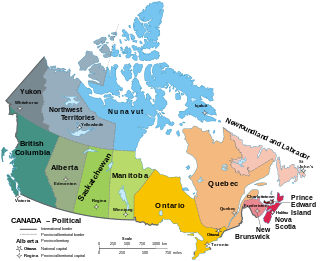
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
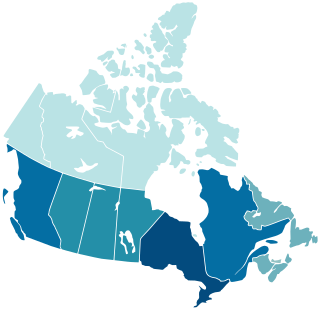
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area are also its most populous; together they account for 86.5 percent of the country's population. The territories account for over a third of Canada's area but are home to only 0.32 percent of its population, which skews the national population density value.

Lloydminster is a city in Canada which has the unusual geographic distinction of straddling the provincial border between Alberta and Saskatchewan. The city is incorporated by both provinces as a single city with a single municipal administration.
The 2001 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. Census day was May 15, 2001. On that day, Statistics Canada attempted to count every person in Canada. The total population count of Canada was 30,007,094. This was a 4% increase over 1996 census of 28,846,761. In contrast, the official Statistics Canada population estimate for 2001 was 31,021,300. This is considered a more accurate population number than the actual count.

Strathmore is a town located in southern Alberta, Canada that is surrounded by Wheatland County. It is along the Trans-Canada Highway approximately 50 kilometres (30 mi) east of Calgary.
Canadian Senate divisions refers to two aspects of the Senate of Canada. First, it refers to the division of Canada into four regional Senate divisions of 24 senators each, as set out in section 22 of the Constitution Act, 1867. The four regions are the Western Provinces, Ontario, Quebec and the Maritimes. These regions are intended to serve the Senate's purpose of providing regional representation in the Parliament of Canada, in contrast to the popular representation that the House of Commons is intended to provide. While not within any of the original four Senate divisions, Senate seats are also allocated to Newfoundland and Labrador and the three territories. The four divisions can be expanded when the need arises to have an extra two senators appointed to each regional division.
Statistics Canada conducts a national census of population and census of agriculture every five years and releases the data with a two-year lag.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:
Smith is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada within the Municipal District of Lesser Slave River No. 124. It is located on Highway 2A, approximately 182 kilometres (113 mi) northwest of Edmonton, at the confluence of the Lesser Slave River and the Athabasca River.
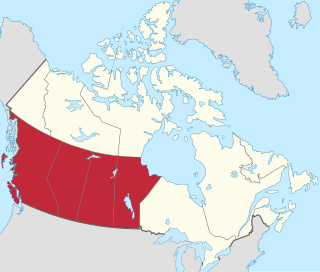
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada–United States border namely British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The people of the region are often referred to as "Western Canadians" or "Westerners", and though diverse from province to province are largely seen as being collectively distinct from other Canadians along cultural, linguistic, socioeconomic, geographic and political lines. They account for approximately 32% of Canada's total population.
The Canada 1921 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census count was taken as at June 1, 1921. The total population count was 8,788,483 representing a 22% increase over the 1911 census population count of 7,206,643. The 1921 census was the sixth comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867. The previous census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1916 census and the following census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1926 census.
The 1936 Canadian census was the fourth of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946. This census was conducted as at June 1, 1936.
The 1946 Canadian census was the fifth, and last, of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946, and ceased when the nationwide census switched from decennial to quinquennial in 1956. This census was conducted as of June 1, 1946.
The Canada 1931 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census count was taken as at June 1, 1931. The total population count was 10,376,379 representing a 17.9% increase over the 1911 census population count of 8,800,249. The 1931 census was the seventh comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867.
The Canada 1941 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The total population count was 11,506,655, representing a 10.9% increase over the 1931 census population count of 10,376,786. The 1941 census was the eighth comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867. The previous census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1936 census and the following census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1946 census.

Interprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. In fiscal year 2019–20, 278,316 Canadians migrated province, representing 0.729% of the population.






