
Gamma-glutamyltransferase is a transferase that catalyzes the transfer of gamma-glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathione to an acceptor that may be an amino acid, a peptide or water. GGT plays a key role in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a pathway for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione as well as drug and xenobiotic detoxification. Other lines of evidence indicate that GGT can also exert a pro-oxidant role, with regulatory effects at various levels in cellular signal transduction and cellular pathophysiology. This transferase is found in many tissues, the most notable one being the liver, and has significance in medicine as a diagnostic marker.

In enzymology, an aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that is very important in the biosynthesis of amino acids in prokaryotes, fungi, and some higher plants. It forms an early branch point in the metabolic pathway forming lysine, methionine, leucine and isoleucine from aspartate. This pathway also produces diaminopimelate which plays an essential role in bacterial cell wall formation. There is particular interest in ASADH as disabling this enzyme proves fatal to the organism giving rise to the possibility of a new class of antibiotics, fungicides, and herbicides aimed at inhibiting it.
In enzymology, a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.41) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase (EC 1.2.1.38) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathionylspermidine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a homoglutathione synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate—L-lysine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-tripeptide—D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.94) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-alanine gamma-glutamyltransferase (EC 2.3.2.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (EC 2.3.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylglutamate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:

In enzymology, a glutamate 5-kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
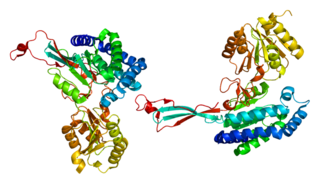
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH18A1 gene. This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, ALDH18A1 deficiency or dominant-negative mutations in P5CS in humans causes a progeroid disease known as De Barsy Syndrome.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 (GGT1), also known as CD224, is a human gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGT5 gene.
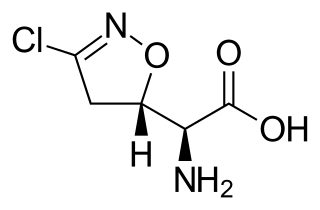
Acivicin is an analog of glutamine. It is an inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transferase.

Ghk.
Gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelate peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
γ-L-Glutamyl-butirosin B γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name γ-L-glutamyl-butirosin B γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







