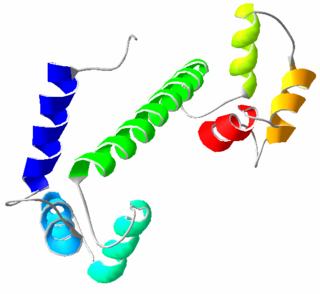
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.
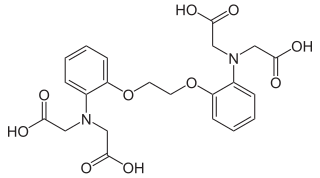
BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid) is a calcium-specific aminopolycarboxylic acid. The presence of four carboxylic acid functional groups makes possible the binding of two calcium ions. The extensive flexibility of the carboxylate ligands is critical to the coordination of calcium and other metal ions. Due to its properties, it is used in research to chelate Ca2+, similarly to EGTA and EDTA.

The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant, with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10,000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the cell. This means that small increases in calcium ions within the cell are easily detected and can bring about important cellular changes (the calcium is said to be a second messenger). Calcium is used to make calcium carbonate (found in chalk) and calcium phosphate, two compounds that the body uses to make teeth and bones. This means that too much calcium within the cells can lead to hardening (calcification) of certain intracellular structures, including the mitochondria, leading to cell death. Therefore, it is vital that calcium ion levels are controlled tightly, and can be released into the cell when necessary and then removed from the cell.

A polyhistidine-tag is an amino acid motif in proteins that typically consists of at least six histidine (His) residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, His6 tag, by the US trademarked name HIS TAG, and most commonly as His-Tag. The tag was invented by Roche, although the use of histidines and its vectors are distributed by Qiagen. Various purification kits for histidine-tagged proteins are available from Qiagen, Sigma, Thermo Scientific, GE Healthcare, Macherey-Nagel, Cube Biotech, Clontech, Bio-Rad, and others.
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a biomolecule from a mixture, based on a highly specific macromolecular binding interaction between the biomolecule and another substance. The specific type of binding interaction depends on the biomolecule of interest; antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptor and ligand, or protein and nucleic acid binding interactions are frequently exploited for isolation of various biomolecules. Affinity chromatography is useful for its high selectivity and resolution of separation, compared to other chromatographic methods.
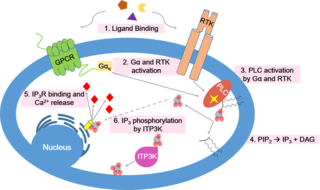
Calcium signaling is the use of calcium ions (Ca2+) to communicate and drive intracellular processes often as a step in signal transduction. Ca2+ is important for cellular signalling, for once it enters the cytosol of the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins. Ca2+ can act in signal transduction resulting from activation of ion channels or as a second messenger caused by indirect signal transduction pathways such as G protein-coupled receptors.
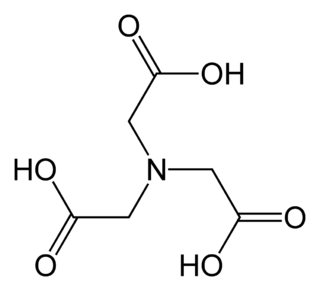
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is the aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula N(CH2CO2H)3. It is a colourless solid that is used as a chelating agent, which forms coordination compounds with metal ions (chelates) such as Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.
Calmodulin-binding proteins are, as their name implies, proteins which bind calmodulin. Calmodulin can bind to a variety of proteins through a two-step binding mechanism, namely "conformational and mutually induced fit", where typically two domains of calmodulin wrap around an emerging helical calmodulin binding domain from the target protein.

The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or motif found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
Calcium-binding proteins are proteins that participate in calcium cell signalling pathways by binding to Ca2+, the calcium ion that plays an important role in many cellular processes. Calcium-binding proteins have specific domains that bind to calcium and are known to be heterogeneous.
The sodium-calcium exchanger (often denoted Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, exchange protein, or NCX) is an antiporter membrane protein that removes calcium from cells. It uses the energy that is stored in the electrochemical gradient of sodium (Na+) by allowing Na+ to flow down its gradient across the plasma membrane in exchange for the countertransport of calcium ions (Ca2+). A single calcium ion is exported for the import of three sodium ions. The exchanger exists in many different cell types and animal species. The NCX is considered one of the most important cellular mechanisms for removing Ca2+.

The inorganic dye ammoniated ruthenium oxychloride, also known as ruthenium red, is used in histology to stain aldehyde fixed mucopolysaccharides.
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5′-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for cAMP and cGMP.

The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) is a transport protein in the plasma membrane of cells and functions to remove calcium (Ca2+) from the cell. PMCA function is vital for regulating the amount of Ca2+ within all eukaryotic cells. There is a very large transmembrane electrochemical gradient of Ca2+ driving the entry of the ion into cells, yet it is very important that they maintain low concentrations of Ca2+ for proper cell signalling. Thus, it is necessary for cells to employ ion pumps to remove the Ca2+. The PMCA and the sodium calcium exchanger (NCX) are together the main regulators of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. Since it transports Ca2+ into the extracellular space, the PMCA is also an important regulator of the calcium concentration in the extracellular space.

The L-type calcium channel is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4.

Troponin C, also known as TN-C or TnC, is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle and is responsible for binding calcium to activate muscle contraction. Troponin C is encoded by the TNNC1 gene in humans for both cardiac and slow skeletal muscle.

Synapsin I, is the collective name for Synapsin Ia and Synapsin Ib, two nearly identical phosphoproteins that in humans are encoded by the SYN1 gene. In its phosphorylated form, Synapsin I may also be referred to as phosphosynaspin I. Synapsin I is the first of the proteins in the synapsin family of phosphoproteins in the synaptic vesicles present in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Synapsin Ia and Ib are close in length and almost the same in make up, however, Synapsin Ib stops short of the last segment of the C-terminal in the amino acid sequence found in Synapsin Ia.
Calcium buffering describes the processes which help stabilise the concentration of free calcium ions within cells, in a similar manner to how pH buffers maintain a stable concentration of hydrogen ions. The majority of calcium ions within the cell are bound to intracellular proteins, leaving a minority freely dissociated. When calcium is added to or removed from the cytoplasm by transport across the cell membrane or sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium buffers minimise the effect on changes in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration by binding calcium to or releasing calcium from intracellular proteins. As a result, 99% of the calcium added to the cytosol of a cardiomyocyte during each cardiac cycle becomes bound to calcium buffers, creating a relatively small change in free calcium.
ParvE101Q is an experimental modification of parvalbumin, designed to delay calcium sequestration in heart muscles to enhance contraction. The protein parvalbumin has EF hand motifs used for calcium binding. EF hands are structural helix-loop-helix protein subunits that have a high affinity for calcium ions, and a moderate affinity for magnesium ions. In muscle, the binding of Ca2+ by parvalbumin efficiently sequesters it following contraction. This increases the speed of muscle relaxation, allowing the muscle to contract again sooner. Although parvalbumin is classified as a delayed calcium buffer, it quickly sequesters Ca2+, usually before the muscle is done fully contracting. Large amounts of parvalbumin allow rapid contractions of muscles at a high contractile speed with the trade-off of having relatively lower contraction force. This decreased force of contraction is due to the rapid sequestration of Ca2+, preventing prolonged contraction which is required for greater force.
Calcium imaging is a microscopy technique to optically measure the calcium (Ca2+) status of an isolated cell, tissue or medium. Calcium imaging takes advantage of calcium indicators, fluorescent molecules that respond to the binding of Ca2+ ions by fluorescence properties. Two main classes of calcium indicators exist: chemical indicators and genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECI). This technique has allowed studies of calcium signalling in a wide variety of cell types. In neurons, electrical activity is always accompanied by an influx of Ca2+ ions. Thus, calcium imaging can be used to monitor the electrical activity in hundreds of neurons in cell culture or in living animals, which has made it possible to dissect the function of neuronal circuits.













