
μ Sculptoris, Latinized as Mu Sculptoris, is a solitary, orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Sculptor. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.30. This star is located approximately 291 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +16 km/s.

1 Aurigae is the original name for a star now in the constellation Perseus. It was the first entry in John Flamsteed's catalogue of stars in Auriga. When Eugène Joseph Delporte drew up simplified boundaries for the constellations on behalf of the International Astronomical Union in 1930, 1 Aurigae ended up over the border in Perseus. To avoid confusion, the star may instead be referred to by its Harvard Revised catalogue number, HR 1533.

4 Sagittarii is a suspected astrometric binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Sagittarius, located approximately 390 light years away based on parallax. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74, The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −18 km/s.

HR 6801 is a single star in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. It was designated as 1 Sagittarii by Flamsteed, but is now often referred to as 11 Sagittarii. Flamsteed's 11 Sgr actually refers to a different, much fainter star. The object is orange in hue and is visible to the naked eye as a faint point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. The distance to this star is approximately 258 light years based on stellar parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +6 km/s.

ε Monocerotis, Latinised as Epsilon Monocerotis, is the Bayer designation of a binary star system in the equatorial constellation Monoceros. Its location is a guide for sky navigation toward the Rosette Nebula.

10 Leonis Minoris is a single variable star in the northern constellation Leo Minor, located approximately 191 light years away based on parallax. It has the variable star designation SU Leonis Minoris; 10 Leonis Minoris is the Flamsteed designation. This body is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.54. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −12 km/s.

28 Monocerotis is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Monoceros. It has an orange-hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.69. The distance to this star is approximately 450 light years based on parallax, and it has an absolute magnitude of −1.00. The star is drifting further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +26.7 km/s.

24 Scorpii is a star that was originally placed by John Flamsteed within the constellation of Scorpius but in now placed within the southeastern constellation of Ophiuchus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.91. Based on the trigonometric parallax published in Gaia Data Release 2, the star lies approximately 121 parsecs or 390 light years away. It is positioned near the ecliptic and thus is subject to lunar occultations.

31 Orionis is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Orion, located near the bright star Mintaka. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.71. The distance to this system is approximately 490 light years away based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a mean radial velocity of +6 km/s.

72 Pegasi is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.97. The system is located approximately 550 light years away from the Sun, based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −25 km/s.

HD 18970 is a class G9.5III star in the constellation Perseus. Its apparent magnitude is 4.77 and it is approximately 211 light years away based on parallax.

54 Persei is a single star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.93. The star is located approximately 220 light years away based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −27 km/s.

QZ Puppis is a class B2.5V star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.5 and it is approximately 650 light years away based on parallax.

OU Puppis is a chemically peculiar class A0 star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is about 4.9 and it is approximately 188 light-years away based on parallax.

HD 61772 is a bright giant star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.98 and it is approximately 660 light years away based on parallax.

HD 50235 is a class K5III star located approximately 811 light years away, in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.99. HD 50235 made its closest approach to the Sun 7.8 million years ago, at the distance of 137 light years, during which it had an apparent magnitude of 1.13.
HD 190056 is a class K1III star in the constellation Sagittarius. Its apparent magnitude is 4.99 and it is approximately 291 light years away based on parallax.
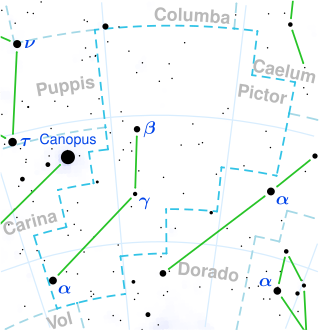
HD 42540, also known as HR 2196, is a giant star in the constellation Pictor. A class K2-3III orange giant, its apparent magnitude is 5.04 and it is approximately 389 light years away based on parallax.

41 Leonis Minoris is a single star in the northern constellation Leo Minor, located near the southern border with the neighboring constellation of Leo. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.08. This object is located approximately 229 light years away from the Sun, based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +18.5 km/s.

Epsilon Octantis, Latinized from ε Octantis, is a star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Octans. It is a faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 5. The annual parallax shift of 11.22 mas yields a distance estimate of around 291 light years. It is moving further from the Sun with a radial velocity of +11.7 km/s.












