Related Research Articles
An international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and nonproprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs are intended to make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.
The nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies is a naming scheme for assigning generic, or nonproprietary, names to monoclonal antibodies. An antibody is a protein that is produced in B cells and used by the immune system of humans and other vertebrate animals to identify a specific foreign object like a bacterium or a virus. Monoclonal antibodies are those that were produced in identical cells, often artificially, and so share the same target object. They have a wide range of applications including medical uses.
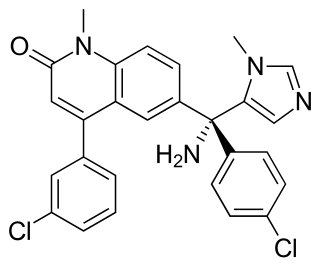
Tipifarnib is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors block the activity of the farnesyltransferase enzyme by inhibiting prenylation of the CAAX tail motif, which ultimately prevents Ras from binding to the membrane, rendering it inactive.
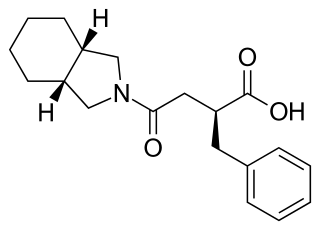
Mitiglinide is a drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are international nonproprietary names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Under the INN system, generic names for drugs are constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into useful categories while keeping related names distinguishable. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.
Perakizumab (INN) is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of arthritis. It binds to IL17A and acts as an immunomodulator.

Pacritinib, sold under the brand name Vonjo, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat myelofibrosis. It is a macrocyclic protein kinase inhibitor. It mainly inhibits Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3\CD135 (FLT3).
Lifastuzumab vedotin is an experimental monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of cancer.
Ulocuplumab is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
Pinatuzumab vedotin is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
Seribantumab is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It binds to extracellular domain of HER3 blocking NRG1 binding and thereby preventing the activation of the receptor.
Brontictuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer.
Lumretuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer.
Landogrozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody and experimental pharmaceutical drug designed for the treatment of muscle wasting disorders.
Plozalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy and arteriovenous graft patency.
Duvortuxizumab (INN) is a chimeric/humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
Oleclumab is a human monoclonal antibody targeting the ectonucleotidase CD73 that was designed for the treatment of pancreatic and colorectal and other cancers.
Carotuximab (INN) (TRC-105) is a chimeric monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer.