Design and description
The Carlisle sub-class was identical with the preceding Ceres sub-class except that their bows were raised for better seakeeping. The ships were 451 feet 6 inches (137.6 m) long overall, with a beam of 43 feet 6 inches (13.3 m) and a mean draught of 15 feet 6 inches (4.7 m). Displacement was 4,290 long tons (4,360 t ) at normal and 5,250 long tons (5,330 t) at deep load. Columbo was powered by two Brown-Curtis steam turbines, each driving one propeller shaft, which produced a total of 40,000 indicated horsepower (30,000 kW). The turbines used steam generated by six Yarrow boilers which gave her a speed of about 29 knots (54 km/h; 33 mph). She carried 935 long tons (950 t) tons of fuel oil. The ship had a crew of about 432 officers and ratings. [3]
The armament of the Carlisle sub-class consisted of five BL 6-inch (152 mm) Mk XII guns that were mounted on the centreline. One superfiring pair of guns was forward of the bridge, one was aft of the two funnels and the last two were in the stern, with one gun superfiring over the rearmost gun. The two QF 3-inch (76 mm) 20-cwt anti-aircraft guns were positioned abreast of the fore funnel. The ships were equipped with eight 21 in (533 mm) torpedo tubes in four twin mounts, two on each broadside. [3]
Construction and war service
Colombo, named after the former capital city of Ceylon, now Sri Lanka, was laid down by Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company on 8 December 1917, and launched on 18 December 1918. She was commissioned too late to see action in the First World War, but went on to serve in the Second World War. In the interwar period she served in the Far East with the Eastern Fleet between June 1919 to 1926, before being reassigned to the North American and West Indies Station. The ship returned to the Eastern Fleet from July 1932 to 1935, before returning to the UK to be put into reserve. [4]
Colombo spent the early part of the war in service with the Home Fleet, during which time she captured the German merchant ship Henning Oldendorff south-east of Iceland. She then returned to the Eastern Fleet between August 1940 and June 1942 before again returning to the UK to undergo a refit and conversion into an anti-aircraft cruiser between June 1942 and March 1943. Colombo survived the war and was sold on 22 January 1948, arriving at the yards of Cashmore, Newport on 13 May 1948 to be broken up. [5]

HMS Cardiff was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was one of the five ships of the Ceres sub-class and spent most of her career as a flagship. Assigned to the Grand Fleet during the war, the ship participated in the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight in late 1917. Cardiff was briefly deployed to the Baltic in late 1918 supporting anti-Bolshevik forces during the British campaign in the Baltic during the Russian Civil War.

HMS Kandahar (F28) was a K-class destroyer built for the Royal Navy during the 1930s, named after the Afghan city of Kandahar.

HMS Cornwall, pennant number 56, was a County-class heavy cruiser of the Kent sub-class built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1920s. The ship spent most of her pre-World War II career assigned to the China Station. Shortly after the war began in August 1939, she was assigned to search for German commerce raiders in the Indian Ocean. Cornwall was transferred to the South Atlantic in late 1939 where she escorted convoys before returning to the Indian Ocean in 1941. She then sank the German auxiliary cruiser Pinguin in May. After the start of the Pacific War in December 1941, she began escorting convoys until she was transferred to the Eastern Fleet in March 1942. The ship was sunk on 5 April by dive bombers from three Japanese aircraft carriers during the Indian Ocean Raid.

HMS Penn was a P-class destroyer built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War.

HMS Bedouin was a Tribal-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War II.

HMS Curlew was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was part of the Ceres sub-class of the C class. The ship survived World War I to be sunk by German aircraft during the Norwegian Campaign in 1940.

HMS Caledon was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was the name ship of the Caledon sub-class of the C class. She survived both world wars to be scrapped in 1948.
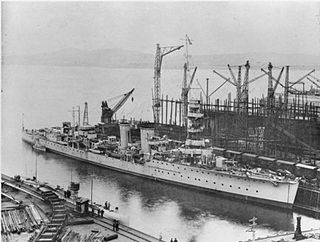
HMS Caradoc was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was one of the four ships of the Caledon sub-class. Assigned to the Grand Fleet during the war, the ship participated in the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight in late 1917. Caradoc was briefly deployed to the Baltic in late 1918 supporting anti-Bolshevik forces during the British campaign in the Baltic and then was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet in early 1919 and spent the next year and a half doing the same thing in the Black Sea during the Russian Civil War. The ship was withdrawn from the Black Sea in mid-1920 to observe the Greco-Turkish War of 1919–22 and the Chanak Crisis of late 1922. Caradoc spent most of the rest of her time between the World Wars overseas or in reserve with deployments to the Far East and the North America and West Indies Station.

HMS Cambrian was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was the name ship of her sub-class of four ships. Assigned to the Grand Fleet upon completion in 1916, the ship played only a small role during the war. Cambrian was assigned to the Atlantic and Mediterranean Fleets during the 1920s and was sent to support British interests in Turkey during the Chanak Crisis of 1922–1923. The ship was placed in reserve in late 1929. She was sold for scrap in 1934.

HMS Conquest was a C-class light cruiser of the Royal Navy that saw service during World War I. She was part of the Caroline group of the C class.

HMS Cordelia was a C-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was one of six ships of the Caroline sub-class and was completed at the beginning of 1915. The ship was assigned to the 1st and 4th Light Cruiser Squadrons (LCS) of the Grand Fleet for the entire war and played a minor role in the Battle of Jutland in mid-1916. Cordelia spent most of her time on uneventful patrols of the North Sea. She served as a training ship for most of 1919 before she was recommissioned for service with the Atlantic Fleet in 1920. The ship was placed in reserve at the end of 1922 and was sold for scrap in mid-1923.

HMS Despatch was a Danae-class light cruiser built for the Royal Navy during World War I. She was part of the Delhi sub-class of the Danae class.

HMS Hawkins was the lead ship of her class of five heavy cruisers built for the Royal Navy during the First World War, although the ship was not completed until 1919. She was assigned to the China Station until 1928 and was briefly assigned to the Atlantic Fleet in 1929–1930, always serving as a flagship, before being placed in reserve. Hawkins was recommissioned in 1932 for service on the East Indies Station, but returned to reserve three years later. The ship was disarmed in 1937–1938 and converted into a cadet training ship in 1938.

HMS Frobisher was one of five Hawkins-class heavy cruisers built for the Royal Navy during the First World War. She was not finished during the war and construction proceeded very slowly after the end of the war in 1918. Completed in 1924, the ship was initially assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet and was transferred to the Atlantic Fleet in 1929, sometimes serving as a flagship. Placed in reserve in 1930, Frobisher was converted into a cadet training ship in 1932 before being returned to reserve in 1937. Two years later she was reactivated to again serve as a training ship.

HMS Pathfinder was a P-class destroyer built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War. She was damaged while serving in the Far East, and was scrapped after the end of the war.

HMS Wolfhound was one of 21 W-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the First World War. Completed in 1918 the ship only played a minor role in the war before its end. The ship was converted into an anti-aircraft escort destroyer during the Second World War and was badly damaged during the Dunkirk evacuation. Wolfhound survived the war and was sold for scrap in 1948.

HMS Carron was one of thirty-two C-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, a member of the eight-ship Ca sub-class. Commissioned in late 1944, she was assigned to the Home Fleet and escorted the fleet's larger ships during operations off German-occupied Norway. Carron was sold for scrap in 1967.

HMS Cavendish was one of eight C-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War. Commissioned in late 1944, she was built as a flotilla leader with additional accommodation for staff officers. The ship was assigned to the Home Fleet in 1945 after working up where she escorted capital ships of the fleet. Cavendish was sold for scrap in 1967.

HMS Caesar was one of thirty-two C-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, a member of the eight-ship Ca sub-class. Commissioned in 1944, she was built as a flotilla leader with additional accommodation for staff officers. The ship was assigned to Home Fleet during 1944–1945 and escorted one Arctic convoy as well as the capital ships of the fleet.

HMS Childers was one of thirty-two C-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, a member of the eight-ship Ch sub-class. Commissioned in 1945, she was built as a flotilla leader with additional accommodation for staff officers.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




















