
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal Metazoa (animal) clade as a sister of the Diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. The branch of zoology that studies sponges is known as spongiology.

Demosponges are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide. They are sponges with a soft body that covers a hard, often massive skeleton made of calcium carbonate, either aragonite or calcite. They are predominantly leuconoid in structure. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges.

Dendroceratida is an order of sponges of the class Demospongiae. They are typically found in shallow coastal and tidal areas of most coasts around the world. They are generally characterized by concentric layers of fibers containing spongin, and by large flagellated chambers that open directly into the exhalant canals. Along with the Dictyoceratida, it is one of the two orders of demosponges that make up the keratose or "horny" sponges, in which a mineral skeleton is minimal or absent and a skeleton of organic spongin-containing fibers is present instead.

Cryptophycins are a family of macrolide molecules that are potent cytotoxins and have been studied for potential antiproliferative properties useful in developing chemotherapy. They are members of the depsipeptide family.
Acanthopolymastia is a small genus of demosponges belonging to the family Polymastiidae. It has three describe species. These small, bristly, cushion-shaped sponges are only known from deep-sea sites in the southern oceans.
Polymastia aurantia is a species of sea sponge belonging to the family Polymastiidae. It is found in intertidal habitats including tide pools in the vicinity of Auckland, New Zealand.

Halichondria is a genus of sea sponges belonging to the family Halichondriidae. These are massive, amorphous sponges with clearly separated inner and outer skeletons consisting of bundles of spicules arranged in a seemingly random pattern.
Clathrina laminoclathrata is a species of calcareous sponge from Australia. The species name is in reference to its unusual lamina.

Palau'amine is a toxic alkaloid compound synthesized naturally by Stylotella agminata, a species of sea sponge found in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the molecule derives from the island nation of Palau, near which the sponges are found.
Sea sponge aquaculture is the process of farming sea sponges under controlled conditions. It has been conducted in the world's oceans for centuries using a number of aquaculture techniques. There are many factors such as light, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen and the accumulation of waste products that influence the growth rate of sponges. The benefits of sea sponge aquaculture are realised as a result of its ease of establishment, minimum infrastructure requirements and the potential to be used as a source of income for populations living in developing countries. Sea sponges are produced on a commercial scale to be used as bath sponges or to extract biologically active compounds which are found in certain sponge species. Techniques such as the rope and mesh bag method are used to culture sponges independently or within an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system setting. One of the only true sustainable sea sponges cultivated in the world occur in the region of Micronesia, with a number of growing and production methods used to ensure and maintain the continued sustainability of these farmed species.

Dictyoceratida is an order of sponges in the subclass Ceractinomorpha containing five families. Along with the Dendroceratida, it is one of the two orders of demosponges that make up the keratose or "horny" sponges, in which a mineral skeleton is minimal or absent and a skeleton of organic fibers containing spongin, a collagen-like material, is present instead.
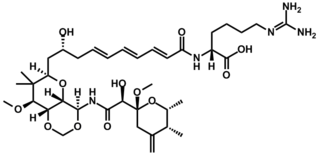
Onnamide A is a bioactive natural product found in Theonella swinhoei, a species of marine sponge whose genus is well known for yielding a diverse set of biologically active natural products, including the swinholides and polytheonamides. It bears structural similarities to the pederins, a family of compounds known to inhibit protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Onnamide A and its analogues have attracted academic interest due to their cytotoxicity and potential for combating the growth and proliferation of cancer cells.

Geodia barretti is a massive deep-sea sponge species found in the boreal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is fairly common on the coasts of Norway and Sweden. It is a dominant species in boreal sponge grounds. Supported by morphology and molecular data, this species is classified in the family Geodiidae.

Verongimorpha is the name of a subclass of sea sponges within the phylum Porifera. It was first authenticated and described by Erpenbeck et al. in 2012.

Thorectidae is a family of sea sponges in the order Dictyoceratida.
Mycale adhaerens, the purple scallop sponge, is a species of marine demosponge in the family Mycalidae. Mycale is a large genus and this species is placed in the subgenus Aegogropila making its full name, Mycale (Aegogropila) adhaerens. It grows symbiotically on the valves of scallop shells and is native to the west coast of North America.
Luffariella is a genus of sea sponges in the family Thorectidae.
Dragmacidon australe is a species of sponge in the family, Axinellidae.
Jean Vacelet is a French marine biologist who specialises in the underwater fauna of the Mediterranean. After earning his licence at the Faculté des Sciences de Marseille and learning to dive in 1954, he specialised in the study of sponges at the Marine station of Endoume, and there he has stayed faithful to both sponges and place for more than half a century. His research has included all aspects of sponges: taxonomy, habitat, biology, anatomy, their bacterial associations, and their place in the evolution of multi-celled animals. He has studied them not only in the Mediterranean but in the Indian Ocean and the Pacific. Exploration of underwater grottoes, together with Jacques Laborel and Jo Hamelin, revealed the existence of sponges dating from very ancient geological periods and the unexpected existence of carnivorous sponges, and surprisingly, the grottoes in some ways mimicked life at much greater depths.
Dysidea etheria, commonly known as the ethereal sponge or heavenly sponge, is a species of lobate sponge within the class Demospongiae. This marine sponge is known for its light blue color and can be found in the Caribbean as well as off the coasts of Florida and Georgia. Like all other poriferans, D. etheria is capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction. The use of spicule collection as well as chemical defenses allows D. etheria to protect itself against predators such as the zebra doris and the orange knobby star. D. etheria is also known as a host species of the invasive brittle star Ophiothela mirabilis. Lastly, various molecular biology studies have utilized D. etheria to both study foreign particle transport in sponges and to isolate novel molecules.









