
Sciaenidae is a family of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Acanthuriformes. They are commonly called drums or croakers in reference to the repetitive throbbing or drumming sounds they make. The family consists of about 293 to 298 species in about 66 or 67 genera.

Krill(Euphausiids) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus Linguatula to a vertebrate tongue; molecular studies point to them being highly-derived crustaceans.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.
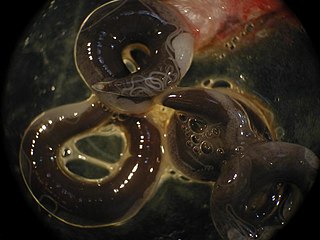
Anguillicoloides crassus is a parasitic nematode worm that lives in the swimbladders of eels and appears to spread easily among eel populations after introduction to a body of water. It is considered to be one of the threats to the sustainability of populations of European eel. It was introduced to the European continent in the 1980s, where it was reported independently from Germany and Italy in 1982, having probably been introduced from Taiwan. It is thought to have reached England in 1987 from continental Europe. It is a natural parasite of the Japanese eel in its native range.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.

Physalopteridae is a family of spirurian nematodes, which belongs to the superfamily Physalopteroidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.

Cystidicolidae is a family of spirurian nematodes. It was described by Skrjabin in 1946. All members of the family are parasites of fish.

Ascarophis is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophis are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of marine and estuarine fishes.

Ascarophisnema is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophisnema are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Ascarophisnema tridentatum.
Metabronemoides is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Metabronemoides are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish.

Moravecnema is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Moravecnema are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Moravecnema segonzaci, which is a parasite in a deep-sea fish.
Cristitectus is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Cristitectus are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Cristitectus congeri, which is a parasite of the European conger.
Spinitectoides is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Spinitectoides are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Spinitectoides berlandi.
Prospinitectus is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Prospinitectus are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of Tuna fish.

Carmen Camacho Velasquez was a Filipino parasitologist. She specialized in parasites of the tropical fish of the Philippines. She is known for her work on the taxonomy of Digenea and was the first to describe the parasitic nematode Capillaria philippinensis, which causes intestinal capillariasis in humans.














