
The Araliaceae are a family of flowering plants composed of about 43 genera and around 1500 species consisting of primarily woody plants and some herbaceous plants commonly called the ginseng family. The morphology of Araliaceae varies widely, but it is predominantly distinguishable based on its woody habit, tropical distribution, and the presence of simple umbels.

Heliophila is a genus of flowering plants in the family Brassicaceae. Members of this genus are either annuals or perennials and some are popular as ornamental plants. Endemic to southern Africa, the majority of the approximately 80 species grow in South Africa, particularly the Cape Floristic Region, while a few extend into the Namib Desert.
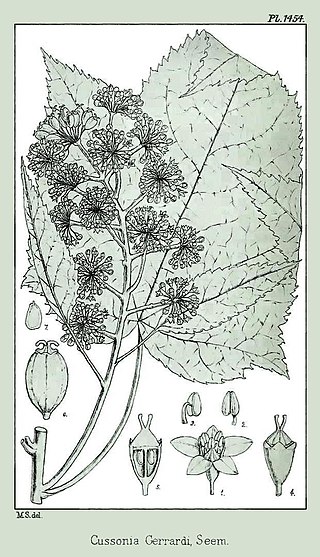
Seemannaralia gerrardii, commonly known as the wild-maple or mock carrot tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Araliaceae. It is the sole member of genus Seemannaralia, and is endemic to South Africa, where it occurs in the Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo and Mpumalanga provinces. It was originally included in genus Cussonia. Seemann- and gerrardii commemorate Berthold Seemann and William Gerrard respectively, while -aralia suggests the family or its type genus, Aralia.

Wachendorfia is a genus of perennial herbaceous plants that is assigned to the bloodroot family. The plants have a perennial rootstock with red sap. From the rootstock emerge lance- or line-shaped, sometime sickle-shaped, pleated, simple leaves set in a fan, that are flattened to create a left and right surface rather than an upper and lower surface. The leaves die when the seeds are shed in three of the species, and are perennial in one species.

Lotononis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae and the tribe Crotalarieae. The genus includes 99 species of annual and perennial herbs, native to the southeastern Europe and Turkey, eastern Africa, and southern Africa.

Melolobium is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes 14 species of small shrubs or perennial herbs native to southern Africa, which are found in southern and eastern Namibia, southwestern Botswana, and most of South Africa.

Phylica is a genus of plants in the family Rhamnaceae. It contains about 150 species, the majority of which are restricted to South Africa, where they form part of the fynbos. A few species occur in other parts of southern Africa, and on islands including Madagascar, the Mascarene Islands, Île Amsterdam, Saint Helena, Tristan da Cunha, and Gough Island. Phylica piloburmensis from the Burmese amber of Myanmar, dating to around 99 million years ago during the mid-Cretaceous, was originally described as the oldest fossil member of the genus, but subsequent studies contested its assignment to the genus Phylica and even to the family Rhamnaceae, with one study placing it in the separate genus Nothophylica.

Aspalathus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. The yellow flowers and spiny habit of some species have suggested a resemblance to Ulex europaeus, the thorny "English gorse" Accordingly, "Cape Gorse" has been proposed as a common name although the resemblance is largely superficial; for instance, gorse is thorny, whereas Aspalathus species are variously spiny or unarmed. The genus belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. There are over 270 species, mainly endemic to southwestern fynbos regions in South Africa, with over fifty occurring on the Cape Peninsula alone. The species Aspalathus linearis is commercially important, being farmed as the source of Rooibos tea.

Searsia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Anacardiaceae. It includes over 100 species native to Africa, the eastern Mediterranean, Arabian Peninsula, Indian subcontinent, Myanmar, and south-central China.

Acrosanthes is a genus of flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae. It is native to the Namibia and South Africa's Cape Provinces in Southern Africa.

Cussonia arborea is a deciduous small to medium sized tree within the family Araliaceae. Extracts of the species are widely used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments.















