Adenylate cyclase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase . It catalyzes the following reaction:
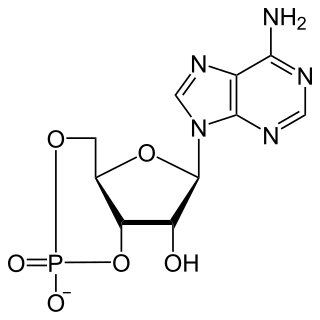
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway.

A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-phosphate nucleotide with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar, very often a ribose.

In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinase whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase. PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase.

Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in response to the binding of membrane-impermeable peptide hormones to the external cell surface. Through protein kinases activation, cGMP can relax smooth muscle. cGMP concentration in urine can be measured for kidney function and diabetes detection.
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA.

Cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channels or CNG channels are ion channels that function in response to the binding of cyclic nucleotides. CNG channels are nonselective cation channels that are found in the membranes of various tissue and cell types, and are significant in sensory transduction as well as cellular development. Their function can be the result of a combination of the binding of cyclic nucleotides and either a depolarization or a hyperpolarization event. Initially discovered in the cells that make up the retina of the eye, CNG channels have been found in many different cell types across both the animal and the plant kingdoms. CNG channels have a very complex structure with various subunits and domains that play a critical role in their function. CNG channels are significant in the function of various sensory pathways including vision and olfaction, as well as in other key cellular functions such as hormone release and chemotaxis. CNG channels have also been found to exist in prokaryotes, including many spirochaeta, though their precise role in bacterial physiology remains unknown.
cGMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase G (PKG) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is activated by cGMP. It phosphorylates a number of biologically important targets and is implicated in the regulation of smooth muscle relaxation, platelet function, sperm metabolism, cell division, and nucleic acid synthesis.

PDE3 is a phosphodiesterase. The PDEs belong to at least eleven related gene families, which are different in their primary structure, substrate affinity, responses to effectors, and regulation mechanism. Most of the PDE families are composed of more than one gene. PDE3 is clinically significant because of its role in regulating heart muscle, vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation. PDE3 inhibitors have been developed as pharmaceuticals, but their use is limited by arrhythmic effects and they can increase mortality in some applications.
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5′-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for cAMP and cGMP.

Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the "large" G proteins are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), directly. These G proteins are made up of alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.
GMP reductase EC 1.7.1.7 is an enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible and NADPH-dependent reductive deamination of GMP into IMP.

Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta is the beta subunit of the protein complex PDE6 that is encoded by the PDE6B gene. PDE6 is crucial in transmission and amplification of visual signal. The existence of this beta subunit is essential for normal PDE6 functioning. Mutations in this subunit are responsible for retinal degeneration such as retinitis pigmentosa or congenital stationary night blindness.

Cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNGA3 gene.

Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel alpha 1, also known as CNGA1, is a human gene encoding an ion channel protein. Heterologously expressed CNGA1 can form a functional channel that is permeable to calcium. In rod photoreceptors, however, CNGA1 forms a heterotetramer with CNGB1 in a 3:1 ratio. The addition of the CNGB1 channel imparts altered properties including more rapid channel kinetics and greater cAMP-activated current. When light hits rod photoreceptors, cGMP concentrations decrease causing rapid closure of CNGA1/B1 channels and, therefore, hyperpolarization of the membrane potential.

Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCN1 gene.

Cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 1, also known as CNGB1, is a human gene encoding an ion channel protein.
The GAF domain is a type of protein domain that is found in a wide range of proteins from all species. The GAF domain is named after some of the proteins it is found in: cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases, adenylyl cyclases and FhlA. The first structure of a GAF domain solved by Ho and colleagues showed that this domain shared a similar fold with the PAS domain. In mammals, GAF domains are found in five members of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase superfamily: PDE2, PDE5, and PDE6 which bind cGMP to the GAF domain, PDE10 which binds cAMP, and PDE11 which binds both cGMP and cAMP.
The cGAS–STING pathway is a component of the innate immune system that functions to detect the presence of cytosolic DNA and, in response, trigger expression of inflammatory genes that can lead to senescence or to the activation of defense mechanisms. DNA is normally found in the nucleus of the cell. Localization of DNA to the cytosol is associated with tumorigenesis, viral infection, and invasion by some intracellular bacteria. The cGAS – STING pathway acts to detect cytosolic DNA and induce an immune response.