Related Research Articles

W Sagittarii is a multiple star system star in the constellation Sagittarius, and a Cepheid variable star.

Beta Sculptoris, Latinized from β Sculptoris, is a single, blue-white hued star in the southern constellation of Sculptor. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.37, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 18.74 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 174 light years from the Sun.

Tau Canis Majoris is a multiple star system in the constellation Canis Major. It is approximately 5,000 light years distant from Earth and is the brightest member of the open cluster NGC 2362.

Mu Columbae is a star in the constellation of Columba. It is one of the few O-class stars that are visible to the unaided eye. The star is known to lie approximately 1,900 light years from the Solar System.

Kappa Cassiopeiae is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia.
Zeta Crucis, Latinized from ζ Crucis, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Crux. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 4.06m. ζ Crucis is located at about 360 light-years from the Sun. It is a member of the Lower Centaurus–Crux subgroup of the Scorpius–Centaurus association.

Kappa Crucis is a spectroscopic binary star in the open cluster NGC 4755, which is also known as the Kappa Crucis Cluster or Jewel Box Cluster.

6 Cassiopeiae is a white hypergiant in the constellation Cassiopeia, and a small-amplitude variable star.
63 Ophiuchi is an O-type giant star in the constellation Sagittarius, despite its name. During a 2009 survey for companions of massive stars, it was observed using speckle interferometry but no companion was found. The small parallax measurement of 0.91±0.09 mas suggest that this extremely luminous star may be located about 3,600 light-years away. An estimate of the distance based on the strength of the Ca II line yields a more modest value of 2,605 ly (799 pc). The star lies only 0.3° north of the galactic plane.
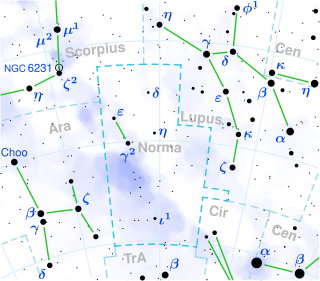
μ Normae, Latinised as Mu Normae, is a blue supergiant star of spectral type O9.7 Iab, located in the constellation of Norma.
16 Sagittarii is a multiple star system in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. It is near the lower limit of brightness for stars that can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.02. The estimated distance to this system is about 4,600 light years. It is a member of the Sgr OB7 cluster. Along with the O-type star 15 Sgr, it is ionizing an H II region along the western edge of the molecular cloud L291.
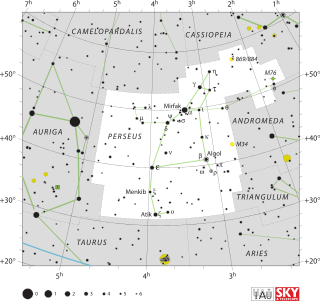
Mu Persei, Latinised from μ Persei, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Perseus. It is visible to the naked eye as a point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.16. The distance to this system is approximately 900 light-years based on parallax measurements. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +26 km/s.

Pi5 Orionis (π5 Ori, π5 Orionis) is a binary star system in the constellation Orion. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.69, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye on a clear night. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 2.43 mas, it is around 1,300 light-years distant from the Sun.
23 Orionis is a double star located around 1,200 light-years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Orion. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white-hued point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.99. The pair are moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +18 km/s, and they are members of the Orion OB1 association, subgroup 1a.

56 Pegasi is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.74. The system is approximately 590 light years away from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −28 km/s. It is listed as a member of the Wolf 630 moving group.

HD 64740 is a single star in the southern constellation Puppis, positioned near the line of sight to the Gum Nebula. It has a blue-white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.63. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of approximately 760 light-years from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +8 km/s.

20 Puppis is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Puppis. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.99. The star lies approximately 990 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. It is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +16.8 km/s.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8
HD 85622 is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Vela. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.58. The distance to HD 85622 can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of 4.3 mas, yielding a value of 750 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +8 km/s.

U Lacertae is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Lacerta.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv: 0708.1752 , Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- 1 2 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- 1 2 Sota, A.; Maíz Apellániz, J.; Morrell, N. I.; Barbá, R. H.; Walborn, N. R.; Gamen, R. C.; Arias, J. I.; Alfaro, E. J. (2014). "The Galactic O-Star Spectroscopic Survey (GOSSS). II. Bright Southern Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 211 (1): 10. arXiv: 1312.6222 . Bibcode:2014ApJS..211...10S. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/211/1/10. S2CID 118847528.
- 1 2 3 Fraser, M.; Dufton, P. L.; Hunter, I.; Ryans, R. S. I. (May 2010), "Atmospheric parameters and rotational velocities for a sample of Galactic B-type supergiants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 404 (3): 1306−1320, arXiv: 1001.3337 , Bibcode:2010MNRAS.404.1306F, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16392.x , S2CID 118674151
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971 , Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006), "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35,495 Hipparcos stars in a common system", Astronomy Letters, 32 (11): 759–771, arXiv: 1606.08053 , Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G, doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065, S2CID 119231169.
- 1 2 Kemp, S. N.; et al. (December 1996), "Further optical and UV spectroscopy of stars in the direction of the Riegel & Crutcher cold cloud", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 283 (3): 1089–1101, Bibcode:1996MNRAS.283.1089K, doi: 10.1093/mnras/283.3.1089 .
- ↑ Martins, F.; et al. (February 2015), "Radial dependence of line profile variability in seven O9-B0.5 stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 574: 38, arXiv: 1409.5057 , Bibcode:2015A&A...574A.142M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201423882, S2CID 118365203, A142.
- ↑ "15 Sgr". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- 1 2 Chini, R.; et al. (August 2012), "A spectroscopic survey on the multiplicity of high-mass stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 424 (3): 1925–1929, arXiv: 1205.5238 , Bibcode:2012MNRAS.424.1925C, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21317.x , S2CID 119120749
- ↑ Marti, J.; et al. (October 1993), "HH 80-81: A Highly Collimated Herbig-Haro Complex Powered by a Massive Young Star", Astrophysical Journal, 416: 208, Bibcode:1993ApJ...416..208M, doi: 10.1086/173227
- ↑ Sana, H.; et al. (November 2014), "Southern Massive Stars at High Angular Resolution: Observational Campaign and Companion Detection", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 215 (1): 35, arXiv: 1409.6304 , Bibcode:2014ApJS..215...15S, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/215/1/15, S2CID 53500788, 15.