
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given population, usually displayed in the form of statistics. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications, and other useful information to coordinate international practices.

Sind was a province of British India from 1 April 1936 to 1947 and Dominion of Pakistan from 14 August 1947 to 14 October 1955. Under the British, it encompassed the current territorial limits excluding the princely state of Khairpur. Its capital was Karachi. After Pakistan's creation, the province lost the city of Karachi, as it became the capital of the newly created country. It became part of West Pakistan upon the creation of the One Unit Scheme.
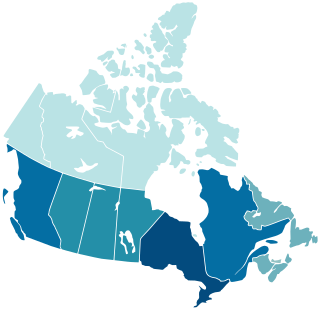
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area are also its most populous; together they account for 86.5 percent of the country's population. The territories account for over a third of Canada's area but are home to only 0.32 percent of its population, which skews the national population density value.

Canada ranks 36th by population among countries of the world, comprising about 0.5% of the world's total, with more than 40 million Canadians as of 2024. Despite being the second-largest country by total area, the vast majority of the country is sparsely inhabited, with most of its population south of the 55th parallel north. Just over 60 percent of Canadians live in just two provinces: Ontario and Quebec. Though Canada's overall population density is low, many regions in the south, such as the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, have population densities higher than several European countries. Canada has six population centres with more than one million people: Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton and Ottawa.
The 2001 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. Census day was May 15, 2001. On that day, Statistics Canada attempted to count every person in Canada. The total population count of Canada was 30,007,094. This was a 4% increase over 1996 census of 28,846,761. In contrast, the official Statistics Canada population estimate for 2001 was 31,021,300. This is considered a more accurate population number than the actual count.

Coincident full censuses have taken place in the different jurisdictions of the United Kingdom every ten years since 1801, with the exceptions of 1941, Ireland in 1921/Northern Ireland in 1931, and Scotland in 2021. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to regional and local service providers by the UK government.

The 2006 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. Census day was May 16, 2006. The following census was the 2011 census. Canada's total population enumerated by the 2006 census was 31,612,897. This count was lower than the official July 1, 2006 population estimate of 32,623,490 people. The previous census was the 2001 census and the following census was in 2011 census.

The United Kingdom Census of 1841 recorded the occupants of every United Kingdom household on the night of Sunday 6 June 1841. The enactment of the Population Act 1840 meant a new procedure was adopted for taking the 1841 census. It was described as the "first modern census" as it was the first to record information about every member of the household, and administered as a single event, under central control, rather than being devolved to a local level. It formed the model for all subsequent UK censuses, although each went on to refine and expand the questions asked of householders.
Statistics Canada conducts a national census of population and census of agriculture every five years and releases the data with a two-year lag.
The 1911 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census was started on June 1, 1911. All reports had been received by February 26, 1912. The total population count of Canada was 7,206,643. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315.

The 1911 census of Ireland was the last census that covered the whole island of Ireland. Censuses were taken at ten-year intervals from 1821 onwards, but the 1921 census was cancelled due to the Irish War of Independence.
The 1906 Canadian census was the first of a series of special censuses conducted by the Government of Canada, covering the rapidly expanding Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These censuses were conducted every ten years from 1906 to 1946.
The 1996 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. Census day was May 14, 1996. On that day, Statistics Canada attempted to count every person in Canada. The total population count of Canada was 28,846,761. This was a 5.7% increase over the 1991 census of 27,296,859.

Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India, founded in 1961 by the Government of India Ministry of Home Affairs, for arranging, conducting and analysing the results of the demographic surveys of India including Census of India and Linguistic Survey of India. The position of Registrar General and Census Commissioner is now held by a civil servant holding the rank of Additional Secretary.
The Canada 1921 census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census count was taken as at June 1, 1921. The total population count was 8,788,483 representing a 22% increase over the 1911 census population count of 7,206,643. The 1921 census was the sixth comprehensive decennial census since Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867. The previous census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1916 census and the following census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1926 census.

The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a 5% change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial census. The official census day was May 10, 2016. Census web access codes began arriving in the mail on May 2, 2016. The 2016 census marked the reinstatement of the mandatory long-form census, which had been dropped in favour of the voluntary National Household Survey for the 2011 census. With a response rate of 98.4%, this census is said to be the best one ever recorded since the 1666 census of New France. This census was succeeded by Canada's 2021 census.

Census in British India refers to the census of India prior to independence which was conducted periodically from 1865 to 1941. The censuses were primarily concerned with administration and faced numerous problems in their design and conduct ranging from the absence of house numbering in hamlets to cultural objections on various grounds to dangers posed by wild animals to census personnel. The sociologist Michael Mann called the census exercise "more telling of the administrative needs of the British than of the social reality for the people of British India". The differences in the nature of Indian society during the British Raj from the value system and the societies of the West were highlighted by the inclusion of "caste", "religion", "profession" and "age" in the data to be collected, as the collection and analysis of that information had a considerable impact on the structure and politics of Indian society.
The 1871 Canadian census marked the first regularly scheduled collection of national statistics of the Canadian population on April 2, 1871, as required by section 8 of the British North America Act. The constitution required a census to be taken in 1871 and every tenth year thereafter. Parliament implemented the requirements of the constitution through the Census Act of May 12, 1870. In the first census, the population of Canada was enumerated to be 3,485,761.
The Census of Canada 1890–91 was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census took place on April 5, 1891. The total population count of Canada was 4,833,239, an increase of 11.8% over the 1881 census of 4,324,810.










