Citizens of Mauritania have limited access to transportation. The single-line railroad serves mining interests with very occasional ad hoc passenger services. Apart from two infrastructural road developments there are few paved roads.

Mauritania, a country in the Western Region of the continent of Africa, is generally flat, its 1,030,700 square kilometres forming vast, arid plains broken by occasional ridges and clifflike outcroppings. Mauritania is the world’s largest country lying entirely below an altitude of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). It borders the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara, Mali and Algeria. It is considered part of both the Sahel and the Maghreb. A series of scarps face southwest, longitudinally bisecting these plains in the center of the country. The scarps also separate a series of sandstone plateaus, the highest of which is the Adrar Plateau, reaching an elevation of 500 metres or 1,640 feet. Spring-fed oases lie at the foot of some of the scarps. Isolated peaks, often rich in minerals, rise above the plateaus; the smaller peaks are called Guelbs and the larger ones Kedias. The concentric Guelb er Richat is a prominent feature of the north-central region. Kediet ej Jill, near the city of Zouîrât, has an elevation of 915 metres or 3,002 feet and is the highest peak.

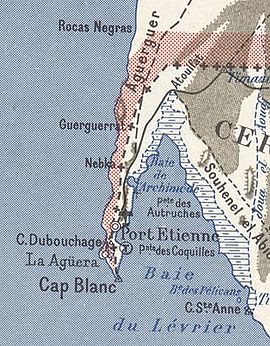
Nouadhibou is the second largest city in Mauritania and serves as a major commercial center. The city has about 173,000 inhabitants. It is situated on a 65-kilometre peninsula or headland called Ras Nouadhibou, Cap Blanc, or Cabo Blanco, of which the western side has the city of La Güera. Nouadhibou is consequently located merely a couple of kilometers from the border between Mauritania and Western Sahara. Its current mayor is Elghassem Ould Bellali, who was installed on 15 October 2018.

Inchiri is a region in western Mauritania. Its capital and only city is Akjoujt. It borders the regions of Adrar to the east, Trarza to the south, and Dakhlet Nouadhibou to the north and west, along with a short Atlantic Ocean coastline. The region is known for its rich copper deposits, and therefore is heavily mined. According to the World Health Organization, there is a malaria risk during the rainy season, which lasts from July to October. Former president Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz was born and raised in Akjoujt.

Dakhlet Nouadhibou region is an administrative division of Mauritania. Its regional capital is Nouadhibou, which is located at its northwestern end and is home to nearly 95% of the region's population. The rest of the shoreline is sparsely populated with villages, but the east of the region is mostly uninhabited.

Zouérat is the largest town in northern Mauritania and the capital of the Tiris Zemmour region, with an approximate population of 62,380 (2023). It lies at the eastern end of the Mauritania Railway to Nouadhibou.

The Bay of Arguin is a bay on the Atlantic shore of Mauritania and the former mouth of the Tamanrasset River, now a Paleo-river.

The Banc d'Arguin National Park of Bay of Arguin lies in Western Africa on the west coast of Mauritania between Nouakchott and Nouadhibou and is the former mouth of the Tamanrasset River. The World Heritage Site is a major site for migratory birds and breeding birds, including flamingos, pelicans and terns. Much of the breeding is on sand banks including the islands of Tidra, Niroumi, Nair, Kijji and Arguim. The surrounding waters are some of the richest fishing waters in western Africa and serve as nesting grounds for the entire western region.

Havre-Saint-Pierre is a municipality located on the north shore of the Gulf of St. Lawrence, in Côte-Nord region, Minganie RCM, Quebec, Canada.
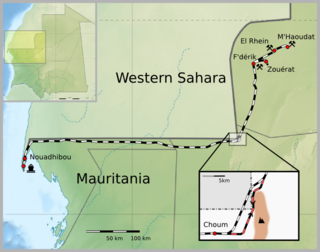
The Mauritania Railway is the national railway of Mauritania. Construction of the line began in 1960, with its opening in 1963. It consists of a single, 704-kilometre (437 mi) railway line linking the iron mining center of Zouérat with the port of Nouadhibou, via Fderik and Choum. The state agency Société nationale industrielle et minière (SNIM) controls the railway line.

Ras Nouadhibou is a 60-kilometre (37 mi) peninsula or headland divided by the border between Mauritania and Western Sahara on the African coast of the Atlantic Ocean. It is internationally known as Cabo Blanco in Spanish or Cap Blanc in French.

Choum is a town in northern Mauritania, lying in the Adrar Region close to the border with Western Sahara.
Nouadhibou Airport is an airport serving Nouadhibou, a city in the Dakhlet Nouadhibou region of Mauritania.

Cansado is a coastal town in north-western Mauritania on the Ras Nouadhibou peninsula. It is located in the Nouadhibou Department in the Dakhlet Nouadhibou region.
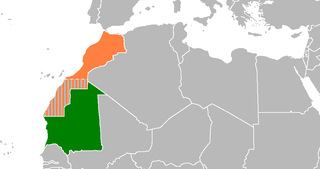
Mauritania and Morocco are both in the Maghreb, Morocco is in North Africa. The two countries have bordered each other since 1975, when Spain abandoned the Western Sahara most of which is now de facto under Moroccan control. The sovereignty of this territory remains disputed.
Mauritania's mineral sector was dominated by iron ore mining and beneficiation. Other mineral commodities produced in the country included cement, copper, gold, gypsum, petroleum, salt, and steel. The 'Ministère des Mines et de l’Industrie' was the Government agency responsible for enacting the Mining Code and for the coordination of all activities in the mining sector. The 'Direction des Mines et de la Géologie' was the entity responsible for promoting the mineral sector and for providing geologic and mining information to potential investors; the 'Direction des Hydrocarbures' was in charge of the development of the petroleum sector; and the 'Office Mauritanien des Recherches Géologiques' was the Government entity responsible for evaluating areas of mineral potential for exploration. The 'Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière (SNIM)' was responsible for iron ore production and benefciation.

The history of rail transport in Mauritania began in 1940, with the commencement of preparatory work for the construction of the Mauritania Railway, a single track, 704 km (437 mi) standard gauge line connecting a then proposed iron mine in Zouerate with the port of Nouadhibou, via Fderik and Choum. Construction of the line began in 1961 and was completed in 1963.

The Tasiast gold mine is a gold deposit located in central western Mauritania, near the coast. The operating licence was granted to Tasiast Mauritanie Limited S.A. (TMLSA), a subsidiary of the Canadian group Kinross Gold Corporation. Mining activities began in 2007.