Bandar Seri Begawan is the capital and largest city of Brunei. It is officially a municipal area with an area of 100.36 square kilometres (38.75 sq mi) and an estimated population of 100,700 as of 2007. It is part of Brunei-Muara District, the smallest yet most populous district which is home to over 70 per cent of the country's population. It is the country's largest urban centre and nominally the country's only city. The capital is home to Brunei's seat of government, as well as a commercial and cultural centre. It was formerly known as Brunei Town until it was renamed in 1970 in honour of Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III, the 28th Sultan of Brunei and the father of the current Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah.

Bycatch, in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juveniles of the target species. The term "bycatch" is also sometimes used for untargeted catch in other forms of animal harvesting or collecting. Non-marine species that are caught but regarded as generally "undesirable" are referred to as rough fish or coarse fish.

The northern red snapper is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico, where it inhabits environments associated with reefs. This species is commercially important and is also sought-after as a game fish.

Brunei-Muara District or simply Brunei-Muara is one of the four districts of Brunei. It has the smallest area among the four districts, with 571 square kilometres (220 sq mi), yet is the most populous, with 289,630 people as of 2016. Bandar Seri Begawan, the country's capital, is located in this district, which is also de facto the district's capital. It is also home to Brunei International Airport, the country's only international airport, as well as Muara Port, the main and only deep-water port in the country. The Brunei River flows within this district and is home to Kampong Ayer, the traditional historic settlement on stilts above the river.

Unsustainable fishing methods refers to the utilization of the various fishing methods in order to capture or harvest fish at a rate which sees the declining of fish populations over time. These methods are observed to facilitate the destructive fishing practices that destroy ecosystems within the ocean, and more readily results in overfishing, the depletion of fish populations at a rate that cannot be sustained.
A payaos is a type of fish aggregating device used in Southeast Asia, particularly in the Philippines. Payaos were traditionally bamboo rafts for handline fishing before World War II, but modern steel payaos use fish lights and fish location sonar to increase yields. While payaos fishing is sustainable on a small scale, the large scale, modern applications have been linked to adverse impacts on fish stocks.

Rasau is an area in Brunei. The area contains one of the two oil fields of Brunei, the Rasau Field, and a small village, Kampong Rasau, which has a population of 103.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.

The fishing industry in the Maldives is the island's second main industry. According to national tradition in the words of former President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, "Fishing is the lifeblood of our nation, it is inborn. From the soil on which we live, to the sea around us, it remains an integral part of our existence. Fishing, and our country and its people, [are] one and shall remain inseparable forever." The Maldives has an abundance of aquatic life and species of fish. Common are tuna, groupers, dolphin fish, barracuda, rainbow runner, trevally and squirrelfish and many more. Aside from being of essential importance to the economy, fishing is also a popular recreational activity in the Maldives, not only among locals but by tourists. The islands have numerous fishing resorts which cater for these activities.

Porgy is the common name in Australia for any fish which belongs to the family Sparidae. They are also called bream. Porgies live in shallow temperate marine waters and are bottom-dwelling carnivores. Most species possess grinding, molar-like teeth. They are often good eating fish, particularly the gilt-head bream and the dentex.
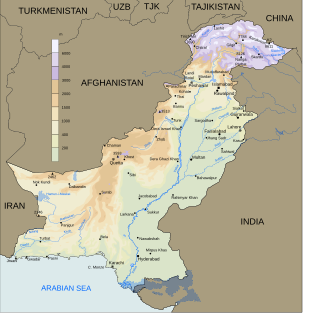
Fishery and fishing industry plays a significant part in the national economy of Pakistan. With a coastline of about 1,120 km, Pakistan has enough fishery resources that remain to be developed. Most of the population of the coastal areas of Sindh and Balochistan depends on fisheries for livelihood. It is also a major source of export earning.

Fish crackers are deep-fried crackers made from fish and spices, originating from Indonesia. The crackers are made mainly with tapioca flour and/or sago flour and then salt, sugar, and MSG as seasonings. Fish crackers can be found throughout Southeast Asia and East Asia. However, they are more commonly found and of greater variety in Indonesia and Malaysia.

The Treaty of Labuan was signed between Great Britain and the Brunei Sultanate on 18 December 1846. Under this treaty, the Sultan of Brunei ceded the island of Labuan to Great Britain.

Transport in Brunei consists of air, land, and sea transport. Previously there was some rail transport in Brunei, but eventually most of it was closed down. Several public and commercial sector organizations are in charge of creating and overseeing these networks and infrastructures. The Ministry of Transport and Infocommunications (MTIC) is in charge of overseeing the maritime and aviation industries, as well as planning and regulating all kinds of land transportation.

Kampong Beribi or commonly known as Beribi, is a village in Brunei-Muara District, Brunei, as well as a neighbourhood in the capital Bandar Seri Begawan. The population was 5,679 in 2016. It is one of the villages within Mukim Gadong 'B'. The postcode is BE1118.

Kampong Kiulap or commonly known as Kiulap, is a village in Brunei-Muara District, Brunei, as well as a neighbourhood and commercial area in the capital Bandar Seri Begawan. It has an area of 176.53 hectares ; the population was 3,400 in 2016. It is one of the villages within Mukim Gadong 'B'. The postcode is BE1518.

Selirong Island, also known as Mosquito Island, is an island located within the Brunei Bay and Mukim Labu, Temburong District, Brunei. The island also sits at the river delta of the Temburong River.
The Department of Fisheries, also referred to as the Fisheries Department, is a department overseen by the Ministry of Primary Resources and Tourism (MPRT). The country's fisheries authority is the Department of Fisheries under the MPRT.

The flora and fauna of Brunei Darussalam is one of its primary draws. Tropical evergreen rainforest makes up the majority of the country's natural vegetation. 81% of the land is covered by forests, with 59% being primary forests and 22% being secondary forests and plantations. With an estimated 2,000 species of trees, Brunei is home to an estimated 15,000 different species of Vascular plants. Brunei's mammal and bird populations are comparable to those of Sumatra, the Malaysian Peninsula, and Borneo as a whole.