This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2007) |
This is a demographic history of Quebec chronicling the evolution of the non-indigenous population in Quebec.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2007) |
This is a demographic history of Quebec chronicling the evolution of the non-indigenous population in Quebec.
| Year | Population | Change | Percent change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1605 | 44 | N/A | N/A |
| 1608 | 28 | -16 | -72.7 |
| 1610 | 18 | -10 | -77.7 |
| 1620 | 60 | 42 | 233.3 |
| 1630 | 100 | 40 | 66.7 |
| 1640 | 359 | 259 | 259 |
| 1653 | 2,000 | 1,641 | 557.1 |
| 1666 | 3,215 | 1,215 | 60.8 |
| 1667 | 3,918 | 703 | 21.9 |
| 1673 | 6,705 | 2,787 | 71.1 |
| 1675 | 7,832 | 1,127 | 16.8 |
| 1679 | 9,400 | 1,568 | 20 |
| 1683 | 12,566 | 3,166 | 33.7 |
| 1686 | 11,786 | -780 | -6.6 |
| 1692 | 12,431 | 645 | 5.5 |
| 1706 | 16,745 | 4,314 | 34.7 |
| 1713 | 18,469 | 1,724 | 10.3 |
| 1720 | 24,594 | 6,125 | 33.2 |
| 1727 | 31,184 | 6,590 | 26.8 |
| 1734 | 37,716 | 6,532 | 20.9 |
| 1739 | 43,362 | 5,646 | 15 |
| 1754 | 55,009 | 11,647 | 26.9 |
| 1765 | 69,810 | 14,801 | 26.9 |
| 1784 | 113,012 | 43,202 | 61.9 |
| 1790 | 161,311 | 48,299 | 42.7 |
| 1806 | 250,000 | 88,689 | 55 |
| 1814 | 335,000 | 85,000 | 34 |
| 1822 | 427,465 | 92,465 | 27.6 |
| 1831 | 553,134 | 125,669 | 29.4 |
| 1844 | 697,084 | 143,950 | 26 |
| 1851 | 890,000 | 192,916 | 27.7 |
| 1861 | 1,112,000 | 222,000 | 24.9 |
| 1871 | 1,192,000 | 80,000 | 7.2 |
| 1881 | 1,360,000 | 168,000 | 14.1 |
| 1891 | 1,489,000 | 129,000 | 9.5 |
| 1901 | 1,649,000 | 160,000 | 10.7 |
| 1906 | 1,815,000 | 166,000 | 10.1 |
| 1911 | 2,006,000 | 191,000 | 10.5 |
| 1916 | 2,182,000 | 176,000 | 8.8 |
| 1921 | 2,361,000 | 179,000 | 8.2 |
| 1926 | 2,573,000 | 212,000 | 9 |
| 1931 | 2,875,000 | 302,000 | 11.7 |
| 1936 | 3,102,000 | 227,000 | 7.9 |
| 1941 | 3,332,000 | 230,000 | 7.4 |
| 1946 | 3,645,000 | 313,000 | 9.4 |
| 1951 | 4,056,000 | 411,000 | 11.3 |
| 1956 | 4,628,000 | 572,000 | 14.1 |
| 1961 | 5,259,000 | 631,000 | 13.6 |
| 1966 | 5,781,000 | 522,000 | 9.9 |
| 1971 | 6,028,000 | 247,000 | 4 |
| 1976 | 6,234,000 | 206,000 | 3.4 |
| 1981 | 6,438,000 | 204,000 | 3.3 |
| 1986 | 6,532,000 | 94,000 | 1.5 |
| 1991 | 6,896,000 | 364,000 | 5.6 |
| 1996 | 7,139,000 | 243,000 | 3.5 |
| 2001 | 7,237,000 | 98,000 | 1.4 |
| 2006 | 7,546,000 | 309,000 | 4.3 |
| 2011 | 7,903,000 | 357,000 | 4.7 |
| 2016 | 8,164,000 | 261,000 | 3.3 |
| 2021 | 8,502,000 | 338,000 | 4.1 |
| 2024 | 9,056,000 | 554,000 | 5.3 |
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area are also its most populous; together they account for 86.5 percent of the country's population. The territories account for over a third of Canada's area but are home to only 0.32 percent of its population, which skews the national population density value.
Statistics Canada, formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in Ottawa.

Rouyn-Noranda is a city on Osisko Lake in the Abitibi-Témiscamingue region of Quebec, Canada.

The Province of Quebec was a colony in British North America which comprised the former French colony of Canada. It was established by the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1763, following the conquest of New France by British forces during the Seven Years' War. As part of the 1763 Treaty of Paris, France gave up its claim to the colony; it instead negotiated to keep the small profitable island of Guadeloupe.

The British North America Act, 1840, also known as the Act of Union 1840, was approved by Parliament in July 1840 and proclaimed February 10, 1841, in Montreal. It abolished the legislatures of Lower Canada and Upper Canada and established a new political entity, the Province of Canada to replace them.
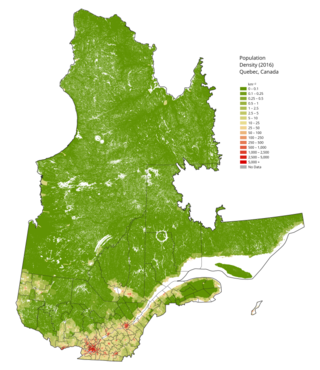
The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the national question. Quebec is the only one of Canada's provinces to feature a Francophone (French-speaking) majority, and where anglophones (English-speakers) constitute an officially recognized minority group. According to the 2011 census, French is spoken by more than 85.5% of the population while this number rises to 88% for children under 15 years old. According to the 2011 census, 95% of Quebec's people are able to conduct a conversation in French, with less than 5% of the population not able to speak French. According to Statistics Canada's population clock, Quebec's population would be around 9,100,000 in early 2024.

Sainte-Catherine is an off-island suburb of Montreal, in southwestern Quebec, Canada, on the St. Lawrence River in the Regional County Municipality of Roussillon. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 16,762.
Indigenous peoples in Quebec total eleven distinct ethnic groups. The one Inuit community and ten First Nations communities number 141,915 people and account for approximately two per cent of the population of Quebec, Canada.
Articles related to Quebec include:

The history of the Jews in Canada goes back to the 1700s. Canadian Jews, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion, form the fourth largest Jewish community in the world, exceeded only by those in Israel, the United States and France. In the 2021 census, 335,295 people reported their religion as Jewish, accounting for 0.9% of the Canadian population. Some estimates have placed the enlarged number of Jews, such as those who may be culturally or ethnically Jewish, though not necessarily religiously, at around 400,000 people. This total would account for approximately 1.4% of the Canadian population.

Villeray–Saint-Michel–Parc-Extension is a borough (arrondissement) in the city of Montreal, Quebec. It had a population of 143,853 according to the 2016 Census and a land area of 16.5 square kilometres (6.4 sq mi).

Saint-Théodore-d’Acton is a municipality in the Regional County Municipality of Acton, in the province of Quebec, Canada. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 1,471.

Canadian Americans are American citizens or in some uses residents whose ancestry is wholly or partly Canadian, or citizens of either country who hold dual citizenship.
La Revanche des berceaux is an expression referring to the high birth rate of French Canadians prior to the late 20th century. The phrase originated in Quebec before the First World War, according to John Robert Colombo's "Colombo's Canadian References." The expression suggests that, although English Canadians dominated Canada in the 19th century, the high birth rate of French Canadians would allow them to remain politically strong in Quebec and also to maintain their demographic weight within Canada - thus permitting resistance to cultural assimilation into English Canadian culture.

The French term pure laine, refers to Québécois people of full French Canadian ancestry, meaning those descended from the original settlers of New France who arrived during the 17th and 18th centuries. Terms with a similar meaning include de souche and old stock as in "Old Stock Canadians".
Québécois(e) or Quebecois(e) may refer to:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Quebec:

Montreal and its suburbs have a substantial Italian Canadian community. As of 2021, 17.3% of the ethnic Italians in Canada live in Greater Montreal.

Interprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. In fiscal year 2019–20, 278,316 Canadians migrated province, representing 0.729% of the population.