| Golden-bellied treeshrew | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Scandentia |
| Family: | Tupaiidae |
| Genus: | Tupaia |
| Species: | T. chrysogaster [2] |
| Binomial name | |
| Tupaia chrysogaster [2] Miller, 1903 | |
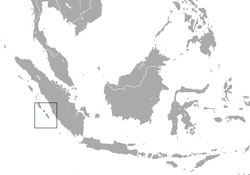 | |
| Golden-bellied treeshrew range | |
The golden-bellied treeshrew (Tupaia chrysogaster) is a treeshrew species within the Tupaiidae. [2] It is also called Mentawai treeshrew as it is endemic to the Indonesian Mentawai islands of Sipora, North and South Pagai. It lives in forests, and is considered endangered due to habitat loss since the islands' forests are continuously logged. [1]
The American zoologist Gerrit Smith Miller Jr. first described a golden-bellied treeshrew from North Pagai Island that was part of a zoological collection obtained by the United States National Museum. He considered it a distinct species as this type specimen differed from the common treeshrew by larger teeth and skull, darker coloured fur on the back and a more coarsely grizzled tail. [3]
