Hyphomycetes are a form classification of fungi, part of what has often been referred to as fungi imperfecti, Deuteromycota, or anamorphic fungi. Hyphomycetes lack closed fruit bodies, and are often referred to as moulds. Most hyphomycetes are now assigned to the Ascomycota, on the basis of genetic connections made by life-cycle studies or by phylogenetic analysis of DNA sequences; many remain unassigned phylogenetically.

Acremonium is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae. It used to be known as Cephalosporium.

Acrophialophora fusispora is a poorly studied ascomycete fungus found in soil, air and various plants. A. fusispora is morphologically similar to the genera Paecilomyces and Masonia, but differ in the presence of pigmented conidiophores, verticillate phialides, and frequent sympodial proliferation. Moreover, A. fusispora is distinguished by its pigmented spindle-shaped conidia, covered with spiral bands. The fungus is naturally found in soils of tropical to temperate regions. The fungus has been identified as a plant and animal pathogen, and has recently been recognized as an emerging opportunistic human pathogen. A. fusispora infection in human is rare and has few documented clinical cases, but due to the rarity of the fungus and potential misidentification, the infections may be underdiagnosed. Clinical cases of A. fusispora include cases of keratitis, pulmonary colonization and infection, and cerebral infections. The fungus also has two documented cases of infection in dogs.

Geotrichum candidum is a fungus which is a member of the human microbiome, notably associated with skin, sputum, and faeces where it occurs in 25–30% of specimens. It is common in soil and has been isolated from soil collected around the world, in all continents.
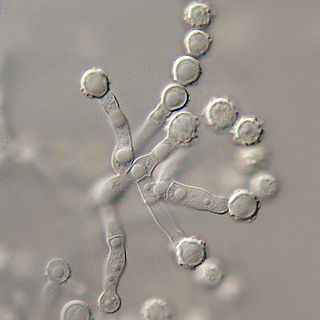
The Microascaceae are a family of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae. The family was published by David Malloch in 1970, an emended description based on Everet Stanley Luttrell's original 1951 publication. Family was updated in 2020.
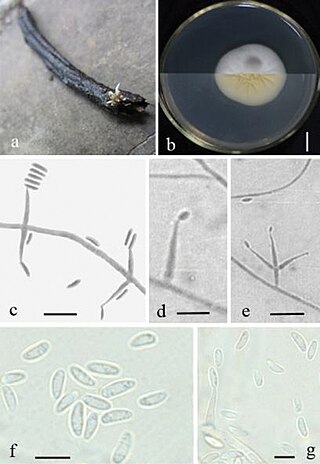
Lecanicillium is a genus of fungi in the order Hypocreales and is described as anamorphic Cordycipitaceae; 21 species are currently described. Some of these entomopathogenic fungus species were previously widely known as Verticillium lecanii (Zimmerman) Viegas. This genus was first named and introduced by Rasoul Zare (IRIPP) and Walter Gams (CBS).

Purpureocillium is a fungal genus in the Ophiocordycipitaceae family. The genus now contains at least 5 species with the type species Purpureocillium lilacinum, a common soil mold. It has been isolated from a wide range of habitats, including cultivated and uncultivated soils, forests, grassland, deserts, estuarine sediments and sewage sludge, and insects. It has also been found in nematode eggs, and occasionally from females of root-knot and cyst nematodes. In addition, it has frequently been detected in the rhizosphere of many crops. The species can grow at a wide range of temperatures – from 8 to 38 °C for a few isolates, with optimal growth in the range 26 to 30 °C. It also has a wide pH tolerance and can grow on a variety of substrates. P. lilacinum has shown promising results for use as a biocontrol agent to control the growth of destructive root-knot nematodes.

Purpureocillium lilacinum is a species of filamentous fungus in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It has been isolated from a wide range of habitats, including cultivated and uncultivated soils, forests, grassland, deserts, estuarine sediments and sewage sludge, and insects. It has also been found in nematode eggs, and occasionally from females of root-knot and cyst nematodes. In addition, it has frequently been detected in the rhizosphere of many crops. The species can grow at a wide range of temperatures – from 8 to 38 °C for a few isolates, with optimal growth in the range 26 to 30 °C. It also has a wide pH tolerance and can grow on a variety of substrates. P. lilacinum has shown promising results for use as a biocontrol agent to control the growth of destructive root-knot nematodes.
Gabarnaudia is a genus of anamorphic fungi that was placed in the family Ceratocystidaceae, until phylogenetic analysis by Hausner and Reid (2004) and De Beer et al. (2013a) showed that Gabarnaudia fimicolaG. betae and G. humicola clustered within genus Sphaeronaemella.
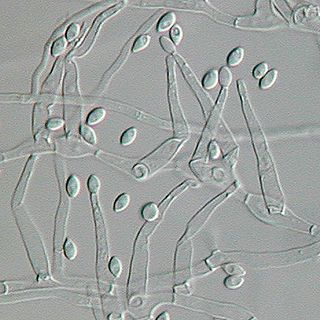
Paecilomyces variotii, also known by the name Byssochlamys spectabilis for the sexual state, is a common environmental mold from the Phylum Ascomycota. It is widespread in the environment and can be found in composts, soils and wood, as well es a common environmental contaminant in indoor air and carpet dust. Ascospores of the sexual state of P. variotii are strongly heat-resistant. As such the fungus is a common contaminant of heat-treated foods and juices. Paecilomyces variotii has been associated with a number of infective diseases of humans and animals.

The Cordycipitaceae are a family of parasitic fungi in the Ascomycota, class Sordariomycetes and order Hypocreales. The family was first published in 1969 by mycologist Hanns Kreisel, but the naming was invalid according to the code of International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. It was validly published in 2007.
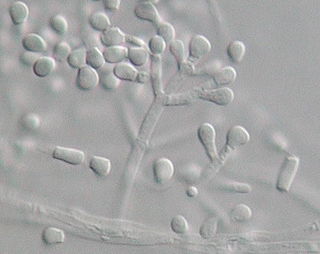
Geomyces pannorum is a yellow-brown filamentous fungus of the phylum Ascomycota commonly found in cold soil environments including the permafrost of the Northern hemisphere. A ubiquitous soil fungus, it is the most common species of the genus Geomyces; which also includes G. vinaceus and G. asperulatus. Geomyces pannorum has been identified as an agent of disfigurement of pigments used in the 15,000-year-old paintings on the walls of the Lascaux caves of France. Strains of Geomyces have been recovered from the Alaskan Fox Permafrost Tunnel and radiocarbon dated to between 14,000 and 30,000 years old.

Exophiala phaeomuriformis is thermophilic fungus belonging to the genus Exophiala and the family Herpotrichiellaceae. it is a member of the group of fungi known as black yeasts, and is typically found in hot and humid locations, such as saunas, bathrooms, and dishwashers. This species can cause skin infections and is typically classified as a Biosafety Risk Group 2 agent.
Petriella setifera is a fungus commonly found in soil and feces. The fungus has also been located on wood rot, plant species, and compost. A significant portion of P. setifera reports are found on sources with no previous association with the fungus. There are no known human cases of fungal infection, but one reported case of a dolphin infection. The fungus may have immunosuppressive characteristics, but it has not been confirmed. Many properties of the fungus are unknown, requiring further research.
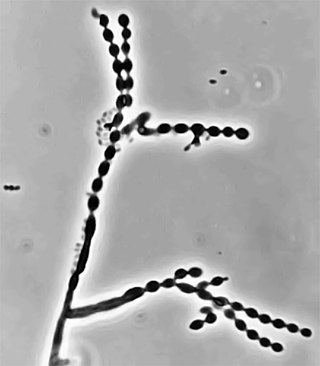
Cladophialophora carrionii is a melanized fungus in the genus Cladophialophora that is associated with decaying plant material like cacti and wood. It is one of the most frequent species of Cladophialophora implicated in human disease. Cladophialophora carrionii is a causative agent of chromoblastomycosis, a subcutaneous infection that occurs in sub-tropical areas such as Madagascar, Australia and northwestern Venezuela. Transmission occurs through traumatic implantation of plant material colonized by C. carrionii, mainly infecting rural workers. When C. carrionii infects its host, it transforms from a mycelial state to a muriform state to better tolerate the extreme conditions in the host's body.
Cladophialophora arxii is a black yeast shaped dematiaceous fungus that is able to cause serious phaeohyphomycotic infections. C. arxii was first discovered in 1995 in Germany from a 22-year-old female patient suffering multiple granulomatous tracheal tumours. It is a clinical strain that is typically found in humans and is also capable of acting as an opportunistic fungus of other vertebrates Human cases caused by C. arxii have been reported from all parts of the world such as Germany and Australia.

Rhinocladiella is a genus of fungi in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It has 17 species. The genus was circumscribed by Swedish botanist John Axel Nannfeldt in 1934 with R. atrovirens as the type species.

Engyodontium aranearum is a species of ascomycete fungus in the family Cordycipitaceae. It parasitizes the long bodied cellar spider. It causes 100% mortality in infected spiders.
Savoryellaceae is a family of aquatic based fungi. It is the only family in the monotypic order Savoryellales within the class Sordariomycetes, division Ascomycota.
Monodictys is a genus of fungi of uncertain familial and ordinal placement in the class Ascomycetes. The genus was circumscribed by Welsh-born Canadian mycologist Stanley Hughes in 1956. He assigned Monodictys putredinis as the type species.













