
The cutlassfishes are about 45 species of predatory ray-finned fish in the family Trichiuridae of the order Scombriformes found in seas throughout the world. Fish of this family are long, slender, and generally steely blue or silver in colour, giving rise to their name. They have reduced or absent pelvic and caudal fins, giving them an eel-like appearance, and large fang-like teeth.

The Gempylidae are a family of scombriform ray-finned fishes commonly known as snake mackerels or escolars. The family includes about 25 species.
Eutrichiurides is an extinct genus of prehistoric cutlass fish.

Grammatorcynus is a genus of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae. This genus together with Acanthocybium and Scomberomorus are comprised by the tribe Scomberomorini, commonly known as the Spanish mackerels or seerfishes.

Rastrelliger is a mackerel genus in the family Scombridae. The three species of Rastrelliger together with the four species of Scomber comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels".
The black snake mackerel is a species of snake mackerel found worldwide in both tropical and temperate waters where they are found at depths of from 914 to 1,646 metres making diel vertical migrations from mesopelagic depths to the surface at night. It can reach a length of 25 centimetres (9.8 in) SL though most do not exceed 15 centimetres (5.9 in) SL. It is important to local peoples as a food fish. This species is currently the only known member of its genus, Nealotus. That genus is therefore said to be monotypic.

The blacksail snake mackerel, known also as the black snoek, is a species of snake mackerel found in the Indo-Pacific from shallow water to a depth of at least 400 m (1,300 ft) where they appear to prefer slopes on seamounts and ridges. They are known for making diel vertical migrations to near-surface waters at night, feeding on fish, squid and crustaceans. This species reaches a total length of 2 m (6.6 ft) though most are around 1 m (3.3 ft). This species is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. It is at the only member of the genus Thyrsitoides, making the genus monotypic.
Nesiarchus nasutus, the Black gemfish, is a species of snake mackerel found in tropical and subtropical waters in most parts of the world, though not in east Pacific and north Indian waters. It occurs at depths of from 200 to 1,200 metres though they make diel vertical migrations from benthopelagic to mesopelagic depths at night. This species can reach a length of 130 centimetres (51 in) SL though most do not exceed 80 centimetres (31 in) SL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. This species is currently the only known member of its genus, Nesiarchus.
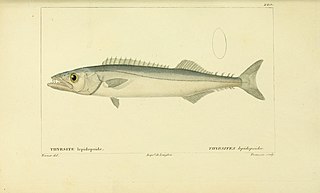
Thyrsitops lepidopoides, the white snake mackerel, is a species of snake mackerel found off the coasts of South America from Brazil on the Atlantic side to Chile on the Pacific side. It can be found at depths of from 30 to 350 metres. This species can reach a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) SL though most do not exceed 25 centimetres (9.8 in) SL. It is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. It is currently the only known member of its genus.
Diplospinus multistriatus, the Striped escolar, is a species of snake mackerel of cosmopolitan distribution at depths of from 50 to 1,000 metres. This species grows to a length of 33 centimetres (13 in) SL though most do not exceed 20 centimetres (7.9 in) SL. This species is important as a food fish to local populations. This species is the only known member of its genus.
Neoepinnula is a genus of snake mackerels, also known as sackfish.
Paradiplospinus is a genus of snake mackerels native to the southern oceans.
Rexea is a genus of snake mackerels found in the Indian and Pacific oceans. It feeds on fishes, crustaceans and cephalopods.
Rexichthys johnpaxtoni, the Paxton's escolar, is a species of snake mackerel found in the western Pacific Ocean from around Australia and New Caledonia where it is found at depths of from 270 to 470 metres. This species grows to a length of 22 centimetres (8.7 in) SL. This species is the only known member of its genus, the specific name honours John R. Paxton, a curator of the collection of fishes of the Australian Museum in Sydney.
Tongaichthys robustus, the Tonga escolar, is a species of snake mackerel known from the Tonga Ridge near Fiji and off of Queensland, Australia from Flinders Reef. It is known to occur at depths of from 288 to 312 metres. This species grows to a length of 30 centimetres (12 in) SL. This species is the only known member of its genus.

Tentoriceps is a monotypic genus of cutlassfish, family Trichiuridae, from the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The sole species is Tentoriceps cristatus. Its common name is crested hairtail.

Lepidopus is a genus of cutlassfishes.
The New Guinea hairtail is a species of cutlassfish which is classified in the monotypic genus Demissolinea. It is known only from the type location Dolak Island off southwestern New Guinea.

Lepturacanthus is a genus of cutlassfish from the Indo-Pacific region. They are benthopelagic species of waters over the continental shelf, it is a predator of a variety of small coastal fishes, squid and crustaceans.

Scombriformes, also known as Pelagia and Pelagiaria, is an order of ray-finned fish within the clade Percomorpha. It contains 287 extant species in 16 families, most of which were previously classified under the suborders Scombroidei and Stromateoidei of the order Perciformes.









