
Pennsylvania Avenue is a primarily diagonal street in Washington, D.C. that connects the United States Capitol with the White House and then crosses northwest Washington, D.C. to Georgetown. Traveling through southeast Washington from the Capitol, it enters Prince George's County, Maryland, and becomes MD Route 4 and then MD Route 717 in Upper Marlboro, and finally Stephanie Roper Highway.

The National Mall is a landscaped park near the downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums of the Smithsonian Institution, art galleries, cultural institutions, and various memorials, sculptures, and statues. It is administered by the National Park Service (NPS) of the United States Department of the Interior as part of the National Mall and Memorial Parks unit of the National Park System. The park receives approximately 24 million visitors each year.

The Lincoln Memorial Reflecting Pool is the largest of the many reflecting pools in Washington, D.C.. It is a 2,030-by-167-foot rectangular pool located on the National Mall, directly east of the Lincoln Memorial, with the World War II Memorial and Washington Monument to the east of the reflecting pool.

Swampoodle was a neighborhood in Washington, D.C. on the border of Northwest and Northeast in the second half of 19th and early 20th century. This neighborhood is no longer known as Swampoodle and has been replaced in large part by NoMa.
The Washington meridians are four meridians that were used as prime meridians in the United States which pass through Washington, D.C. The four that have been specified are:
- through the Capitol
- through the White House
- through the old Naval Observatory
- through the new Naval Observatory.

Constitution Avenue is a major east–west street in the northwest and northeast quadrants of the city of Washington, D.C., in the United States. It was originally known as B Street, and its western section was greatly lengthened and widened between 1925 and 1933. It received its current name on February 26, 1931, though it was almost named Jefferson Avenue in honor of Thomas Jefferson.

There are many outdoor sculptures in Washington, D.C. In addition to the capital's most famous monuments and memorials, many figures recognized as national heroes have been posthumously awarded with his or her own statue in a park or public square. Some figures appear on several statues: Abraham Lincoln, for example, has at least three likenesses, including those at the Lincoln Memorial, in Lincoln Park, and the old Superior Court of the District of Columbia. A number of international figures, such as Mohandas Gandhi, have also been immortalized with statues. The Statue of Freedom is a 19½-foot tall allegorical statue that rests atop the United States Capitol dome.

The Ulysses S. Grant Memorial is a presidential memorial in Washington, D.C., honoring American Civil War general and 18th president of the United States, Ulysses S. Grant. It sits at the base of Capitol Hill, below the west front of the United States Capitol. Its central sculpture of Grant on horseback faces west, overlooking the Capitol Reflecting Pool and facing toward the Lincoln Memorial, which honors Grant's wartime president, Abraham Lincoln. Grant's statue is raised on a pedestal decorated with bronze reliefs of the infantry; flanking pedestals hold statues of protective lions and bronze representations of the Union cavalry and artillery. The whole is connected with marble covered platforms, balustrades, and stairs. The Grant and Lincoln memorials define the eastern and western ends, respectively, of the National Mall.
The Inner Loop was two planned freeways around downtown Washington, D.C. The innermost loop would have formed an oval centered on the White House, with a central freeway connecting the southern segment to the northern segment and then continuing on to Interstate 95. Interstate 95 would have met Interstate 66, Interstate 295, Interstate 695, and US 50 while traversing the Inner Loop. A second loop was an arc across the northern section of the city, beginning at East Capitol Street at the Anacostia River and using the Missouri Avenue NW and Nebraska Avenue NW commercial corridors to terminate in Georgetown.

The Peace Monument, also known as the Naval Monument, stands on the western edge of the United States Capitol Complex in Washington, D.C. It is in the middle of Peace Circle, where First Street and Pennsylvania Avenue NW intersect. The surrounding area is Union Square, which the monument shares with the Ulysses S. Grant Memorial, James A. Garfield Monument, and the Capitol Reflecting Pool. The front of the monument faces west towards the National Mall while the east side faces the United States Capitol.
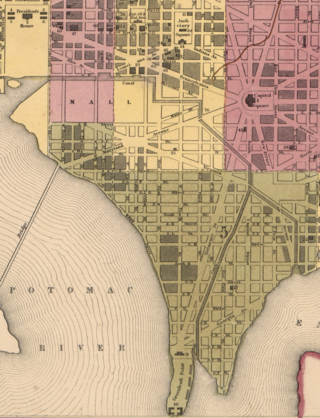
The Washington City Canal was a canal in Washington, D.C., that operated from 1815 until the mid-1850s. The canal connected the Anacostia River, termed the "Eastern Branch" at that time, to Tiber Creek, the Potomac River, and later the Chesapeake and Ohio (C&O) Canal. The canal fell into disuse during the late 19th century and the city government covered over or filled in various sections in 1871.

Grant Circle is a traffic circle in the Petworth neighborhood of Northwest Washington, D.C. New Hampshire and Illinois Avenues NW, Varnum Street NW, and 5th Street NW all intersect at this circle. The park within the circle and the adjoining triangles is owned and administered by the National Park Service through its Rock Creek Park unit. The circle and the buildings flanking it were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2015.
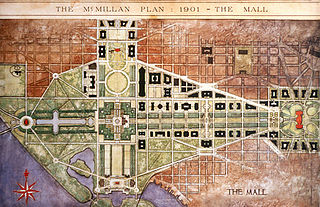
The McMillan Plan is a comprehensive planning document for the development of the monumental core and the park system of Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States. It was written in 1902 by the Senate Park Commission. The commission is popularly known as the McMillan Commission after its chairman, Senator James McMillan of Michigan.

Downtown is the central business district of Washington, D.C., located in Northwest D.C. It is the third largest central business district in the United States. The "Traditional Downtown" has been defined as an area roughly between Union Station in the east and 16th Street NW in the west, and between the National Mall on the south and Massachusetts Avenue on the north, including Penn Quarter. However, nowadays, Downtown D.C. usually refers to a larger area, as the DC Office of Planning states:
…most residents, workers, and visitors think of Downtown in a broader sense — including areas as far north as Dupont Circle, as far west as Foggy Bottom, and as far east as Capitol Hill. Only about half of the central city workforce is located within the city’s traditional Downtown.

Washington, D.C., is administratively divided into four geographical quadrants of unequal size, each delineated by their ordinal directions from the medallion located in the Crypt under the Rotunda of the Capitol. Street and number addressing, centered on the Capitol, radiates out into each of the quadrants, producing a number of intersections of identically named cross-streets in each quadrant. Originally, the District of Columbia was a near-perfect square but contained more than one settlement; the Capitol was to be the center of the City of Washington. Thus, the Capitol was never located at the geographic center of the whole territory, which was eventually north of the Potomac River, consolidated into one city. As a result, the quadrants are of greatly varying size. Northwest is quite large, encompassing over a third of the city's geographical area, while Southwest is little more than a few neighborhoods, large parks, and a military base.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to District of Columbia:

The Rainbow Pool was a reflecting pool located on the National Mall in Washington D.C., USA. It was designed by landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted Jr., and was situated between the Lincoln Memorial Reflecting Pool, and 17th Street NW. The pool was renamed the Rainbow Pool on October 15, 1924, after it was noticed that its 124 nozzles created a "perfect rainbow" when turned on.

The George Gordon Meade Memorial, also known as the Meade Memorial or Major General George Gordon Meade, is a public artwork in Washington, D.C. honoring George Meade, a career military officer from Pennsylvania who is best known for defeating General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg. The monument is sited on the 300 block of Pennsylvania Avenue NW in front of the E. Barrett Prettyman United States Courthouse. It was originally located at Union Square, but was removed and placed in storage for fourteen years before being installed at its current location. The statue was sculpted by Charles Grafly, an educator and founder of the National Sculpture Society, and was a gift from the state of Pennsylvania. Prominent attendees at the dedication ceremony in 1927 included President Calvin Coolidge, Governor John Stuchell Fisher, Secretary of the Treasury Andrew W. Mellon, and Senator Simeon D. Fess.

The statue of John Aaron Rawlins, a United States Army general who served during the Civil War and later as Secretary of War, is a focal point of Rawlins Park, a small public park in Washington, D.C.'s Foggy Bottom neighborhood. It was installed in 1874, but relocated several times between 1880 and 1931. The statue was sculpted by French-American artist Joseph A. Bailly, whose best known work is the statue of George Washington in front of Independence Hall in Philadelphia.

Union Square is an 11-acre public plaza at the foot of Capitol Hill in Washington, D.C., United States. It encompasses the Ulysses S. Grant Memorial (1924) and the 6-acre Capitol Reflecting Pool (1971) and is just west of the United States Capitol building. Views differ as to whether the Square is just east of the National Mall or is itself the eastern end.




















