1815. They are a cosmopolitan beetle family characterized by the unusual click mechanism they possess. There are a few other families of Elateroidea in which a few members have the same mechanism, but most elaterid subfamilies can click. A spine on the prosternum can be snapped into a corresponding notch on the mesosternum, producing a violent "click" that can bounce the beetle into the air. Clicking is mainly used to avoid predation, although it is also useful when the beetle is on its back and needs to right itself. There are about 9300 known species worldwide, and 965 valid species in North America.

Kniphofia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae, first described as a genus in 1794. All species of Kniphofia are native to Africa. Common names include tritoma, red hot poker, torch lily and poker plant.

Joseph Marie Henry Alfred Perrier de la Bâthie was a French botanist who specialized in the plants of Madagascar.

Anthonomus is a genus of weevils. This genus includes major agricultural pests such as the boll weevil, strawberry blossom weevil, and pepper weevil, as well as promising biological pest control agents such as Anthonomus santacruzi.

Haworthia is a large genus of small succulent plants endemic to Southern Africa (Mozambique, Namibia, Lesotho, Eswatini and South Africa).

Patersonia, is a genus of plants whose species are commonly known as native iris or native flag and are native to areas from Malesia to Australia.

Dillwynia is a genus of about 20 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, and is endemic to Australia. Plants in this genus are shrubs with simple leaves and yellow or red and yellow flowers similar to others in the family.

Ardisia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Primulaceae. It was in the former Myrsinaceae family now recognised as the myrsine sub-family Myrsinoideae. They are distributed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands, mainly in the tropics. There are over 700 accepted species. One species, Ardisia japonica is one of the 50 fundamental herbs in traditional Chinese medicine.

Gethyllis, commonly called Kukumakranka, Koekemakranka, or Kroekemakrank, is a genus of bulbous plant in the amaryllid family with some 33 accepted species. It is native to the Cape Provinces, the Northern Provinces and the Free State of South Africa, as well as Botswana and Namibia.

Austrostipa is a primarily Australian genus of plants in the grass family, commonly called speargrass.

Randia, commonly known as indigoberry, is a mostly Neotropical genus of shrubs or small trees in the Rubiaceae. As of February 2022 Plants of the World Online lists a total of 112 accepted species in the genus. Several Australian species have been reassigned to the genus Atractocarpus. These include the garden plants Atractocarpus chartaceus and A. fitzalanii.

Rhadinothamnus is a small genus of shrubs in the family Rutaceae. The genus, which is endemic to Western Australia, was formally described in 1971.
Manjekia is a monotypic genus of palm for a species of palm native to Biak island, Indonesia, off the northwest coast of New Guinea. The genus was proposed in 2014.

Kailarsenia is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Gardenieae of the family Rubiaceae. Its native range is Indo-China to West Malesia.

Malachra is a genus of flowering plants in the family Malvaceae, native to the Americas and Africa, and introduced in places in Asia. They lack an epicalyx, an autapomorphy within their tribe Hibisceae, which is known for having epicalyces.


















