
Pycnodus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish from the Eocene period. It is wastebasket taxon, although many fossils from Jurassic or Cretaceous are assigned to this genus, only Eocene species, P. apodus is valid. As its name suggests, it is the type genus of Pycnodontiformes.

Globidens is an extinct genus of mosasaurid oceanic lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily. Globidens belongs to the family Mosasauridae, which consists of several genera of predatory marine lizards of various sizes that were prevalent during the Late Cretaceous. Specimens of Globidens have been discovered in Angola, Brazil, Morocco, Syria and the United States. Among mosasaurs, Globidens is probably most well known for the highly rounded, globe-like teeth that give it its name.
Ocepesuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian, related to modern gharials. Ocepesuchus is the oldest known crocodilian of Africa, and is known only from a single species, O. eoafricanus. It lived in Morocco during the late Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous.

Pycnodontiformes is an extinct order of primarily marine bony fish. The group first appeared during the Late Triassic and disappeared during the Eocene. The group has been found in rock formations in Africa, Asia, Europe, North and South America.

Coccodus is an extinct genus of marine pycnodontid fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The various species had a pair of massive, curved spines emanating from the lower sides of the head, and one curved spine on the top of its head. Unlike most pycnodontids, Coccodus species had a comparatively long body, giving the living animals a superficial resemblance to a scaly chimaera.

Acrotemnus is an extinct genus of marine pycnodontid ray-finned fish from various areas of the Tethys Sea that lived during the Turonian stage of the Upper Cretaceous. The genus comprises three species A. faba, A. streckeri, and A. megafrendodon.

Anomoeodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Pycnodontidae. This genus primarily lived during the mid-to-late Cretaceous period, ranging from the Albian to the very end of the Maastrichtian age, and possibly into the Danian. The first fossils of Anomoeodus were described by Louis Agassiz in 1833, although they were described under Pycnodus. Some studies have recovered it as a wastebasket taxon.
Athrodon is an extinct genus of marine pycnodontid fish that lived in shallow seas in what is now England, Germany, Spain and France from the Late Jurassic until the genus' extinction during the start of the late Cretaceous. The various species are very similar in splenial bone and tooth morphology to Mesodon. Otherwise, no articulated or complete specimen is known: all fossil specimens are bone fragments and disarticulated teeth. This genus is thought to be diagnosed by the presence of four lateral tooth rows. The presence of this genusin the Cretaceous is disputed, as the remains of Cretaceous species could belong to other genera.

Brembodus is an extinct marine pycnodontid fish, the type genus of the family Brembodontidae. It contains a single species, B. ridens, known from the Late Triassic Calcare di Zorzino formation of Cene, Italy.

Coelodus is an extinct genus of marine and possibly freshwater pycnodont fish. It contains only one definitive species, C. saturnusHeckel, 1854, from the Late Cretaceous of Slovenia. Other species from the Late Jurassic to the Eocene have also been attributed to this genus based on isolated dental elements, but their assignment to Coelodus is uncertain, and this genus likely represents a non-monophyletic wastebasket taxon. A potential diagnostic trait is a prearticular tooth row with three regular highly elongated teeth.
Gyronchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish from the Jurassic. This genus is currently treated as a wastebasket taxon used for pycnodonts like Macromesodon and Turbomesodon.

Coccodontidae is a family of extinct pycnodontid fish that lived during the lower Cenomanian. The various genera had massive, curved spines.

Pannoniasaurus is an extinct genus of tethysaurine mosasauroid known from the Late Cretaceous Csehbánya Formation and Ajka Coal Formation of Hungary. It contains a single species, Pannoniasaurus inexpectatus, dubbed "unexpected" because it was discovered in freshwater sediments, unlike other mosasaurs, which were marine predators. It was a medium-sized mosasaur, reaching up to 6 metres (20 ft) in length.

The Sannine Formation, also called the Sannine Limestone, is a Cretaceous geologic formation in Lebanon. It is a Konservat-Lagerstätte that contains a high diversity of well-preserved fish, reptiles, and invertebrates from the Tethys Ocean within its three main localities: Haqel, Hjoula, and Nammoura.

Pycnodontidae is an extinct family of ray-finned fishes, ranging from the Jurassic period until the Eocene. It was the largest and most derived family of the successful Mesozoic fish order Pycnodontiformes, and one of only two families to survive into the Cenozoic.

Eichstaettisaurus is a genus of lizards from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Germany, Spain, and Italy. With a flattened head, forward-oriented and partially symmetrical feet, and tall claws, Eichstaettisaurus bore many adaptations to a climbing lifestyle approaching those of geckoes. The type species, E. schroederi, is among the oldest and most complete members of the Squamata, being known by one specimen originating from the Tithonian-aged Solnhofen Limestone of Germany. A second species, E. gouldi, was described from another skeleton found in the Matese Mountains of Italy. Despite being very similar to E. schroederi, it lived much later, during the Albian stage. Fossils of both species show exceptional preservation due to deposition in low-oxygen marine environments.
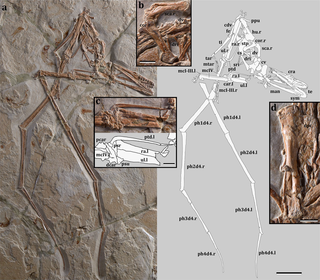
Mimodactylus is a genus of istiodactyliform pterosaur that lived in what is now Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous, 95 million years ago. The only known specimen was discovered in a limestone quarry near the town of Hjoula, belonging to the Sannine Formation. The owner of the quarry allowed the specimen to be prepared and scientifically described by an international team of researchers, and when it was eventually sold, the buyer donated it to the MIM Museum in Beirut. In 2019, the researchers named the new genus and species Mimodactylus libanensis; the generic name refers to the MIM Museum, combined with the Greek word daktylos for "digit", and the specific name refers to Lebanon. The well-preserved holotype specimen is the first complete pterosaur from the Afro-Arabian continent, and the third pterosaur fossil known from Lebanon.
Agassizilia is an extinct genus of both freshwater and marine pycnodont fishes from the mid-late Cretaceous. The genus is named after paleontologist Louis Agassiz.

Neoproscinetes is a genus of extinct pycnodontid fish from the Cretaceous Santana Formation of Brazil. Fossils of this species have also been discovered in the Riachuelo Formation.
Njoerdichthys is an extinct genus of pycnodontid fish from the Cretaceous Hesseltal Formation in Germany.













