
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World.

Korean is the native language for about 80 million people, mostly of Korean descent. It is the official and national language of both North Korea and South Korea, but over the past 75 years of political division, the two Koreas have developed some noticeable vocabulary differences. Beyond Korea, the language is recognised as a minority language in parts of China, namely Jilin Province, and specifically Yanbian Prefecture and Changbai County. It is also spoken by Sakhalin Koreans in parts of Sakhalin, the Russian island just north of Japan, and by the Koryo-saram in parts of Central Asia. The language has a few extinct relatives which—along with the Jeju language (Jejuan) of Jeju Island and Korean itself—form the compact Koreanic language family. Even so, Jejuan and Korean are not mutually intelligible with each other. The linguistic homeland of Korean is suggested to be somewhere in contemporary Northeast China. The hierarchy of the society from which the language originates deeply influences the language, leading to a system of speech levels and honorifics indicative of the formality of any given situation.

North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically.

North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and Tumen rivers, and South Korea to the south at the Korean Demilitarized Zone. North Korea's border with South Korea is a disputed border as both countries claim the entirety of the Korean Peninsula. The country's western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. North Korea, like its southern counterpart, claims to be the legitimate government of the entire peninsula and adjacent islands. Pyongyang is the capital and largest city.

North Carolina is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park.

North Africa, or Northern Africa, is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal.

Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral. Presbyterian churches derive their name from the presbyterian form of church government by representative assemblies of elders. Many Reformed churches are organised this way, but the word Presbyterian, when capitalized, is often applied to churches that trace their roots to the Church of Scotland or to English Dissenter groups that formed during the English Civil War.

In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes, which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

The Norse exploration of North America began in the late 10th century, when Norsemen explored areas of the North Atlantic colonizing Greenland and creating a short term settlement near the northern tip of Newfoundland. This is known now as L'Anse aux Meadows where the remains of buildings were found in 1960 dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. This discovery helped reignite archaeological exploration for the Norse in the North Atlantic. This single settlement, located on the island of Newfoundland and not on the North American mainland, was abruptly abandoned.
The National League is an association football league in England consisting of three divisions, the National League, National League North, and National League South. It was called the "Alliance Premier League" from 1979 until 1986. Between 1986 and 2015, the league was known as the "Football Conference".

The dire wolf is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor Smilodon. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene epochs. The species was named in 1858, four years after the first specimen had been found. Two subspecies are recognized: Aenocyon dirus guildayi and Aenocyon dirus dirus. The largest collection of its fossils has been obtained from the Rancho La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles.

The Sahara is a desert on the African continent. With an area of 9,200,000 square kilometres (3,600,000 sq mi), it is the largest hot desert in the world and the third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Arctic.

An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification Cfb, typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters, with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand.

The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 and 1937. It existed from roughly 11,500 to 10,800 years Before Present at the end of the last glacial period and is characterized by the manufacture of "Clovis points" and distinctive bone and ivory tools.

A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot summers and freezing cold winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often does have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below 0 °C (32.0 °F) or −3 °C (26.6 °F) depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above 10 °C (50 °F). In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler Dfb, Dwb, and Dsb subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates.

NATO is an international military alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary. Article 6 of the treaty limits the scope of Article 5 to the islands north of the Tropic of Cancer, the North American and European mainlands, the entirety of Turkey, and French Algeria. As such, an attack on Hawaii, Puerto Rico, French Guiana, Ceuta, or Melilla, among other places, would not trigger an Article 5 response.
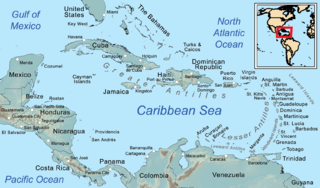
The Caribbean is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.
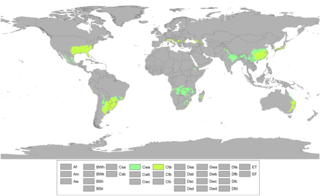
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It is a landlocked country bordering Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.


















