Defunct political party in Denmark
 |
|---|
|
|
The Free Social Democrats (Danish : Frie Socialdemokrater) were a political party in Denmark.
 |
|---|
The Free Social Democrats (Danish : Frie Socialdemokrater) were a political party in Denmark.
The party was established in March 1920 by Emil Marott, [1] a Member of Parliament between 1903 and 1920 for the Social Democrats. In 1920 he was expelled from the party because of diverging opinions on the Schleswig issue.
The party ran on a platform of returning Flensburg to Danish rule following the Schleswig Plebiscites, and contested all three Folketing elections held in 1920, but failed to win a seat. [1]
| Date | Votes | Seats | Position | Size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | ± pp | No. | ± | |||
| April 1920 | 7,260 | 0.71 | New | 0 / 140 | New | Extra-parliamentary | 7th |
| July 1920 | Did not run. | ||||||
| September 1920 | 6,460 | 0.53 | 0 / 149 | Extra-parliamentary | |||

Southern Schleswig is the southern half of the former Duchy of Schleswig in Germany on the Jutland Peninsula. The geographical area today covers the large area between the Eider river in the south and the Flensburg Fjord in the north, where it borders Denmark. Northern Schleswig, congruent with the former South Jutland County, forms the southernmost part of Denmark. The area belonged to the Crown of Denmark until Prussia and Austria declared war on Denmark in 1864. Denmark wanted to give away the German-speaking Holsten and set the new border at the small river Ejderen. Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck concluded that this justified a war, and even proclaimed it a "holy war". He also turned to the Emperor of Austria, Franz Joseph I of Austria for help. A similar war in 1848 had gone poorly for the Prussians. With Prussia's modern weapons and the help from both the Austrians and General Moltke, the Danish army was destroyed or forced to make a disorderly retreat. The Prussian-Danish border was then moved from the Elbe up in Jutland to the Kongeåen creek.

The Duchy of Schleswig was a duchy in Southern Jutland covering the area between about 60 km north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English.
The history of Denmark as a unified kingdom began in the 8th century, but historic documents describe the geographic area and the people living there—the Danes—as early as 500 AD. These early documents include the writings of Jordanes and Procopius. With the Christianization of the Danes c. 960 AD, it is clear that there existed a kingship. King Frederik X can trace his lineage back to the Viking kings Gorm the Old and Harald Bluetooth from this time, thus making the Monarchy of Denmark the oldest in Europe. The area now known as Denmark has a rich prehistory, having been populated by several prehistoric cultures and people for about 12,000 years, since the end of the last ice age.

The Danish ethnic minority in Southern Schleswig, Germany, has existed by this name since 1920, when the Schleswig Plebiscite split German-ruled Schleswig into two parts: Northern Schleswig with a Danish majority and a German minority was united with Denmark, while Southern Schleswig remained a part of Germany and had a German majority and Danish and Frisian minority populations. Their historic roots go back to the beginning of Danish settlement after the emigration of the Angles. One of the most common names they use to describe themselves is danske sydslesvigere.
The Social Democrats is a social democratic political party in Denmark. A member of the Party of European Socialists, the Social Democrats have 50 out of 179 members of the Danish parliament, Folketing, and three out of fourteen MEPs elected from Denmark.

The South Schleswig Voters' Association is a regionalist political party in Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. The party represents the Danish and Frisian minorities of the state.

Carl Theodor Zahle, was a Danish lawyer and politician who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1909 to 1910 and again from 1913 to 1920. In 1895, he was elected as a member of the lower chamber of the Danish parliament, the Folketing, for the Liberal Party (Venstrereformpartiet). A campaigner for peace, in 1905 he co-founded the Social Liberal Party together with other disgruntled members of Venstrereformpartiet. He continued on as a member of the Folketinget for Det Radikale Venstre until 1928, when he became a member of the upper chamber of parliament (Landsting). In 1929 he became Justice Minister, a post which he held until 1935.

Poul Holmskov Schlüter was a Danish politician who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1982 to 1993. He was the first member of the Conservative People's Party to become Prime Minister, as well as the first conservative to hold the office since 1901. Schlüter was a member of the Folketing for the Conservative People's Party from 1964 to 1994. He was also Chairman of the Conservative People's Party from 1974 to 1977 and from 1981 to 1993.

Erik Julius Christian Scavenius was the Danish foreign minister from 1909 to 1910, 1913 to 1920 and 1940 to 1943, and prime minister from 1942 to 1943, during the occupation of Denmark until the Danish elected government ceased to function. He was the foreign minister during some of the most important periods of Denmark's modern history, including the First World War, the plebiscites over the return of northern Schleswig to Denmark, and the German occupation. Scavenius was a member of the Landsting from 1918 to 1920 and from 1925 to 1927 representing the Social Liberal Party. He was chairman of its party organization from 1922 to 1924.

The Danish Social Liberal Party is a social-liberal political party in Denmark. The party was founded as a split from the Venstre Reform Party in 1905.

Knud Kristensen was Prime Minister of Denmark from 7 November 1945 to 13 November 1947 in the first elected government after the German occupation of Denmark during World War II. After the October 1945 election, Knud Kristensen formed the Cabinet of Knud Kristensen, a minority government consisting only of his liberal party.

The Communist Party of Denmark is a communist party in Denmark. The DKP was founded on 9 November 1919 as the Left-Socialist Party of Denmark, through a merger of the Socialist Youth League and Socialist Labour Party of Denmark, both of which had broken away from the Social Democrats in March 1918. The party adopted its present name in November 1920, when it joined the Comintern.
The Easter Crisis was a constitutional crisis in Denmark around Easter in 1920. It was a significant event in the development of constitutional monarchy in Denmark. It began with the dismissal of the elected government by the reigning monarch, King Christian X, a reserve power which was granted to him by the Danish constitution, because he thought that the government did not try to reclaim enough land from Germany in Schleswig. After protests, the King agreed to install a caretaker government who could hold a general election, and no Danish monarch has since interfered in politics.

Peter Rochegune Munch was a prominent Danish historian and politician. He was a leading member of the Radikale Venstre, and represented Langeland in parliament.
The Schleswig plebiscites were two plebiscites, organized according to section XII, articles 109 to 114 of the Treaty of Versailles of 28 June 1919, in order to determine the future border between Denmark and Germany through the former Duchy of Schleswig. The process was monitored by a commission with representatives from France, the United Kingdom, Norway and Sweden.

The Province of Schleswig-Holstein was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia.
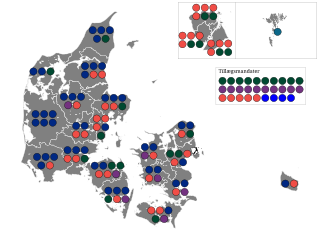
Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 26 April 1920, except in the Faroe Islands, where they were held on 20 May. The election campaign was the most aggressive and bitter in Denmark in the 20th century. Voter turnout was 80.6% in Denmark proper and 58.8% in the Faroe Islands.

The Schleswig Party is a regional political party in Denmark representing the North Schleswig Germans and the Danish minority of Southern Schleswig.

Stefan Seidler is a Danish-German politician of the South Schleswig Voters' Association (SSW), the party representing the interests of the Danish and Frisian minority populations in Germany. He was elected to the Bundestag from Schleswig-Holstein in the 2021 German federal election. His election represented the first time the SSW won a seat since 1949. The SSW last contested a federal election in the 1961 West German election.