Evolutionary economics is part of mainstream economics as well as a heterodox school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Much like mainstream economics, it stresses complex interdependencies, competition, growth, structural change, and resource constraints but differs in the approaches which are used to analyze these phenomena.
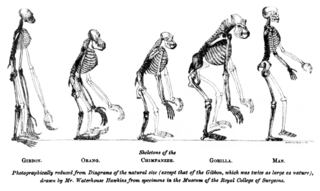
Evolutionary anthropology is the interdisciplinary study of the evolution of human physiology and human behaviour and the relation between hominids and non-hominid primates. Evolutionary anthropology is based in natural science and social science. Various fields and disciplines of evolutionary anthropology are:

Evolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. Modern medical research and practice have focused on the molecular and physiological mechanisms underlying health and disease, while evolutionary medicine focuses on the question of why evolution has shaped these mechanisms in ways that may leave us susceptible to disease. The evolutionary approach has driven important advances in our understanding of cancer, autoimmune disease, and anatomy. Medical schools have been slower to integrate evolutionary approaches because of limitations on what can be added to existing medical curricula.

Boasian anthropology was a school within American anthropology founded by Franz Boas in the late 19th century.

Donald Thomas Campbell was an American social scientist. He is noted for his work in methodology. He coined the term "evolutionary epistemology" and developed a selectionist theory of human creativity. A Review of General Psychology survey, published in 2002, ranked Campbell as the 33rd most cited psychologist of the 20th century.
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: genetic evolution and cultural evolution. Genes and culture continually interact in a feedback loop, changes in genes can lead to changes in culture which can then influence genetic selection, and vice versa. One of the theory's central claims is that culture evolves partly through a Darwinian selection process, which dual inheritance theorists often describe by analogy to genetic evolution.
Life history theory is an analytical framework designed to study the diversity of life history strategies used by different organisms throughout the world, as well as the causes and results of the variation in their life cycles. It is a theory of biological evolution that seeks to explain aspects of organisms' anatomy and behavior by reference to the way that their life histories—including their reproductive development and behaviors, life span and post-reproductive behavior—have been shaped by natural selection. A life history strategy is the "age- and stage-specific patterns" and timing of events that make up an organism's life, such as birth, weaning, maturation, death, etc. These events, notably juvenile development, age of sexual maturity, first reproduction, number of offspring and level of parental investment, senescence and death, depend on the physical and ecological environment of the organism.
Evolutionary developmental psychology (EDP) is a research paradigm that applies the basic principles of Darwinian evolution, particularly natural selection, to understand the development of human behavior and cognition. It involves the study of both the genetic and environmental mechanisms that underlie the development of social and cognitive competencies, as well as the epigenetic processes that adapt these competencies to local conditions.
Cultural selection theory is the study of cultural change modelled on theories of evolutionary biology. Cultural selection theory has so far never been a separate discipline. However it has been proposed that human culture exhibits key Darwinian evolutionary properties, and "the structure of a science of cultural evolution should share fundamental features with the structure of the science of biological evolution". In addition to Darwin's work the term historically covers a diverse range of theories from both the sciences and the humanities including those of Lamark, politics and economics e.g. Bagehot, anthropology e.g. Edward B. Tylor, literature e.g. Ferdinand Brunetière, evolutionary ethics e.g. Leslie Stephen, sociology e.g. Albert Keller, anthropology e.g. Bronislaw Malinowski, Biosciences e.g. Alex Mesoudi, geography e.g. Richard Ormrod, sociobiology and biodiversity e.g. E.O. Wilson, computer programming e.g. Richard Brodie, and other fields e.g. Neoevolutionism, and Evolutionary archaeology.
Evolutionary educational psychology is the study of the relation between inherent folk knowledge and abilities and accompanying inferential and attributional biases as these influence academic learning in evolutionarily novel cultural contexts, such as schools and the industrial workplace. The fundamental premises and principles of this discipline are presented below.

The tree of knowledge (ToK) system is a theoretical approach to the unification of psychology developed by Gregg Henriques, associate professor and director of the Combined-Integrated Doctoral Program in Clinical and School Psychology at James Madison University.
Biocultural anthropology can be defined in numerous ways. It is the scientific exploration of the relationships between human biology and culture. "Instead of looking for the biology underlying biological roots of human behavior, biocultural anthropology attempts to understand how culture affects our biological capacities and limitations."
Evolutionary psychology has generated substantial controversy and criticism. The criticism includes but is not limited to: disputes about the testability of evolutionary hypotheses, alternatives to some of the cognitive assumptions frequently employed in evolutionary psychology, alleged vagueness stemming from evolutionary assumptions, differing stress on the importance of non-genetic and non-adaptive explanations, and political and ethical issues.
Cognitive science of religion is the study of religious thought and behavior from the perspective of the cognitive and evolutionary sciences. The field employs methods and theories from a very broad range of disciplines, including: cognitive psychology, evolutionary psychology, cognitive anthropology, artificial intelligence, neurotheology, developmental psychology, and archaeology. Scholars in this field seek to explain how human minds acquire, generate, and transmit religious thoughts, practices, and schemas by means of ordinary cognitive capacities.
Mark Schaller is a psychological scientist who has made many contributions to the study of human psychology, particularly in areas of social cognition, stereotyping, evolutionary psychology, and cultural psychology. He is Professor of Psychology at the University of British Columbia.
Evolutionary psychology has traditionally focused on individual-level behaviors, determined by species-typical psychological adaptations. Considerable work, though, has been done on how these adaptations shape and, ultimately govern, culture. Tooby and Cosmides (1989) argued that the mind consists of many domain-specific psychological adaptations, some of which may constrain what cultural material is learned or taught. As opposed to a domain-general cultural acquisition program, where an individual passively receives culturally-transmitted material from the group, Tooby and Cosmides (1989), among others, argue that: "the psyche evolved to generate adaptive rather than repetitive behavior, and hence critically analyzes the behavior of those surrounding it in highly structured and patterned ways, to be used as a rich source of information out of which to construct a 'private culture' or individually tailored adaptive system; in consequence, this system may or may not mirror the behavior of others in any given respect.".
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation and other forms of social transmission". Cultural evolution is the change of this information over time.
There are two main approaches currently used to analyze archaeological remains from an evolutionary perspective: evolutionary archaeology and behavioral ecology. The former assumes that cultural change observed in the archaeological record can be best explained by the direct action of natural selection and other Darwinian processes on heritable variation in artifacts and behavior. The latter assumes that cultural and behavioral change results from phenotypic adaptations to varying social and ecological environments.





