
Ficus is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (F. carica) is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region, which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses.

Musa is one of three genera in the family Musaceae. The genus includes 83 species of flowering plants producing edible bananas and plantains. Though they grow as high as trees, banana and plantain plants are not woody and their apparent "stem" is made up of the bases of the huge leaf stalks. Thus, they are technically gigantic herbaceous plants.

Ficus tinctoria, also known as dye fig, or humped fig is a hemiepiphytic tree of genus Ficus. It is also one of the species known as strangler fig.

Frangula californica is a species of flowering plant in the buckthorn family native to western North America. It produces edible fruits and seeds. It is commonly known as California coffeeberry and California buckthorn.

Berberis vulgaris, also known as common barberry, European barberry or simply barberry, is a shrub in the genus Berberis native to the Old World. It produces edible but sharply acidic berries, which people in many countries eat as a tart and refreshing fruit.

Garuga is a genus of shrubs and trees in the incense or torchwood family Burseraceae. Its members are found from India to the southwest Pacific.

Olea europaea subsp. cuspidata is a subspecies of the well-known olive tree, which until recently was considered a separate species and is still mentioned as such in many sources. Native to mostly dry areas across sub-saharan Africa, West Asia, the Himalayan region and southern China, it has various common names, including wild olive, African olive, brown olive and Indian olive.

Rhamnus crocea, the spiny redberry, is a species of plant in the family Rhamnaceae. It is native from California to northern Mexico. As of March 2024, five subspecies are recognized.

Pyracantha crenulata, the Nepalese firethorn, Nepal firethorn or Himalayan firethorn, is a species of firethorn. The native range of this shrub species stretches from northern Pakistan to northwestern India and China.

Ficus americana, commonly known as the West Indian laurel fig or Jamaican cherry fig, is a tree in the family Moraceae which is native to the Caribbean, Mexico in the north, through Central and South America south to southern Brazil. It is an introduced species in Florida, USA. The species is variable; the five recognised subspecies were previously placed in a large number of other species.

Barleria prionitis is a shrub in the family Acanthaceae, native to Island and Mainland Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula and northeastern Africa. It is widely spread as an ornamental and weed, occurring in naturalised populations around the world. It used not only as an ornamental but also as a hedge and extensively as a component of folk medicines. As a weed it is regarded as problematic in many areas.

Rubus ellipticus, commonly known as ainselu, golden evergreen raspberry, golden Himalayan raspberry, or yellow Himalayan raspberry, is an Asian species of thorny fruiting shrub in the rose family. Its native range stretches from the Indian subcontinent to southern China and Indochina and the Philippines.

Elaeocarpus lanceifolius is a tree species in the family Elaeocarpaceae. It is found across tropical Asia from Thailand to Yunnan to Nepal to Karnataka, India. It is used for its wood, fruit, and nuts.

Cassia javanica, also known as Java cassia, pink shower, apple blossom tree and rainbow shower tree, is a species of tree in the family Fabaceae. Its origin is in Southeast Asia, but it has been extensively grown in tropical areas worldwide as a garden tree owing to its beautiful crimson and pink flower bunches.

Ficus auriculata is a type of fig tree, native to subtropical and tropical mainland Asia. It is noted for its big and round leaves and edible fruit.

Berberis asiatica, is a species of shrub, in the family Berberidaceae. It is native to the Himalayas, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal and Tibet.
Daphne mucronata is a shrub, of the family Thymelaeaceae. It is native to western Asia, ranging from eastern Turkey to the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and the western Himalayas.

Terminalia hadleyana is a tree of the family Combretaceae native to northern Australia.
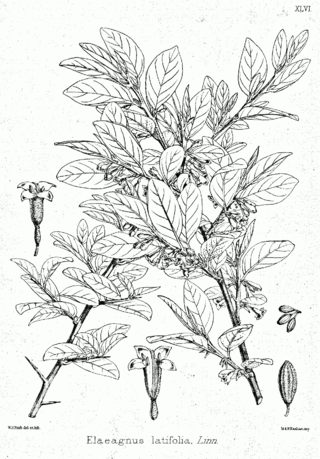
Elaeagnus latifolia, known as the bastard oleaster, or soh-sang, is a species of Elaeagnus native to India and Southeast Asia.

Grewia tenax, called the phalsa cherry, white crossberry, raisin bush, gangara, gangu, or kanger, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. It is native to Africa, from the Sahara to Tanzania and parts of southern Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and on to the Indian Subcontinent. The ripe fruit is edible and is consumed by local peoples either fresh, dried, or powered in drinks.



















