
The Percidae are a family of ray-finned fish, part of the order Perciformes, which are found in fresh and brackish waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The majority are Nearctic, but there are also Palearctic species. The family contains more than 200 species in 11 genera. The perches and their relatives are in this family; well-known species include the walleye, sauger, ruffe, and three species of perch. However, small fish known as darters are also a part of this family.

The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families.

The Lamniformes are an order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks. It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the great white, as well as more unusual representatives, such as the goblin shark and megamouth shark.

Groupers are fish of any of a number of genera in the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae, in the order Perciformes.

Moray eels, or Muraenidae, are a family of eels whose members are found worldwide. There are approximately 200 species in 15 genera which are almost exclusively marine, but several species are regularly seen in brackish water, and a few are found in fresh water.

Parrotfishes are a group of fish species traditionally regarded as a family (Scaridae), but now often treated as a subfamily (Scarinae) or tribe (Scarini) of the wrasses (Labridae). With roughly 95 species, this group's largest species richness is in the Indo-Pacific. They are found in coral reefs, rocky coasts, and seagrass beds, and can play a significant role in bioerosion.

Carpet sharks are sharks classified in the order Orectolobiformes. Sometimes the common name "carpet shark" is used interchangeably with "wobbegong", which is the common name of sharks in the family Orectolobidae. Carpet sharks have five gill slits, two spineless dorsal fins, and a small mouth that does not extend past the eyes. Many species have barbels.

The Exocoetidae are a family of marine ray-finned fish in the order Beloniformes, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird does, flying fish can make powerful, self-propelled leaps out of the water where their long wing-like fins enable gliding for considerable distances above the water's surface. The main reason for this behavior is thought to be to escape from underwater predators, which include swordfish, mackerel, tuna, and marlin, among others, though their periods of flight expose them to attack by avian predators such as frigate birds.

The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.
Gyrosteus is an extinct genus of very large ray-finned fish belonging to the family Chondrosteidae. It comprises the type species, Gyrosteus mirabilis, which lived during the early Toarcian in what is now northern Europe. A possible second species, "Gyrosteus" subdeltoideus, is known from otoliths.

The Distichodontidae are a family of African freshwater fishes of the order Characiformes.

Sebastolobus, the thornyheads, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. These fishes are native to the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean. They are generally found in deep waters.

Strepsodus is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish that lived throughout the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in eastern Canada, Britain, and Queensland, Australia; indeterminate species of Strepsodus have also been found in the late Devonian deposits of Turkey, Iran and Colombia. A large individual is measured up to 3.5 metres (11.5 ft) long.
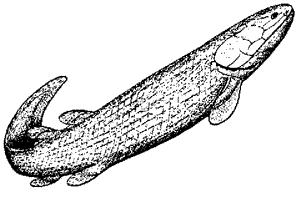
Ectosteorhachis is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish that lived during the Permian period. It belonged to the group of Tetrapodomorpha and to the family of Megalichthyidae. Ectosteorhachis was a fresh water fish.
Gigantopterus is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic epoch.
Rhinconichthys is an extinct genus of bony fish which existed during the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.

The Nemacheilidae, or stone loaches, are a family of cypriniform fishes that inhabit stream environments, mostly in Eurasia, with one genus, Afronemacheilus found in Africa. The family includes about 790 species.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
John Ernest "Jack" Randall was an American ichthyologist and a leading authority on coral reef fishes. Randall described over 800 species and authored 11 books and over 900 scientific papers and popular articles. He spent most of his career working in Hawaii. He died in April 2020 at the age of 95.















