
Vanilloideae is one of the subfamilies of orchids belonging to the large family Orchidaceae.

Adrorhizinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Vandeae.

Laeliinae is a Neotropical subtribe including 40 orchid genera, such as Brassavola, Laelia and Cattleya. The genus Epidendrum is the largest within this subtribe, containing about 1500 species. This is followed by the genus Encyclia, with over 120 species.

Pogoniopsis is a genus of orchids. It contains two known species, both endemic to Brazil. It was previously included in the subfamily Vanilloideae, but is now placed in the tribe Triphoreae of the subfamily Epidendroideae.

Arethuseae is a mid-sized tribe of orchids in the subfamily Epidendroideae. This tribe was initially categorized by John Lindley in 1840. Its largest subtribes are Arethusinae and Coelogyninae.

Bletiinae is a small-sized subtribe of orchids in the tribe Epidendreae of the subfamily Epidendroideae.

Disperis is a genus of plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has about 78 species. Most of the species are from tropical and southern Africa, as well as Indian Ocean islands. A few are native to the tropical or the warmer subtropical regions of Asia and Malesia.

Wullschlaegelia is a genus of orchids,, consisting of two species in the Caribbean Islands and to much of Latin America from southern Mexico to northern Argentina. These are myco-heterotrophic plants, lacking chlorophyll and subsisting entirely on nutrients obtained from soil fungi. The genus has previously been included in the tribe Calypsoeae, but is now included as the only genus in the tribe Wullschlaegelieae, pending further study.
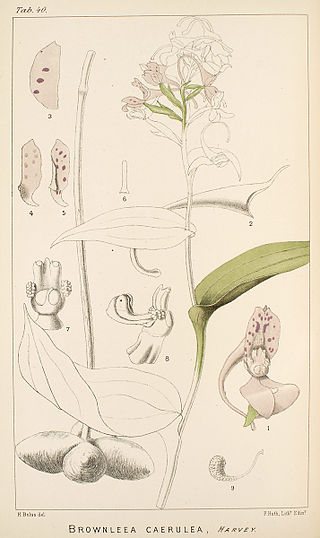
Brownleea is a genus of flowering plants from the family Orchidaceae native to Africa and Madagascar. Eight species are known.
- Brownleea coeruleaHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea galpiniiBolus
- Brownleea graminicolaMcMurtry
- Brownleea macrocerasSond.
- Brownleea maculataP.J.Cribb
- Brownleea mulanjiensisH.P.Linder
- Brownleea parvifloraHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea recurvataSond.

Discyphus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is the only genus in the subtribe Discyphinae of the tribe Cranichideae. It contains only one currently recognized species, Discyphus scopulariae, with two accepted varieties:
Vargasiella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two species, both endemic to South America: It has been treated as the only genus in the subtribe Vargasiellinae, but more recently has been included in the subtribe Zygopetalinae.
Hederorkis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two known species, both native to islands in the Indian Ocean.
Thaia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. The sole species is Thaia saprophytica, native to Laos and Thailand.

Pachites is a genus of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two known species, both endemic to South Africa. One of these, Pachites appressus, is very rare.
Risleya is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. The sole species is Risleya atropurpurea. It is native to the Himalayas of Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan, Bhutan, India, Sikkim, Assam and Myanmar. It was previously included in the subtribe Malaxidinae but is now placed in the tribe Collabieae.

Angraecinae is a subtribe in the family Orchidaceae. The subtribe consists of approximately 47 genera. The type genus is Angraecum. Most of the genera are endemic to Africa, Madagascar and other Indian Ocean Islands, a few genera can also be found in the Americas.

Dendrobieae is a tribe in the subfamily Epidendroideae, in the family Orchidaceae. The Dendrobieae are mostly tropical, epiphytic orchids which contain pseudobulbs.

Diseae is an orchid tribe in the subfamily Orchidoideae. It was recognized in Genera Orchidacearum volume 2, which was published in 2001. It consisted of 12 genera in five subtribes. In molecular phylogenetic studies that were published after 1999, it was shown that Diseae is paraphyletic over the tribe Orchideae. In a classification of orchids that was published in 2015, Diseae was not recognized, but was instead placed in synonymy under Orchideae.

Calypsoinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Epidendreae of subfamily Epidendroideae. It has previously been recognized as tribe Calypsoeae in the subfamily Epidendroideae.

Disinae is a subtribe of orchids that has been differently defined and placed in the two classification systems that are currently in use for orchids. Genera Orchidacearum, which is currently the definitive work on orchid taxonomy, delimits Disinae as consisting of two closely related genera, Disa and Schizodium, and it places Disinae in the mostly African tribe Diseae, along with four other subtribes: Brownleeinae, Huttonaeinae, Coryciinae, and Satyriinae. In the classification for orchids that was published by Chase et alii in 2015, Schizodium was placed in synonymy under Disa, while Pachites and Huttonaea were transferred to Disinae. In Genera Orchidacearum, Pachites and Satyrium form the subtribe Satyriinae, and Huttonaea is the sole genus in the subtribe Huttonaeinae. The transfer of Pachites and Huttonaea to Disinae by Chase et alii (2015) was done with considerable doubt, and was based upon uncertainty about the relationships of these two genera. In 2009, a molecular phylogenetic study found only weak statistical support for a sister relationship between Huttonaea and Disa.


















