
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping. “Fishing” may include catching aquatic animals other than fish, such as molluscs, cephalopods, crustaceans, and echinoderms. The term is not normally applied to catching farmed fish, or to aquatic mammals, such as whales where the term whaling is more appropriate. In addition to being caught to be eaten, fish are caught as recreational pastimes. Fishing tournaments are held, and caught fish are sometimes kept as preserved or living trophies. When bioblitzes occur, fish are typically caught, identified, and then released.

The Nile perch is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is widespread throughout much of the Afrotropic ecozone, being native to the Congo, Nile, Senegal, Niger and Lake Chad, Volta, Lake Turkana, and other river basins. It also occurs in the brackish waters of Lake Maryut in Egypt. The Nile perch is a fish of substantial economic and food-security importance in East Africa. Originally described as Labrus niloticus, among the marine wrasses, the species has also been referred to as Centropomus niloticus. Common names include African snook, Victoria perch, and a large number of local names in various African languages, such as the Luo name mbuta or mputa. In Tanzania, it is called sangara, sankara, or chenku. In Francophone African countries, it is known as capitaine and in Egypt/Sudan as am'kal. Its name in the Hausa language is giwan ruwa, meaning "water elephant".
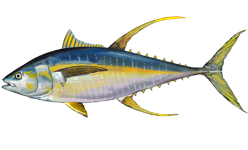
The yellowfin tuna is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.

Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to a small amount of countries around the earth, but those who practice it as an industry must often pursue fish far into the ocean under adverse conditions. Large-scale commercial fishing is also known as industrial fishing. This profession has gained in popularity with the development of shows such as Deadliest Catch, Swords, and Wicked Tuna. The major fishing industries are not only owned by major corporations but by small families as well. The industry has had to adapt through the years in order to keep earning a profit. A study taken on some small family-owned commercial fishing companies showed that they adapted to continue to earn a living but not necessarily make a large profit. It is the adaptability of the fishermen and their methods that cause some concern for fishery managers and researchers; they say that for those reasons, the sustainability of the marine ecosystems could be in danger of being ruined.

The live fish trade can refer to the live food fish trade or to the ornamental fish trade. The fish can come from many places, but most comes from Southeast Asia.
Cyanide fishing is a method of collecting live fish mainly for use in aquariums, which involves spraying a sodium cyanide mixture into the desired fish's habitat in order to stun the fish. The practice hurts not only the target population, but also many other marine organisms, including coral and coral reefs.

The fishing industry in Scotland comprises a significant proportion of the United Kingdom fishing industry. A recent inquiry by the Royal Society of Edinburgh found fishing to be of much greater social, economic and cultural importance to Scotland than it is relative to the rest of the UK. Scotland has just 8.4% of the UK population but lands at its ports over 60% of the total catch in the UK.

Fishing in India is a major industry in its coastal states, employing over 14 million people. In 2016-17, the country exported 11,34,948 metric tonnes of seafood worth US$ 5.78 billion, frozen shrimp being the top item of export. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, fish production has increased more than tenfold since 1947 and doubled between 1990 and 2010.

Fishing in Ghana is made up of both ocean caught fish, as well as freshwater fishing in lakes and rivers.
Lake Chad, with its two major rivers and many runoff zones, was ranked high among Africa's producers of inland freshwater fish in the 1970s. With the drought and diversion of the waters of some rivers, however, production declined in the 1980s. Traditionally, fish have been an important source of protein for those living along the rivers and lakes, and fishing was also a means of earning money. Because it was practiced in an entirely traditional manner and totally outside the control of government or modern commercial enterprises, there was no accurate statistical information on fishing.
Fishing in Angola is mainly performed by foreign fleets. Some of the foreign fishing fleets operating in Angolan waters were required by the government to land a portion of their catch at Angolan ports to increase the local supply of fish. Fishing agreements of this kind were reached with several countries, including with Spain, Japan, and Italy.

There are two major sources of fish in Uganda; one is from aquaculture, the other from fishing in rivers and lakes. The latter has made up the largest and most significant share of all fishing. Open water covers 15.3 percent of Uganda's surface and comprises five major lakes (Lake Victoria, Lake Albert, Lake Kyoga, Lake Edward and Lake George which are the main sources of fish in the country. Lake Victoria continues to be the most important water body in Uganda both in size and contribution to the total fish catch, followed by Lake Albert and Lake Kyoga.

Canada's fishing industry is a key contributor to the success of the Canadian economy. In 2016, Canada's fishing industry exported $6.6 billion in fish and seafood products and employed approximately 72,000 people in the industry. Aquaculture, which is the farming of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in fresh or salt water, is the fastest growing food production activity in the world and a growing sector in Canada. In 2015, aquaculture generated over $1 billion in GDP and close to $3 billion in total economic activity. The Department Of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) oversees the management of Canada's aquatic resources and works with fishermen across the country to ensure the sustainability of Canada's oceans and in-land fisheries.
Norges Sildesalgslag is a national sales organization for the sale of pelagic fish. The pelagic sector forms an important part of the seafood industry, which is Norway's second largest export trade.

China, with one-fifth of the world's population, accounts for one-third of the world's reported fish production and two-thirds of the worlds reported aquaculture production.

Cod fisheries are fisheries for cod. Cod is the common name for fish of the genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae, and this article is confined to the three species that belong to this genus: the Atlantic cod, the Pacific cod and the Greenland cod.
Agriculture in Oman has been important for centuries. The government's economic development policy emphasizes the expansion of such non-oil sectors as agriculture, fishing, industry, and mining in its bid to diversify the economy and diminish its dependence on oil exports. The goal is to establish a sustainable economic base in preparation for the time when hydrocarbon reserves are depleted. The government launched several economic campaigns, naming 1988 and 1989 as Years of Agriculture and 1991 and 1992 as Years of Industry. Through these campaigns, the government has encouraged private-sector investment by allocating generous amounts of cash support for private industry to be disbursed mainly through official development banks. For example, the Oman Bank for Agriculture and Fisheries, created in 1981, extends loans at concessionary rates to individuals for whom farming or fishing is the principal activity. The bank acts as a distributive institution, receiving an interest subsidy from the government. In 1990 there were 1,308 loans, totaling RO4.7 million. Development programs also incorporate the government's policy of indigenization, with a large component of funds.
Despite the low rainfall and poor soil, agriculture in Bahrain historically was an important sector of the economy. Before the development of the oil industry, date palm cultivation dominated Bahrain's agriculture, producing sufficient dates for both domestic consumption and export. At least twenty-three varieties of dates are grown, and the leaves, branches, buds, and flowers of the date palm also are used extensively. From the 1950s through the 1970s, changing food consumption habits, as well as the increasing salinity of the aquifers that served as irrigation sources, led to a gradual decline in date cultivation. By the 1980s, a significant number of palm groves had been replaced by new kinds of agricultural activities, including vegetable gardens, nurseries for trees and flowers, poultry production, and dairy farms.

Fishing in Cornwall, England, UK, has traditionally been one of the main elements of the economy of the county. Pilchard fishing and processing was a thriving industry in Cornwall from around 1750 to around 1880, after which it went into an almost terminal decline. During the 20th century the varieties of fish taken became much more diverse and crustaceans such as crab and lobster are now significant. Much of the catch is exported to France due to the higher prices obtainable there. Though fishing has been significantly damaged by overfishing, . However, as of 2007, stocks are improving.
Ethnoichthyology is an area in anthropology that examines human knowledge of fish, the uses of fish, and importance of fish in different human societies. It draws on knowledge from many different areas including ichthyology, economics, oceanography, and marine botany.

















