
The streaked Spanish mackerel is found mainly in and around India, especially along the Maharashtra and Gujarat coasts. The peak season for fishing this fish is from October to December. It is also known by other names, such as streaked seer, hazard (French), sawara, and carite (Spanish). It is found off Asian coasts from the west coast of India and Sri Lanka east to Java and does not extend east of Wallace's Line. It is an important quarry species for fisheries where it occurs.

The black flounder, also known by the Māori language name mohoao, is a species of flatfish in the family Rhombosoleidae, found around New Zealand in shallow enclosed waters and coastal freshwater lakes. Its adult length ranges from 20 to 45 cm.
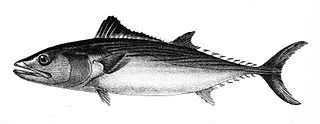
Sarda chiliensis, the eastern Pacific bonito, is a marine species of bonito. It ranges from Ecuador to Chile. Sarda lineolata, which ranges from Alaska to Mexico was formerly considered a subspecies, as Sarda chiliensis lineolata, but this treatment renders the species geographically disjunct.

The frigate tuna, frigate mackerel or alagaduwa is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found around the world in tropical oceans. The eastern Pacific population is now regarded as a separate species by some authorities, Auxis brachydorax.

Ancylopsetta dilecta, the three-eye flounder, is a species of large-tooth flounder found along the Atlantic and Caribbean coasts of North and Central America. It is found down to depths of 137 m (449 ft). This species grows to 25 cm (9.8 in) in total length.

Benthodesmus tenuis, the slender frostfish or ribbon scabbardfish, is a species of cutlassfish in the family Trichiuridae.
Cynoglossus browni, commonly known as the Nigerian tonguesole is a species of tonguefish. It is commonly found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the coast of west Africa, from Senegal to Angola. It is found on soft substrates such as mud or sand between depths of 15m and 40 m. Its main food is small benthic invertebrates.
Cynoglossus cadenati, commonly known as the Ghanaian tonguesole is a species of tonguefish. It is commonly found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the coast of west Africa from Mauritania to Angola, including the Cape Verde Islands. It is found on sand and mud bottoms of coastal waters.

Cynoglossus canariensis, commonly known as the Canary tonguesole is a species of tonguefish. It is commonly found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off western Africa, from Mauritania and Western Sahara south to Angola, including the Canary Islands and Cape Verde Islands. It is a demersal species found at depths of 10-300m, it has been found in brackish water, but is normally a coastal species which occurs over substrates of sand or mud. It feeds on small fish and crustaceans. This species is targeted in trawl fisheries throughout its range and in many areas, it appears to have undergone significant declines. For example, in Gabon the mixed Cynoglossus stock is considered overexploited, while in other parts of western Africa such as Mauritania the stocks of Cynoglossus had declined by over 60% in the five or six years up to 2015. The IUCN list C. canariensis as Near Threatened due to is dependence on conservation.
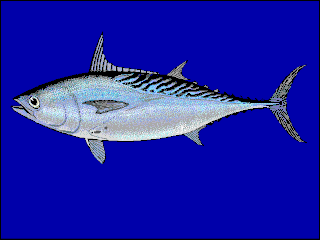
Euthynnus is a genus of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, or mackerel family, and in the tribe Thunnini, more commonly known as the tunas.

Thunnus tonggol is a species of tuna of tropical Indo-West Pacific waters.

The leaping bonito is a species of saltwater finfish from the Scombridae (Mackerel) family. Scombridae includes such tribes as the mackerels, tunas, and bonitos – of the latter of which, the Sardini tribe, this fish is a member. It is the only member of the genus Cybiosarda, which is therefore called a monotypic taxon. Since the bonitos and tunas are close relatives, this fish has variously been referred to by such other common names as Australian tuna, striped bonito, and Watson's bonito.

Citharus linguatula, the spotted flounder or Atlantic spotted flounder, is a species of fish in the Citharidae, a family of flounders. It is native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, where it is found to a depth of 300 m (980 ft). This species grows to a total length of 30 cm (12 in). It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. This species is the only known member of its monotypic genus.
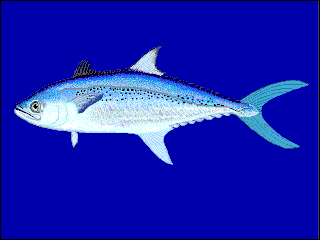
The Korean mackerel also known as the Korean seerfish, is a ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, better known as the mackerel family. Within that family, this fish is a member of the tribe Scomberomorini, the Spanish mackerels. It has an Indo-Pacific distribution which extends from the east coast of India and Sri Lanka along the Asian continental shelf to Sumatra, then north to Korea and Wakasa Bay in the Sea of Japan. This species is of minor commercial importance in some parts of its range, where it is caught using gill nets and is marketed either fresh or dried-salted. The Korean mackerel is an important quarry species for the drift net fishery in Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar in India.
Vanstraelenia chirophthalma, the African solenette, is a species of sole native to the Atlantic coast of Africa where it is found from Guinea-Bissau south to Angola. Occurring at depths of from 8 to 100 metres, this species is of importance to local commercial fisheries. This species grows to a length of 28 centimetres (11 in) TL. This species is the only known member of its genus.

The sand sole is a fish species in the family Soleidae. It is a marine, subtropical, demersal fish up to 40 centimetres (16 in) long.

Dysalotus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Chiasmodontidae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Bothus podas, also known as the wide-eyed flounder, is a flounder in the genus Bothus, native to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Coast of Africa.

Scombriformes, also known as Pelagia and Pelagiaria, is an order of ray-finned fish within the clade Percomorpha. It contains 287 extant species in 16 families, most of which were previously classified under the suborders Scombroidei and Stromateoidei of the order Perciformes.
Heteromycteris proboscideus, the true sole, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Soleidae. It is found in the Southeast Atlantic Ocean near Mauritania to south of Angola. The scientific name of the species was first validly published in 1925 by Paul Chabanaud.

















