
Pantodontidae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Osteoglossiformes. It contains the living freshwater butterflyfish of Africa, as well as several extinct marine species from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of the Sannine Formation in Lebanon.

Belonostomus is a genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that was described by Louis Agassiz in 1844. It is a member of the order Aspidorhynchiformes, a group of fish known for their distinctive elongated rostrums.

Bananogmius is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that was found in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Cretaceous, from the Cenomanian to the Santonian. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway, which split North America in two during the Late Cretaceous, as well as the proto-North Sea of Europe.
Libanopristis is an extinct genus of ganopristid sclerorhynchoid that lived in Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous. One female specimen with nine embryos preserved in situ represents one of the first fossil evidence of batoid ovoviviparity.

Pycnodontiformes is an extinct order of primarily marine bony fish. The group first appeared during the Late Triassic and disappeared during the Eocene. The group has been found in rock formations in Africa, Asia, Europe, North and South America.

Trewavasia carinata is an extinct pycnodontid fish in the family Coccodontidae that lived during the lower Cenomanian of what is now Lebanon. It had a large, forward-pointing horn-like spine between its eyes, and a massive stump-like spine emanating from the back of its head. T. carinata is closely related the genera Corusichthys and Hensodon, as well as Coccodus.

Coccodus is an extinct genus of marine pycnodontid fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The various species had a pair of massive, curved spines emanating from the lower sides of the head, and one curved spine on the top of its head. Unlike most pycnodontids, Coccodus species had a comparatively long body, giving the living animals a superficial resemblance to a scaly chimaera.

Aphanepygus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine holostean ray-finned fish that lived during the upper Cenomanian. It inhabited the former Tethys Ocean, with remains known from Lebanon and Croatia. Its exact affinities are uncertain, although it is usually recovered as a relative of the macrosemiids. However, other authorities recover it in the Ionoscopiformes.

Lissoberyx is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish belongon to the family Trachichthyidae. Lissoberyx is a trachichthyid, but it shows more resemblance to the holocentrids than any other trachichthyid.
Ligulella is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo during the Middle Jurassic epoch. It contains one species, Ligulella sluysi. Ligulella is the only member of the family Ligulellidae and the order Ligulelliformes.

Hulettia is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish known from United States. This fish genus contains two species, H. americana and H. hawesi.

Coccodontidae is a family of extinct pycnodontid fish that lived during the lower Cenomanian. The various genera had massive, curved spines.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.

Micropristis is an extinct genus of ganopristid sclerorhynchoid that lived in the Middle East and Europe during the Late Cretaceous. The type specimen is known from the Cenomanian of Lebanon, and other specimens referrable to this genus have been found in Santonian-Campanian age rocks of Europe.

Halecomorphi is a taxon of ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The only extant Halecomorph species are the bowfin and eyespot bowfin, but the group contains many extinct species in several families in the order Amiiformes, as well as the extinct orders Ionoscopiformes, Panxianichthyiformes, and Parasemionotiformes. The fossil record of halecomorphs goes back at least to the Early Triassic epoch.

The Sannine Formation, also called the Sannine Limestone, is a Cretaceous geologic formation in Lebanon. It is a Konservat-Lagerstätte that contains a high diversity of well-preserved fish, reptiles, and invertebrates from the Tethys Ocean within its three main localities: Haqel, Hjoula, and Nammoura.

Pycnodontidae is an extinct family of ray-finned fishes, ranging from the Jurassic period until the Eocene. It was the largest and most derived family of the successful Mesozoic fish order Pycnodontiformes, and one of only two families to survive into the Cenozoic.

Corusichthys megacephalus is an extinct pycnodontid that lived during the lower Cenomanian of what is now Lebanon. C. megacephalus is known from a 34 mm long fossil. It had plates arranged like a helmet around its head, and had a massive, triangular spine on its dorsal side. C. megacephalus is closely related the genera Trewavasia and Hensodon, as well as Coccodus.

Gebrayelichthyidae is a family of extinct pycnodontid fish, with a superficially shrimpfish-like appearance that lived during the lower Cenomanian.
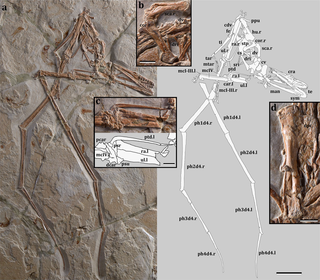
Mimodactylus is a genus of istiodactyliform pterosaur that lived in what is now Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous, 95 million years ago. The only known specimen was discovered in a limestone quarry near the town of Hjoula, belonging to the Sannine Formation. The owner of the quarry allowed the specimen to be prepared and scientifically described by an international team of researchers, and when it was eventually sold, the buyer donated it to the MIM Museum in Beirut. In 2019, the researchers named the new genus and species Mimodactylus libanensis; the generic name refers to the MIM Museum, combined with the Greek word daktylos for "digit", and the specific name refers to Lebanon. The well-preserved holotype specimen is the first complete pterosaur from the Afro-Arabian continent, and the third pterosaur fossil known from Lebanon.


















