The Bishop of Wakefield is an episcopal title which takes its name after the city of Wakefield in West Yorkshire, England. The title was first created for a diocesan bishop in 1888, but it was dissolved in 2014. The Bishop of Wakefield is now an area bishop who has oversight of an episcopal area in the Diocese of Leeds.

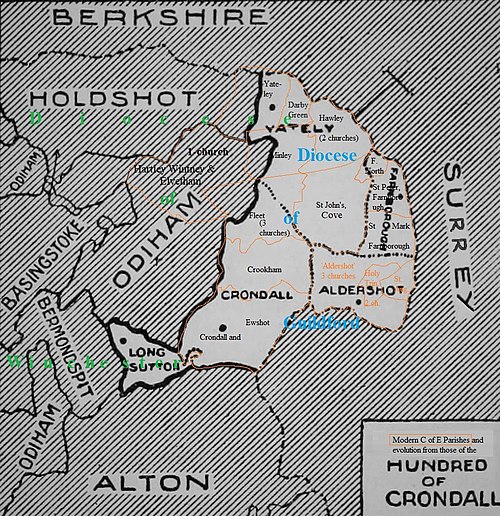
The Diocese of Winchester forms part of the Province of Canterbury of the Church of England. Founded in 676, it is one of the older dioceses in England. It once covered Wessex, many times its present size which is today most of the historic enlarged version of Hampshire.

The Diocese of Southwark is one of the 42 dioceses of the Church of England, part of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The diocese forms part of the Province of Canterbury in England. It was created on 1 May 1905 from part of the ancient Diocese of Rochester that was served by a suffragan bishop of Southwark (1891–1905). Before 1877 most of the area was part of the Diocese of Winchester, some being part of the Diocese of London.

The Diocese of Salisbury is a Church of England diocese in the south of England, within the ecclesiastical Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers the historic county of Dorset, and most of Wiltshire. The diocese is led by Stephen Lake, Bishop of Salisbury, and by the diocesan synod. The bishop's seat is at Salisbury Cathedral.

The Diocese of St Albans forms part of the Province of Canterbury in England and is part of the wider Church of England, in turn part of the worldwide Anglican Communion.

The Diocese of Rochester is a Church of England diocese in the English county of Kent and the Province of Canterbury. The cathedral church of the diocese is Rochester Cathedral in the former city of Rochester. The bishop's Latin episcopal signature is: " (firstname) Roffen", Roffensis being the genitive case of the Latin name of the see.

The Diocese of Oxford is a Church of England diocese that forms part of the Province of Canterbury. The diocese is led by the Bishop of Oxford, and the bishop's seat is at Christ Church Cathedral, Oxford. It contains more church buildings than any other diocese and has more paid clergy than any other except London.
The Bishop of Croydon is an episcopal title used by an area bishop of the Church of England Diocese of Southwark, in the Province of Canterbury, England. The Croydon Archdeaconry was transferred from Canterbury Diocese to Southwark in 1984.
The Diocese of Manchester is a Church of England diocese in the Province of York, England. Based in the city of Manchester, the diocese covers much of the county of Greater Manchester and small areas of the counties of Lancashire and Cheshire.

The Diocese of York is an administrative division of the Church of England, part of the Province of York. It covers the city of York, the eastern part of North Yorkshire, and most of the East Riding of Yorkshire.

The Diocese of Chester is a Church of England diocese in the Province of York covering the pre-1974 county of Cheshire and therefore including the Wirral and parts of Stockport, Trafford and Tameside.

The Diocese of Chichester is a Church of England diocese based in Chichester, covering Sussex. It was founded in 681 as the ancient Diocese of Selsey, which was based at Selsey Abbey, until the see was translated to Chichester in 1075. The cathedral is Chichester Cathedral and the diocesan bishop is the Bishop of Chichester. The diocese is in the Province of Canterbury.

The Diocese of Gloucester is a Church of England diocese based in Gloucester, covering the non-metropolitan county of Gloucestershire. The cathedral is Gloucester Cathedral and the bishop is the Bishop of Gloucester. It is part of the Province of Canterbury.
A deanery is an ecclesiastical entity in the Roman Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Anglican Communion, the Evangelical Church in Germany, and the Church of Norway. A deanery is either the jurisdiction or residence of a dean.
The Bishop of Dorking is an episcopal title used by a suffragan bishop of the Church of England Diocese of Guildford, in the Province of Canterbury, England. The title takes its name from the town of Dorking in Surrey. However, the bishop of Dorking lives in Guildford.

The Archdeaconry of Surrey is the ecclesiastical officer in charge of the archdeaconry of Surrey, a subdivision of the Church of England Diocese of Guildford in the Province of Canterbury.

The Anglican Diocese of Leeds is a diocese of the Church of England, in the Province of York. It is the largest diocese in England by area, comprising much of western Yorkshire: almost the whole of West Yorkshire, the western part of North Yorkshire, the town of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, and most of the parts of County Durham, Cumbria and Lancashire which lie within the historic boundaries of Yorkshire. It includes the cities of Leeds, Bradford, Wakefield and Ripon. It was created on 20 April 2014 following a review of the dioceses in Yorkshire and the dissolution of the dioceses of Bradford, Ripon and Leeds, and Wakefield.
The Archdeacons in the Diocese of Southwark are senior clergy in the Church of England in South London and Surrey. They currently include: the archdeacons of Southwark, of Reigate and of Lewisham & Greenwich, the Archdeacon of Croydon and the archdeacons of Wandsworth and of Lambeth. Each one has responsibility over a geographical area within the diocese.

Richard Paul Davies is a British Anglican bishop. Since September 2023, he has been Bishop of Dorking in the Church of England's Diocese of Guildford. He was Archdeacon of Bangor from 2012 to 2017 and then Archdeacon of Surrey from 2017 until becoming a bishop.
The Archdeacon of Dorking is a senior ecclesiastical officer in the Diocese of Guildford, responsible for clergy discipline and church buildings within the area of her/his archdeaconry.