
The regulation of therapeutic goods, defined as drugs and therapeutic devices, varies by jurisdiction. In some countries, such as the United States, they are regulated at the national level by a single agency. In other jurisdictions they are regulated at the state level, or at both state and national levels by various bodies, as in Australia.

Lumiracoxib is a COX-2 selective inhibitor nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.

The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of pharmaceutical products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).

Caspofungin is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It works by inhibiting the enzyme (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase and thereby disturbing the integrity of the fungal cell wall. Caspofungin was the first inhibitor of fungal (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthesis to be approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration. Caspofungin is administered intravenously.
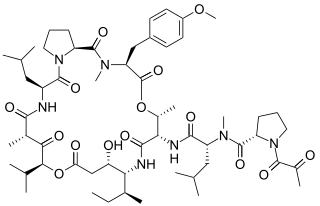
Plitidepsin is a chemical compound extracted from the ascidian Aplidium albicans. It is currently undergoing clinical trial testing. It is a member of the class of compounds known as didemnins.
Besilesomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody labelled with the radioactive isotope technetium-99m. It is used to detect inflammatory lesions and metastases. It binds to an immunoglobulin, IgG1 isotype. SCINTIMUN has been used since 1992 mainly in Hungary, Czech Republic, and Switzerland on the basis of local marketing authorizations, and in Germany. Between 1992 and 2009, an estimated 90,000 patients has been studied. In 2009, the EMEA has approved SCINTIMUN for marketing in all European countries.

Insulin lispro, sold under the brand name Humalog among others, is a modified type of medical insulin used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin or within an insulin pump. Onset of effects typically occurs within 30 minutes and lasts about 5 hours. Often a longer-acting insulin like insulin NPH is also needed.
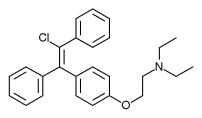
Enclomifene (INN), or enclomiphene (USAN), a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator of the triphenylethylene group acts by antagonizing the estrogen receptor (ER) in the pituitary gland, which reduces negative feedback by estrogen on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thereby increasing gonadotropin secretion and hence gonadal production of testosterone. It is one of the two stereoisomers of clomifene, which itself is a mixture of 38% zuclomifene and 62% enclomifene. Enclomifene is the (E)-stereoisomer of clomifene, while zuclomifene is the (Z)-stereoisomer. Whereas zuclomifene is more estrogenic, enclomifene is more antiestrogenic. In accordance, unlike enclomifene, zuclomifene is antigonadotropic due to activation of the ER and reduces testosterone levels in men. As such, isomerically pure enclomifene is more favorable than clomifene as a progonadotropin for the treatment of male hypogonadism.

Rubitecan is an oral topoisomerase inhibitor, developed by SuperGen.

Garenoxacin (INN) is a quinolone antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.

Casopitant (INN), former tentative trade names Rezonic (U.S.) and Zunrisa (Europe), is an NK1 receptor antagonist which was undergoing research for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It was under development by GlaxoSmithKline. In July 2008, the company filed a marketing authorisation application with the European Medicines Agency. The application was withdrawn and development was discontinued in September 2009 because GlaxoSmithKline decided that further safety assessment was necessary. However, a 2022 review listed casopitant as under development as a potential novel antidepressant for the treatment of major depressive disorder, with a phase 2 clinical trial having been completed.
Technetium (99mTc) votumumab is a human monoclonal antibody labelled with the radionuclide technetium-99m. It was developed for the detection of colorectal tumors, but has never been marketed.
Tanezumab is a monoclonal antibody against nerve growth factor as a treatment for pain via a novel mechanisms different from conventional pain-killer drugs. Tanezumab was discovered and developed by Rinat Neuroscience and was acquired by Pfizer in 2006.

Cabotegravir, sold under the brand name Vocabria among others, is a antiretroviral medication used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is available in the form of tablets and as an intramuscular injection, as well as in an injectable combination with rilpivirine under the brand name Cabenuva.

Etirinotecan pegol is a drug developed by Nektar Therapeutics for the treatment of certain kinds of breast cancer with brain metastases. The European Medicines Agency refused to grant it a marketing authorisation in 2017.
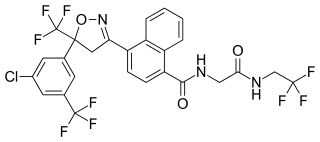
Afoxolaner (INN) is an insecticide and acaricide that belongs to the isoxazoline chemical compound group.
Mirikizumab, sold under the brand name Omvoh, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. It is designed to attach to interleukin-23 (IL-23) and block its activity.
Tagraxofusp, sold under the brand name Elzonris, is an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN).
Regdanvimab, sold under the brand name Regkirona, is a human monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of COVID-19. The antibody is directed against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. It is developed by Celltrion. The medicine is given by infusion (drip) into a vein.
Olipudase alfa, sold under the brand name Xenpozyme, is a medication used for the treatment of non-central nervous system (CNS) manifestations of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD) type A/B or type B.












