
Sea slug is a common name for some marine invertebrates with varying levels of resemblance to terrestrial slugs. Most creatures known as sea slugs are gastropods, i.e. they are sea snails that, over evolutionary time, have either entirely lost their shells or have seemingly lost their shells due to having a significantly reduced or internal shell. The name "sea slug" is often applied to nudibranchs and a paraphyletic set of other marine gastropods without apparent shells.

Sacoglossa are a superorder of small sea slugs and sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks that belong to the clade Heterobranchia known as sacoglossans. There are 284 valid species recognized within this superorder. Sacoglossans live by ingesting the cellular contents of algae, hence they are sometimes called "sap-sucking sea slugs". Some sacoglossans simply digest the fluid which they suck from the algae, but in some other species, the slugs sequester and use within their own tissues living chloroplasts from the algae they eat, a very unusual phenomenon known as kleptoplasty, for the "stolen" plastids. This earns them the title of the "solar-powered sea slugs", and makes them unique among metazoan organisms, for otherwise kleptoplasty is known only among other euthyneurans and single-celled protists.

Elysia subornata is a species of small sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Plakobranchidae.

Elysia chlorotica is a small-to-medium-sized species of green sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusc. This sea slug superficially resembles a nudibranch, yet it does not belong to that clade. Instead it is a member of the clade Sacoglossa, the sap-sucking sea slugs. Some members of this group use chloroplasts from the algae they eat for photosynthesis, a phenomenon known as kleptoplasty. Elysia chlorotica is one species of such "solar-powered sea slugs". It lives in a subcellular endosymbiotic relationship with chloroplasts of the marine heterokont alga Vaucheria litorea.

Elysia viridis, the sap-sucking slug, is a small-to-medium-sized species of green sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae.

Elysia is a genus of sea slugs, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Plakobranchidae. These animals are colorful sea slugs, and they can superficially resemble nudibranchs, but are not very closely related to them. Instead they are sacoglossans, commonly known as sap-sucking slugs.

Elysia ornata, commonly known as ornate elysia or ornate leaf slug, is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusk. This sea slug superficially resembles a nudibranch, yet it does not belong to that suborder of gastropods. Instead it is a member of the closely related clade Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs.

Elysia timida is a species of sacoglossan sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusk. Found in the Mediterranean and nearby parts of the Atlantic, it is herbivorous, feeding on various algae in shallow water.

Elysia pusilla is a species of small sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Plakobranchidae. It is a sacoglossan.

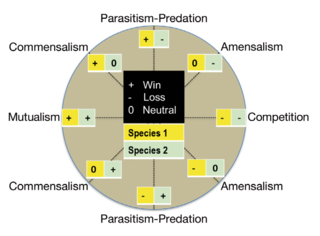
Chemical defense is a strategy employed by many organisms to avoid consumption by producing toxic or repellent metabolites or chemical warnings which incite defensive behavioral changes. The production of defensive chemicals occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria, as well as invertebrate and vertebrate animals. The class of chemicals produced by organisms that are considered defensive may be considered in a strict sense to only apply to those aiding an organism in escaping herbivory or predation. However, the distinction between types of chemical interaction is subjective and defensive chemicals may also be considered to protect against reduced fitness by pests, parasites, and competitors. Repellent rather than toxic metabolites are allomones, a sub category signaling metabolites known as semiochemicals. Many chemicals used for defensive purposes are secondary metabolites derived from primary metabolites which serve a physiological purpose in the organism. Secondary metabolites produced by plants are consumed and sequestered by a variety of arthropods and, in turn, toxins found in some amphibians, snakes, and even birds can be traced back to arthropod prey. There are a variety of special cases for considering mammalian antipredatory adaptations as chemical defenses as well.

Elysia margaritae is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc.
Elysia lobata is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch, but it is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead it is a sacoglossan.

Elysia australis is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch, but it is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead it is a sacoglossan. It occurs in Australia.

Elysia obtusa is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch but is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead it is a sacoglossan.

Elysia trisinuata is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch but is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead belonging to another clade, Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs.
Elysia serca, the seagrass elysia or Caribbean seagrass elysia, is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. Although this sea slug resembles a nudibranch, it is not a nudibranch; it belongs to the clade, Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs. It was first described by Marcus in 1955 from specimens found in Brazil.
Microbial symbiosis in marine animals was not discovered until 1981. In the time following, symbiotic relationships between marine invertebrates and chemoautotrophic bacteria have been found in a variety of ecosystems, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Symbiosis is a way for marine organisms to find creative ways to survive in a very dynamic environment. They are different in relation to how dependent the organisms are on each other or how they are associated. It is also considered a selective force behind evolution in some scientific aspects. The symbiotic relationships of organisms has the ability to change behavior, morphology and metabolic pathways. With increased recognition and research, new terminology also arises, such as holobiont, which the relationship between a host and its symbionts as one grouping. Many scientists will look at the hologenome, which is the combined genetic information of the host and its symbionts. These terms are more commonly used to describe microbial symbionts.
Jeanette Davis is a marine microbiologist, Policy Analyst for NOAA and children's book author.

Elysia marginata is a marine gastropod in the family Plakobranchidae. It is known for its ability to regenerate its whole body and heart after autotomizing it from its head.
















