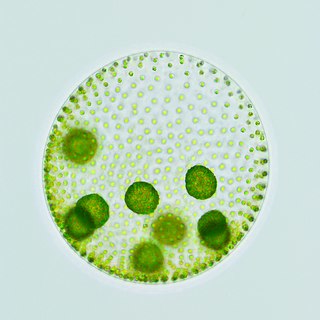
The Volvocaceae are a family of unicellular or colonial biflagellates, including the typical genus Volvox. The family was named by Ehrenberg in 1834, and is known in older classifications as the Volvocidae. All species are colonial and inhabit freshwater environments.
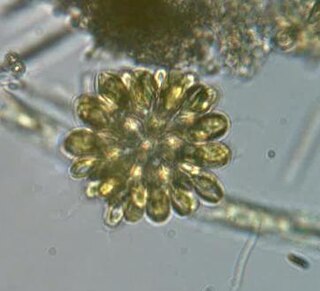
The synurids are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales.

Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was a German naturalist, zoologist, botanist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. He is considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time.
Cryptomonas is the name-giving genus of the Cryptomonads established by German biologist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1831. The algae are common in freshwater habitats and brackish water worldwide and often form blooms in greater depths of lakes. The cells are usually brownish or greenish in color and are characteristic of having a slit-like furrow at the anterior. They are not known to produce any toxins. They are used to feed small zooplankton, which is the food source for small fish in fish farms. Many species of Cryptomonas can only be identified by DNA sequencing. Cryptomonas can be found in several marine ecosystems in Australia and South Korea.

Pompanos are marine fish in the genus Trachinotus in the family Carangidae. Pompano may also refer to various other, similarly shaped members of the Carangidae, or the order Perciformes. Their appearance is of deep-bodied fishes, exhibiting strong lateral compression, with a rounded face and pronounced curve to the anterior portion of their dorsal profile. Their ventral profile is noticeably less curved by comparison, while their anterior profile is straight-edged, tapering sharply to a narrow caudal peduncle. Their dorsal and anal fins are typically sickle-shaped, with very long anterior rays and a succession of much shorter rays behind, with a similarly long & curved, deeply forked tail which has a narrow base. They are typically overall silvery in color, sometimes with dark or yellowish fins, and one or a few black markings on the side of their body. They are toothless and are relatively large fish, up to about 1.2 m (3.9 ft) long, although most species reach no more than half or two-thirds of that size. They are found worldwide in warmer seas, sometimes also entering brackish waters.

The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 230 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.

Bodo is a genus of microscopic kinetoplastids, flagellate excavates first described in 1831 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. The genus is small, as it has recently been redefined to include only four species. Bodo includes free-living, phagotrophic organisms that can be found in many marine and freshwater environments as well as some terrestrial environments. Being phagotrophic, Bodo feeds on bacteria and other microorganisms that it finds while swimming through its water-based habitats. The swimming-like movement is facilitated by the two unequal flagella that Bodo possesses which arise from an anteriorly located flagellar pocket. Bodo is roughly bean-shaped and is often missed in samples from water or terrestrial environments due to its small size.

Chromodorididae, or chromodorids, are a taxonomic family of colourful sea slugs; dorid nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Doridoidea. “Chromodorid nudibranchs are among the most gorgeously coloured of all animals.” The over 360 described species are primarily found in tropical and subtropical waters, as members of coral reef communities, specifically associated with their sponge prey. The chromodorids are the most speciose family of opisthobranchs. They range in size from <10mm to over 30 cm, although most species are approximately 15–30 mm in size.

Chaetoceros is a genus of diatoms in the family Chaetocerotaceae, first described by the German naturalist C. G. Ehrenberg in 1844. Species of this genus are mostly found in marine habitats, but a few species exist in freshwater. It is arguably the common and most diverse genus of marine planktonic diatoms, with over 200 accepted species. It is the type genus of its family.
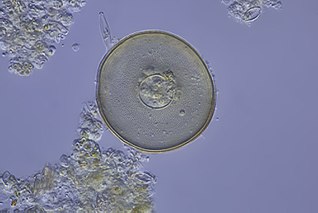
Arcella is a genus of testate amoebae in the order Arcellinida, usually found in freshwaters and mosses, and rarely in soils. A key characteristic of Arcella is the circular test with a hole on its center from where finger-like pseudopods emerge. It is one of the largest testacean genera.

Climacostomum is a genus of unicellular ciliates, belonging to the class Heterotrichea.

Synchaeta is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Synchaetidae.

Tripos is a genus of marine dinoflagellates in the family Ceratiaceae. It was formerly part of Ceratium, then separated out as Neoceratium, a name subsequently determined to be invalid.

Eunotia is a genus of diatoms. They are fresh water diatoms, specifically common in lakes, and they are also common in fossil records, although their siliceous wall design may have been lost and they appear plane, an example is Eunotia tetradon.

Heterodactyla is a genus of sea anemones of the family Thalassianthidae. The genus was first described in 1834 by Wilhelm Hemprich and Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.
Notommata is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Notommatidae.

Dissotrocha is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Philodinidae. The species of this genus are found in Europe, Australia and North America.

Gomphonema is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Gomphonemataceae.
Epiphanidae is a family of rotifers belonging to the order Ploima.

Odontosyllis is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Syllidae.

















