Related Research Articles

Arlington National Cemetery is a United States military cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C., in whose 639 acres (259 ha) the dead of the nation's conflicts have been buried, beginning with the Civil War, as well as reinterred dead from earlier wars. The United States Department of the Army, a component of the United States Department of Defense (DoD), controls the cemetery.

The World War II Memorial is a memorial of national significance dedicated to Americans who served in the armed forces and as civilians during World War II.

Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial, formerly named the Custis-Lee Mansion, is a Greek revival style mansion located in Arlington, Virginia, United States that was once the home of Confederate Army General Robert E. Lee. It overlooks the Potomac River and the National Mall in Washington, D.C. During the American Civil War, the grounds of the mansion were selected as the site of Arlington National Cemetery, in part to ensure that Lee would never again be able to return to his home. The United States has since designated the mansion as a National Memorial. Although the United States Department of the Army controls Arlington National Cemetery, the National Park Service, a component of the United States Department of the Interior, administers Arlington House.

The Women In Military Service For America Memorial, also known as Military Women's Memorial, is a memorial established by the U.S. federal government which honors women who have served in the United States Armed Forces. The memorial is located at the western end of Memorial Avenue at the entrance to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, in the United States. The structure in which the memorial is housed was originally known as the Hemicycle, and built in 1932 to be a ceremonial entrance to the cemetery. It never served this purpose, and was in disrepair by 1986. Congress approved the memorial in 1985, and the Hemicycle approved as the site for the memorial in 1988. An open design competition was won by New York City architects Marion Weiss and Michael Manfredi. Their original design was leaked to the public, and caused significant controversy. Two years of fund-raising and design revision followed. A revised preliminary design was approved in July 1992, and the final design in March 1995. Ground was broken for the memorial in June 1995, and the structure was dedicated on October 18, 1997.
The National Capital Parks was a unit of the National Park System of the United States, now divided into multiple administrative units. It encompasses a variety of federally owned properties in and around the District of Columbia including memorials, monuments, parks, interiors of traffic circles and squares, triangles formed by irregular intersections, and other open spaces.

The United States Air Force Memorial honors the service of the personnel of the United States Air Force and its heritage organizations. The Memorial is located in Arlington County, Virginia, on the former grounds of the Navy Annex near The Pentagon and Arlington National Cemetery. The Memorial is southwest of the intersection of Columbia Pike and South Joyce Street and is accessible from the north side of Columbia Pike. It was the last project of American architect James Ingo Freed with the firm Pei Cobb Freed & Partners.
The Adams Memorial is a proposed United States presidential memorial to honor the second President John Adams; his wife and prolific writer Abigail Adams; their son, the sixth President John Quincy Adams; John Quincy Adams' wife Louisa Catherine Adams; and other members of the Adams family including John Quincy Adams' son Charles Francis Adams, Sr., a Civil War diplomat, politician, and editor; and Charles' two sons, Henry Adams, a noted historian and autobiographer, and academician Brooks Adams. As of March 2022, ten of the twelve members of the Adams Memorial Commission had yet to be appointed, with two vacancies to be filled by the U.S. president and eight by Congress.

The National World War I Memorial is a national memorial commemorating the service rendered by members of the United States Armed Forces in World War I. The 2015 National Defense Authorization Act authorized the World War I Centennial Commission to build the memorial in Pershing Park, located at 14th Street and Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C. The park, which has existed since 1981, also contains the John J. Pershing General of the Armies commemorative work. In January 2016, the design commission selected the submission "The Weight of Sacrifice", by a team consisting of Joseph Weishaar, Sabin Howard, Phoebe Lickwar, and GWWO Architects, as the winning design, which is expected to be completed by 2024.
The National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission is an independent agency of the United States government responsible for approving and siting memorials within Washington, D.C., and the D.C. metropolitan area. Previously known as the National Capital Memorial Advisory Committee, the agency was established by the Commemorative Works Act of 1986 and its name was changed to the National Capital Memorial Commission. The agency's name was changed again in 2003 to the National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission.
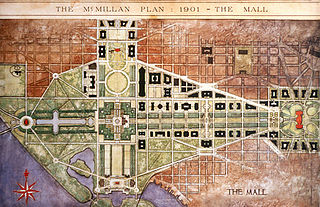
The McMillan Plan is a comprehensive planning document for the development of the monumental core and the park system of Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States. It was written in 1902 by the Senate Park Commission. The commission is popularly known as the McMillan Commission after its chairman, Senator James McMillan of Michigan.

The National Capital Planning Commission (NCPC) is a U.S. government executive branch agency that provides planning guidance for Washington, D.C., and the surrounding National Capital Region. Through its planning policies and review of development proposals, the Commission seeks to protect and enhance the extraordinary resources of the national capital.

The American Veterans Disabled for Life Memorial is a memorial in Washington, D.C., which honors veterans of the armed forces of the United States who were permanently disabled during the course of their national service. Congress adopted legislation establishing the memorial on October 23, 2000, authorizing the Disabled Veterans for Life Memorial Foundation to design, raise funds for, and construct the memorial. The fundraising goal was reached in mid-2010, and ground for the memorial broken on November 10, 2010. The memorial was dedicated by President Barack Obama on October 5, 2014.
The National Liberty Monument was a proposed national memorial to honor the more than 5,000 enslaved and free persons of African descent who served as soldiers or sailors or provided civilian assistance during the American Revolutionary War. The memorial is an outgrowth of a failed effort to erect a Black Revolutionary War Patriots Memorial, which was authorized in 1986 but whose memorial foundation dissolved in 2005. Congress authorized the National Liberty Monument in January 2013, but authorization expired in 2021.

The Commemorative Works Act of 1986 (CWA) is a United States federal law which bars the construction of commemorative works near the National Mall and on federal land in the National Capital Area unless they are approved by the National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission (NCMAC). The law also establishes criteria a memorial must meet in order to be approved the NCMAC, and establishes a seven-year deadline by which construction must begin or the memorial loses its congressional authorization. As of April 2014, the law has been amended five times, most notably by the Commemorative Works Clarification and Revision Act of 2003.

The National Desert Storm and Desert Shield Memorial is under planning to be constructed in Washington, D.C. near the Lincoln Memorial. It will honor members of the armed forces who participated in Operation Desert Storm or Operation Desert Shield.
The Peace Corps Commemorative is a proposed national commemorative work in Washington, D.C. honoring the historic founding of the Peace Corps and the enduring American ideals that motivated its founding and are expressed in Peace Corps service. The Peace Corps is a volunteer-sending program run by the United States government. Congress authorized the Peace Corps Commemorative in January 2014.
References
- 1 2 "Memorial Legislation." National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission. June 22, 2013. Archived April 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine Accessed 2014-04-04.
- ↑ "Authorized Memorials - Status of Authorities." National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission. April 15, 2013. Archived April 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine Accessed 2014-04-04.
- 1 2 A Commemorative Work for Gold Star Mothers: Site Selection Analysis (PDF). National Capital Memorial Advisory Commission. December 12, 2013. pp. 4–5. Retrieved April 5, 2014.