Related Research Articles

Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early-2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications, and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM.

The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture ("P6") and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million transistors. However, its L2 cache subsystem was a downgrade when compared to the Pentium Pros.

The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications. While the Pentium and Pentium MMX had 3.1 and 4.5 million transistors, respectively, the Pentium Pro contained 5.5 million transistors. Later, it was reduced to a more narrow role as a server and high-end desktop processor and was used in supercomputers like ASCI Red, the first computer to reach the trillion floating point operations per second (teraFLOPS) performance mark. The Pentium Pro was capable of both dual- and quad-processor configurations. It only came in one form factor, the relatively large rectangular Socket 8. The Pentium Pro was succeeded by the Pentium II Xeon in 1998.
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand. The Pentium M processors had a maximum thermal design power (TDP) of 5–27 W depending on the model, and were intended for use in laptops. They evolved from the core of the last Pentium III–branded CPU by adding the front-side bus (FSB) interface of Pentium 4, an improved instruction decoding and issuing front end, improved branch prediction, SSE2 support, and a much larger cache. The first Pentium M–branded CPU, code-named Banias, was followed by Dothan. The Pentium M-branded processors were succeeded by the Core-branded dual-core mobile Yonah CPU with a modified microarchitecture.

Xeon is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture. They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Quick Path Interconnect (QPI) bus.

Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.

The DECstation was a brand of computers used by DEC, and refers to three distinct lines of computer systems—the first released in 1978 as a word processing system, and the latter two both released in 1989. These comprised a range of computer workstations based on the MIPS architecture and a range of PC compatibles. The MIPS-based workstations ran ULTRIX, a DEC-proprietary version of UNIX, and early releases of OSF/1.

The O2 was an entry-level Unix workstation introduced in 1996 by Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) to replace their earlier Indy series. Like the Indy, the O2 used a single MIPS microprocessor and was intended to be used mainly for multimedia. Its larger counterpart was the SGI Octane. The O2 was SGI's last attempt at a low-end workstation.

SGI Visual Workstation is a series of workstation computers that are designed and manufactured by SGI. Unlike its other product lines, which used the 64-bit MIPS RISC architecture, the line used Intel Pentium II and III processors and shipped with Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 as its operating system in lieu of IRIX. However, the Visual Workstation 320 and 540 models deviated from the architecture of IBM-compatible PCs by using SGI's ARCS firmware instead of a traditional BIOS, internal components adapted from its MIPS-based products, and other proprietary components that made them incompatible with internal hardware designed for standard PCs and hence unable to run other versions of Microsoft Windows, especially Windows 9x. By contrast, the remaining models in the line are standard PCs, using VIA Technologies chipsets, Nvidia video cards, and standard components.

Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium was released in 1993. After that, the Pentium II and Pentium III were released.

The Personal Computer Series, or PC Series, was IBM's follow-up to the Personal System/2 and PS/ValuePoint. Announced in October 1994 and withdrawn in October 2000, it was replaced by the IBM NetVista, apart from the Pentium Pro-based PC360 and PC365, which were replaced by the IBM IntelliStation.
The IntelliStation was originally a workstation-class personal computer announced in March 1997 developed by IBM as the follow-on to the PC Series 360 and 365. Certain IntelliStation M Pro Series were near hardware identical to low end IBM Netfinity 1000 Series network servers. In February 2002, POWER processor-based workstations, previously sold directly under the eServer pSeries brand, were also placed under the IntelliStation umbrella.
The DECpc AXP 150, code-named Jensen, is an entry-level workstation developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation. Introduced on 25 May 1993, the DECpc AXP 150 was the first Alpha-based system to support the Windows NT operating system and the basis for the DEC 2000 AXP entry-level servers. It was discontinued on 28 February 1994, succeeded by the entry-level Multia and the entry-level and mid-range models of the AlphaStation family. The charter for the development and production of the DEC 2000 AXP was held by Digital's Entry Level Solutions Business, based in Ayr, Scotland.

The Alpha 21064 is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation that implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). It was introduced as the DECchip 21064 before it was renamed in 1994. The 21064 is also known by its code name, EV4. It was announced in February 1992 with volume availability in September 1992. The 21064 was the first commercial implementation of the Alpha ISA, and the first microprocessor from Digital to be available commercially. It was succeeded by a derivative, the Alpha 21064A in October 1993.

The Alpha 21164, also known by its code name, EV5, is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation that implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). It was introduced in January 1995, succeeding the Alpha 21064A as Digital's flagship microprocessor. It was succeeded by the Alpha 21264 in 1998.
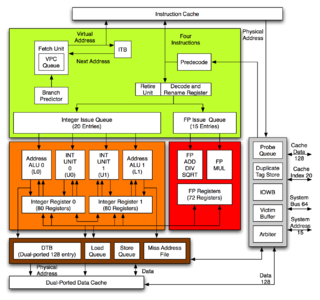
The Alpha 21264 is a Digital Equipment Corporation RISC microprocessor launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA).
References
- ↑ "Retired Alpha workstations". Hewlett-Packard. May 3, 2004. Archived from the original on May 17, 2008. Retrieved October 22, 2008.
- ↑ "DIGITAL Personal Workstation 180i, 200i, 200i² for Windows NT". Digital Equipment Corporation. March 6, 1997. Archived from the original on June 14, 2011. Retrieved October 22, 2008.
- ↑ "DIGITAL Personal Workstation a/au-Series User Information" (PDF). Digital Equipment Corporation. Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- ↑ ""Natural Dictation Wins Best of Comdex". Byte, August 1997". Archived from the original on October 13, 2008. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
- ↑ The FreeBSD Documentation Project (January 17, 2008). "FreeBSD/alpha 6.3-RELEASE Hardware Notes". www.freebsd.org. Retrieved October 21, 2008.
- ↑ "Digital Personal Workstation 433a".
- Jim Davis (May 5, 1997). "Digital has 600-MHz workstation". CNET News . Retrieved October 21, 2008.
- Weiss, Kenneth M.; House, Kenneth A. (1997). "Digital Personal Workstations: The design of high-performance, low-cost Alpha systems". Digital Technical Journal9 (20): pp. 45–56.