
Trillium is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. Trillium species are native to temperate regions of North America and Asia, with the greatest diversity of species found in the southern Appalachian Mountains in the southeastern United States.

Erythronium, the fawn lily, trout lily, dog's-tooth violet or adder's tongue, is a genus of Eurasian and North American plants in the lily family, most closely related to tulips. The name Erythronium derives from Ancient Greek ἐρυθρός (eruthrós) "red" in Greek, referring to the red flowers of E. dens-canis.

Convolvulaceae, known commonly as the bindweed or morning glory family, is a family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species of mostly herbaceous vines, but also trees, shrubs and herbs, and also including the sweet potato and a few other food tubers.

Wisteria is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae), that includes ten species of woody climbing bines that are native to China, Korea, Japan, and the Eastern United States. Some species are popular ornamental plants. An aquatic flowering plant with the common name wisteria or 'water wisteria' is in fact Hygrophila difformis, in the family Acanthaceae.

The Ulmaceae are a family of flowering plant that includes the elms, and the zelkovas. Members of the family are widely distributed throughout the north temperate zone, and have a scattered distribution elsewhere except for Australasia.

Anthurium, is a genus of about 1000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, and laceleaf.

Lycopodium clavatum is the most widespread species in the genus Lycopodium in the clubmoss family.
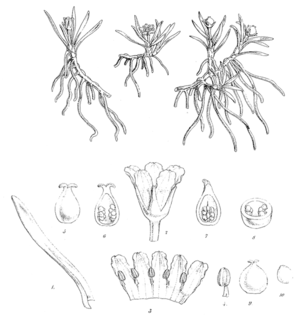
Liparophyllum gunnii, commonly known as alpine marshwort, is a species of aquatic flowering plants in the family Menyanthaceae. It is the type for the genus Liparophyllum. It is a wetland plant having a rhizomatous root structure and alternate linear leaves. Its flowers occur singly, are five-petalled, and white. Flowers bud and open from December to February; fruits form from December through April. L. gunnii is indigenous to Tasmania and New Zealand.

Weigela is a genus of between six and 38 species of deciduous shrubs in the family Caprifoliaceae, growing to 1–5 m (3–15′) tall. All are natives of eastern Asia. The genus is named after the German scientist Christian Ehrenfried Weigel.

Ageratina altissima, also known as white snakeroot, richweed, or white sanicle, is a poisonous perennial herb in the family Asteraceae, native to eastern and central North America. An older binomial name for this species is Eupatorium rugosum, but the genus Eupatorium has undergone taxonomic revision by botanists, and a number of the species that were once included in it have been moved to other genera.

Calla is a genus of flowering plant in the family Araceae, containing the single species Calla palustris.

Polystichum is a genus of ferns in the family Dryopteridaceae, subfamily Dryopteridoideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016. The genus has about 500 species and has a cosmopolitan distribution. The highest diversity is in eastern Asia, with about 208 species in China alone; the region from Mexico to Brazil has at least 100 additional species; Africa, North America, and Europe have much lower diversity. Polystichum species are terrestrial or rock-dwelling ferns of warm-temperate and montane-tropical regions. They are often found in disturbed habitats such as road cuts, talus slopes, and stream banks.

Physocarpus, commonly called ninebark, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rosaceae, native to North America and northeastern Asia.

Andropogon is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family, native to much of Asia, Africa, and the Americas as well as southern Europe and various oceanic islands.

Symphyotrichum is a genus of over 90 species of herbaceous annual and perennial plants in the composite family (Asteraceae) that were formerly treated within the genus Aster. The majority are endemic to North America, but several species also occur in the West Indies, Central and South America, as well as in eastern Eurasia. Many species have been introduced to Europe as garden specimens, most notably New England aster and New York aster.

Dillenia is a genus of about 100 species of flowering plants in the family Dilleniaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions of southern Asia, Australasia, and the Indian Ocean islands.

Allium cernuum, known as nodding onion or lady's leek, is a perennial plant in the genus Allium. It grows in dry woods, rock outcroppings, and prairies. It has been reported from much of the United States, Canada and Mexico including in the Appalachian Mountains from Alabama to New York State, the Great Lakes Region, the Ohio and Tennessee River Valleys, the Ozarks of Arkansas and Missouri, and the Rocky and Cascade Mountains of the West, from Mexico to Washington. It has not been reported from California, Nevada, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey, Delaware, New England, or much of the Great Plains. In Canada, it grows from Ontario to British Columbia.

Penstemon digitalis is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family, Plantaginaceae. The flowers are white and are borne in summer. It is native to eastern Canada and the eastern and southeastern United States.

Linnaea chinensis, synonyms Abelia chinensis and Abelia rupestris, is a species of flowering plant in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae. It was described by Robert Brown in 1818, and transferred to the genus Linnaea in 1872, although this move was not widely accepted until 2013. The plant inhabits China, Taiwan and Japan. It is a compact deciduous shrub with reddish stems and glossy, small leaves that become reddish-brown before autumn. It is one of the most cold-resistant species within the genus.

Cressa cretica is a species of flowering plant in the morning glory family. It is found in northern and central Africa, southern Europe and western Asia, as well as parts of southeastern Asia and Australia. It has long been used in traditional medicine and research has demonstrated that it has some therapeutic effects.




















