This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2019) |
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (1,1,1,3,3,3-2H6)Propan-2-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 1702935 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.514 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1090 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C32H6O or C3D6O | |||
| Molar mass | 64.1161 g mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.872 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −94 °C (−137 °F; 179 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 56 °C (133 °F; 329 K) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 24.5-25.3 kPa (at 20°C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H319, H336 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds | Acetone | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
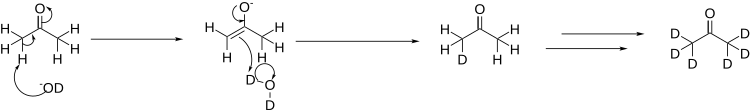
Deuterated acetone ((CD3)2CO), also known as acetone-d6, is a form (isotopologue) of acetone (CH3)2CO in which the hydrogen atom (H) is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope (2H or D). Deuterated acetone is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy. [1]