
Caladenia flava, commonly known as cowslip orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a relatively common orchid with a single, hairy leaf and up to three yellow flowers which often have red markings. In 2001 three subspecies were named and a fourth is recognised but not as yet formally described.

Leptoceras menziesii, commonly known as rabbit orchid, is a plant in the orchid family, Orchidaceae and the only member of the genus Leptoceras. It is a slender plant, usually found in large colonies and which only flowers after fire. The flowers are small, white, pink and red on a stem up to 30 cm (10 in) tall and is endemic to southern Australia. It was one of the first orchids from Western Australia to be described and was given the name Caladenia menziesii, a name still used by some authorities.

Cymbidium canaliculatum, commonly known as the channelled boat-lip orchid, tiger boat-lip orchid, native cymbidium or tiger orchid is a plant in the orchid family and is endemic to Australia. It is a clump-forming epiphyte with large, greyish green pseudobulbs, each with up to six curved, deeply channelled leaves and up to sixty fragrant, variably coloured flowers that often have spots and blotches and a white to cream-coloured labellum with red markings. This orchid usually grows in the forks or hollows of trees and is found from New South Wales to the northern parts of Western Australia.

Sarcochilus falcatus, commonly known as the orange blossom orchid, is a small epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to eight, leathery leaves with fine teeth on the edges and up to twelve white to cream-coloured flowers with a white labellum that has orange and purple markings.

Cyrtostylis reniformis, commonly known as common gnat-orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It usually has a single kidney-shaped leaf and a flowering spike with up to eight reddish flowers with a shelf-like labellum.

Westringia dampieri, commonly known as shore westringia, is a flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, it grows in South Australia and Western Australia. It is a small, dense shrub with white, mauve, cream or purple flowers.

Caladenia flava subsp. flava, commonly known as the cowslip orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a relatively common orchid with a single, hairy leaf and up to three golden-yellow flowers which often have red markings.

Caladenia flava subsp. maculata, commonly known as the Kalbarri cowslip orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a single, hairy leaf and up to three lemon-yellow flowers with brownish-fawn spots on some parts. It mainly occurs in near-coastal areas north of Geraldton.

Caladenia flava subsp. sylvestris, commonly known as the karri cowslip orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a single, hairy leaf and up to three pale yellow and cream-coloured flowers which are white near the tips of the sepals and petals and marked with bright red or pink.

Caladenia major, commonly known as the waxlip orchid, parson-in-the-pulpit, or purple cockatoo is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae, and is endemic to Australia. It is a ground orchid with a single hairy leaf and one or two purple to mauve flowers. It has been known as Glossodia major since its description by the prolific Scottish botanist Robert Brown in 1810, but recent discoveries suggest its inclusion in the genus Caladenia.

Pterostylis longifolia, commonly known as the common leafy greenhood or tall greenhood, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. Flowering plants have up to seven flowers which are green, partly transparent and which have a labellum which is pale green and hairy with a blackish central stripe. Non-flowering plants have a rosette of leaves but flowering plants lack the rosette, instead having five to eight stem leaves. A similar species, Pterostylis melagramma has paler green flowers which have a less hairy labellum.

Diuris alba, commonly called the white donkey orchid, is a species of orchid which is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to three leaves, and a flowering stem with up to seven white flowers with purplish markings.
Diuris emarginata, commonly called the late donkey orchid, is a species of orchid which is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has up to six leaves and a flowering stem with up to eight yellow flowers with brown markings but only after fires the previous summer.

Diuris pedunculata, commonly known as the small snake orchid, is a species of orchid which is endemic to New South Wales. It usually has two leaves at its base and one or two yellow and orange flowers with purple markings. It originally occurred in scattered populations between Tenterfield and the Hawkesbury River but because of habitat loss is now only known from the New England Tableland.

Diuris setacea, commonly called the bristly donkey orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a tuft of up to ten twisted leaves at its base and up to seven yellow flowers with a few brown markings. It grows in moist soil on granite outcrops and flowers much more prolifically after fire the previous summer.

Thelymitra venosa, commonly known as the large veined sun orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to New South Wales. It has a single fleshy, channelled leaf and up to six relatively large, bright-blue flowers with darker veins. The arms on the side of the column are twisted and yellow, but not toothed at the tip. Unlike most other thelymitras, the flowers do not usually close on cloudy days.
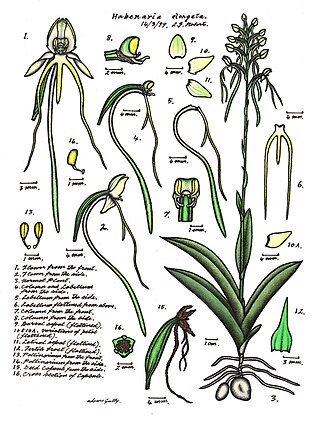
Habenaria elongata, commonly known as the white rein orchid, or Kimberley spider orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to northern Australia. It has up to four leaves at its base and up to twenty small white flowers with yellowish tips and thread-like lobes on the labellum.

Westringia longifolia, commonly known as long-leaved westringia, is a flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae and is endemic to southeastern Australia. It is a small shrub, with linear leaves and mostly white flowers.
Diuris pauciflora, commonly known as swamp bee orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has two to four linear leaves and up to four yellow flowers with brown markings in November or December.

















