Related Research Articles

Messier 18 or M18, also designated NGC 6613, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and included in his list of comet-like objects. From the perspective of Earth, M18 is situated between the Omega Nebula (M17) and the Small Sagittarius Star Cloud (M24).
Lambda1 Tucanae is the Bayer designation for one member of a pair of stars sharing a common proper motion through space, which lie within the southern constellation of Tucana. As of 2013, the pair had an angular separation of 20.0 arc seconds along a position angle of 82°. Together, they are barely visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 6.21. Based upon an annual parallax shift for both stars of approximately 16.5 mas as seen from Earth, this system is located roughly 198 light years from the Sun.
39 Boötis is a triple star system located around 224 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with a combined apparent magnitude of 5.68. The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −31 km/s.
12 Cancri is a star in the zodiac constellation Cancer. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.25, placing just below the normal limit for stars visible to the naked eye in good seeing conditions. The star displays an annual parallax shift of 12.7 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, which places it at a distance of about 257 light-years. It is moving toward the Sun with a radial velocity of around −10 km/s.

V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 8,900 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 685 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

Nu Phoenicis is a F-type main-sequence star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.95. This is a solar analogue, meaning its observed properties appear similar to the Sun, although it is somewhat more massive. At an estimated distance of around 49.5 light years, this star is located relatively near the Sun.
Eta Leporis, Latinised from η Leporis, is a single, yellow-white-hued star in the southern constellation of Lepus, the hare. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of approximately 3.72. The annual parallax shift of 67.21 mas yields a distance estimate of 49 light-years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −1.6 km/s.

HD 211575 is a star in the constellation Aquarius in between "Gamma Aquarii", "Pi Aquarii" and "Sadalmelik". It is a member of the corona of the Ursa Major moving group.
HD 114837 is a suspected binary star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus. The brighter star is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.90. It has a magnitude 10.2 candidate common proper motion companion at an angular separation of 4.2″, as of 2014. The distance to this system, based on an annual parallax shift of 55.0143″ as seen from Earth's orbit, is 59.3 light years. It is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −64 km/s, and will approach to within 21.8 ly in around 240,600 years.
Mu Persei, Latinised from μ Persei, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Perseus. It is visible to the naked eye as a point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.16. The distance to this system is approximately 900 light-years based on parallax measurements. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +26 km/s.

Theta Delphini, a name Latinized from θ Delphini, is a single star in the northern constellation of Delphinus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of about 5.7, meaning that it is just barely visible to the naked eye under excellent viewing conditions. The distance to this star is approximately 2,050 light years from the Sun based on parallax. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −15 km/s.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8
139 Tauri is a single, blue-white hued star in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.81. The distance to this star, as determined from an annual parallax shift of 2.10±0.19 mas, is roughly 1,600 light years. Because this star is located near the ecliptic, it is subject to occultations by the Moon. One such event was observed April 28, 1990.
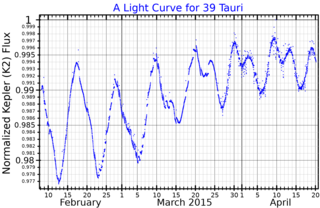
39 Tauri is a binary star in the northern constellation of Taurus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.90, so, according to the Bortle scale, it is faintly visible from suburban skies at night. Measurements made with the Hipparcos spacecraft show an annual parallax shift of 0.0594728″, which is equivalent to a distance of around 55 light years from the Sun.
HD 166066 is a solitary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.10, making it readily visible in binoculars, but not to the naked eye. The object is located 223 light years away from the Solar System, but is drifting away with a poorly constrained radial velocity of about 2.93 km/s.

BO Carinae, also known as HD 93420, is an irregular variable star in the constellation Carina.

Westerlund 1-20 (abbreviated to Wd 1-20 or just W20) is a red supergiant (RSG) located in the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. Its radius was calculated to be around 965 solar radii (6.72 × 108 km, 4.48 au), making it one of the largest stars discovered so far. This corresponds to a volume 899 million times bigger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the photosphere of Westerlund 1-20 would almost reach the orbit of Jupiter.

Westerlund 1-75 or Wd 1-75 is a red supergiant (RSG) located in the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. Its radius is calculated to be around 668 solar radii (4.65 × 108 km, 3.10 au). This corresponds to a volume 298 million times bigger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, Westerlund 1-75 would engulf the inner limits of the asteroid belt.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "SIMBAD query result: GCIRS 7 -- Star". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Paumard, T; Pfuhl, O; Martins, F; Kervella, P; Ott, T; Pott, J-U; Le Bouquin, JB; Breitfelder, J; Gillessen, S; Perrin, G; Burtscher, L; Haubois, X; Brandner, W (2014). "GCIRS 7, a pulsating M1 supergiant at the Galactic centre . Physical properties and age". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 568 (85): A85. arXiv: 1406.5320 . Bibcode:2014A&A...568A..85P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201423991. S2CID 119233940.
- 1 2 Tsuboi, Masato; Kitamura, Yoshimi; Tsutsumi, Takahiro; Miyawaki, Ryosuke; Miyoshi, Makoto; Miyazaki, Atsushi (2020-04-01). "Sub-millimeter detection of a Galactic center cool star IRS 7 by ALMA". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 72 (2): 36. arXiv: 2002.01620 . Bibcode:2020PASJ...72...36T. doi:10.1093/pasj/psaa013. ISSN 0004-6264. S2CID 211032112.
- 1 2 Carr, John S.; Sellgren, K.; Balachandran, Suchitra C. (2000). "The First Stellar Abundance Measurements in the Galactic Center: The M Supergiant IRS 7". The Astrophysical Journal. 530 (1): 307. arXiv: astro-ph/9909037 . Bibcode:2000ApJ...530..307C. doi:10.1086/308340. S2CID 12036617.
- ↑ Pott, J.-U.; Eckart, A.; Glindemann, A.; Kraus, S.; Schöde, R.; Ghez, A. M.; Woillez, J.; Weigelt, G. (2008). "First VLTI infrared spectro-interferometry on GCIRS 7". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 487: 413–418. arXiv: 0805.4408 . Bibcode:2008A&A...487..413P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200809829. S2CID 14697759.