
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, red currants, white currants and blackcurrants. In Britain, soft fruit is a horticultural term for such fruits.
Fragaria is a genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, commonly known as strawberries for their edible fruits. There are more than 20 described species and many hybrids and cultivars. The most common strawberries grown commercially are cultivars of the garden strawberry, a hybrid known as Fragaria × ananassa. Strawberries have a taste that varies by cultivar, and ranges from quite sweet to rather tart. Strawberries are an important commercial fruit crop, widely grown in all temperate regions of the world.

The garden strawberry is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus Fragaria, collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as jam, juice, pies, ice cream, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in products such as candy, soap, lip gloss, perfume, and many others.

Fragaria iturupensis, the Iturup strawberry, is a species of wild strawberry, endemic to Iturup in the Kuril Islands. It is noted to have relatively large berries for a wild species, similar in appearance to those of Fragaria virginiana.

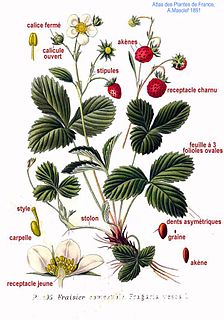
Fragaria vesca, commonly called wild strawberry, woodland strawberry, Alpine strawberry, Carpathian strawberry, European strawberry, or fraisier des bois, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the rose family that grows naturally throughout much of the Northern Hemisphere, and that produces edible fruits.

Fragaria × vescana is a hybrid strawberry cultivar that was created in an effort to combine the best traits of the garden strawberry, which has large berries and vigorous plants, with the woodland strawberry, which has an exquisite flavour, but small berries.

Fragaria chiloensis, the beach strawberry, Chilean strawberry, or coastal strawberry, is one of two species of wild strawberry that were hybridized to create the modern garden strawberry. It is noted for its large berries. Its natural range is the Pacific Ocean coasts of North and South America, and also Hawaii. Migratory birds are thought to have dispersed F. chiloensis from the Pacific coast of North America to the mountains of Hawaii, Chile, and Argentina.

Fragaria iinumae is a species of strawberry native to Japan and eastern Russia.

Fragaria nipponica is a species of wild strawberry native to the western side of the Japanese island of Honshū, with a variety Fragaria nipponica var. yakusimensis on Yakushima. Some botanists treat it as a synonym of Fragaria yezoensis.

Fragaria yezoensis is a species of wild strawberry native to the eastern side of the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, and the adjacent Kuril Islands and Sakhalin in Russia. It is of no economic value. Some botanists include the very similar Fragaria nipponica in F. yezoensis as a synonym.

Creamy strawberry is a species of strawberry native to Europe and central Asia. It has fruits with fine flavour. They have surprisingly little of the usual strawberry aroma, but a refreshing acidity, and sometimes ripen without becoming red. When they are plucked from the plant, the calyx will usually adhere and they will detach with a noticeable snapping sound.

Fragaria daltoniana is a species of strawberry native to the Himalayas. Its fruit has a poor flavor, and is of no commercial value.

Fragaria nilgerrensis is a species of wild strawberry native to southern and southeast Asia. Its fruit are white to light pink, with poor flavour, and the fruit is of no commercial value. It is similar in appearance to F. moupinensis.

Fragaria nubicola is a species of wild strawberry native to the Himalayas. It is of no commercial value.

There are several commercially important hybrids between Fragaria and Comarum species in existence. A name for Fragaria × Comarum is available as × Comagaria Büscher & G.H. Loos in Veroff. [Bohumer Bot. Ver. 2(1): 6. 2010], along with the combination × Comagaria rosea (Mabb.) Büscher & G.H. Loos.

George McMillan Darrow (1889–1983) was an American horticulturist and the foremost authority on strawberries. He worked for the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA-ARS) for forty-six years as the pomologist in charge of research on deciduous fruit production, and authored a multitude of papers on planting and cultivating small fruits.
The Marshall strawberry is a cultivated variety of Fragaria ananassa, that is known for an "exceptional" taste and had been described as "the finest eating strawberry" in America.
Arthur Bridgman Howard was an American horticulturalist.

The breeding of strawberries started with the selection and cultivation of European strawberry species in western Europe in the 15th century while a similar discovery and cultivation occurred in Chile. The most commonly consumed strawberry species in modern times is the garden strawberry, a species derived from hybridization of two other species, with the scientific name Fragaria × ananassa, but there are many species of strawberries, several others of which are cultivated to some extent. The strawberry species fall into several different genetic types, based on their number of chromosomes. Strawberry growers have employed many breeding techniques, starting with traditional plant breeding and then moving on to molecular breeding and genetic engineering in the 20th century.


















