
Gamma Doradus variables are variable stars which display variations in luminosity due to non-radial pulsations of their surface. The stars are typically young, early F or late A type main sequence stars, and typical brightness fluctuations are 0.1 magnitudes with periods on the order of one day. This class of variable stars is relatively new, having been first characterized in the second half of the 1990s, and details on the underlying physical cause of the variations remains under investigation.

28 Andromedae is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation Andromeda. 28 Andromedae is the Flamsteed designation. It also bears the variable star name GN Andromedae. Its apparent magnitude is 5.214, varying by less than 0.1 magnitudes.

26 Arietis is a variable star in the northern constellation of Aries. 26 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the variable star designation UU Arietis. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 6.14, which, according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, is within the naked eye visibility limit in dark rural skies. The annual parallax shift of 13.78 mas is equivalent to a distance of approximately 215 light-years from Earth. The star is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +15 km/s.

28 Aquilae, abbreviated 28 Aql, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. 28 Aquilae is its Flamsteed designation though it also bears the Bayer designation A Aquilae, and the variable star designation V1208 Aquilae. It has an apparent visual magnitude is 5.5, making this a faint star that requires dark suburban skies to view. The annual parallax shift of 9.6 mas means this star is located at a distance of approximately 340 light-years from Earth.

38 Cancri is a variable star in the zodiac constellation Cancer, located around 607 light years from the Sun. This object has the variable star designation BT Cancri; 38 Cancri is the Flamsteed designation. It is a member of the Praesepe cluster but is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.65. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +32 km/s.

4 Canum Venaticorum is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici, located around 425 light years away. It has the variable star designation AI Canum Venaticorum; 4 Canum Venaticorum is its Flamsteed designation. Its brightness varies from magnitude +5.89 to +6.15 with a period of 2.8 hours, which places it around the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye. This was found to be a binary by Schmid et al. in 2014, based on periodic, non-sinusoidal changes in its radial velocity. It is a single-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 124.4 days and an eccentricity of 0.31.

HD 15082 is a star located roughly 397 light years away in the northern constellation of Andromeda. The star is a Delta Scuti variable and a planetary transit variable. A hot Jupiter type extrasolar planet, named WASP-33b or HD 15082b, orbits this star with an orbital period of 1.22 days. It is the first Delta Scuti variable known to host a planet.

SX Phoenicis is a variable star in the southern constellation Phoenix. With an apparent visual magnitude ranging around 7.33, it is too faint to be readily seen with the naked eye and requires binoculars. It is located 272 light years from the Sun, as determined from an annual parallax shift of 12 mas.

UY Scuti (BD-12°5055) is a red supergiant star, located 5,900 light-years away in the constellation Scutum. It is also a pulsating variable star, with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.29 and a minimum of magnitude 10.56, which is too dim for naked-eye visibility. It is considered to be one of the largest known stars, with a radius estimated at 909 solar radii, thus a volume of 750 million times that of the Sun. This estimate implies if it were placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would extend past the orbit of Mars or even the asteroid belt.

CC Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation Andromeda. It is a pulsating star of the Delta Scuti type, with an apparent visual magnitude that varies between 9.19 and 9.46 with a periodicity of 3 hours.
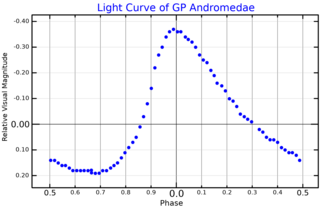
GP Andromedae is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation Andromeda. It is a pulsating star, with its brightness varying with an amplitude of 0.55 magnitudes around a mean magnitude of 10.7.

AZ Phoenicis is a variable star in the constellation of Phoenix. It has an average visual apparent magnitude of 6.47, so it is at the limit of naked eye visibility. From parallax measurements by the Gaia spacecraft, it is located at a distance of 322 light-years from Earth. Its absolute magnitude is calculated at 1.65.

Rho Phoenicis is a variable star in the constellation of Phoenix. From parallax measurements by the Gaia spacecraft, it is located at a distance of 245 light-years from Earth.

FG Virginis is a well-studied variable star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It is a dim star, near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye, with an apparent visual magnitude that ranges from 6.53 down to 6.58. The star is located at a distance of 273.5 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +16 km/s. Because of its position near the ecliptic, it is subject to lunar occultations.

AI Velorum is a variable star in the southern constellation of Vela, abbreviated AI Vel. It is a prototype for a class of high amplitude Delta Scuti variables. The apparent visual magnitude of this star fluctuates around 6.56, which is just bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye. The distance to AI Vel is approximately 327 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of about 9 km/s.
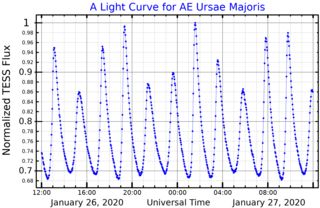
AE Ursae Majoris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major, abbreviated AE UMa. It is a variable star that ranges in brightness from a peak apparent visual magnitude of 10.86 down to 11.52. The distance to this star is approximately 2,400 light years based on parallax measurements.

VZ Cancri is a variable star in the constellation Cancer, abbreviated VZ Cnc. It varies in brightness with a period of 0.178364 days, from an apparent visual magnitude of 7.18 down to 7.91, which lies below the typical threshold of visibility for the naked eye. The distance to this star is approximately 724 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is receding from the Sun with a radial velocity of 25 km/s.

HD 40372, also known as 59 Orionis, V1004 Orionis and HR 2100, is a variable star in the constellation Orion. Its apparent magnitude varies between magnitude 5.88 and 5.92, making it faintly visible to the naked eye for an observer far from light polluted urban areas. HD 40372 exhibits two types of variability; it is an eclipsing binary star and one of the two stars is a Delta Scuti variable star.
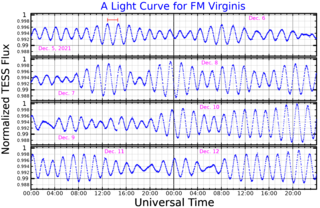
32 Virginis, also known as FM Virginis, is a star located about 250 light years from the Earth, in the constellation Virgo. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 5.20 to 5.28, making it faintly visible to the naked eye of an observer well away from city lights. 32 Virginis is a binary star, and the more massive component of the binary is a Delta Scuti variable star which oscillates with a dominant period of 103.51 minutes.
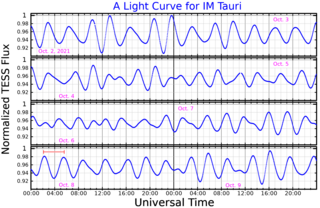
44 Tauri, also known as HD 1287 and IM Tauri, is a star located about 210 light years from the Earth, in the constellation Taurus. It is a 5th magnitude star, making it faintly visible to the naked eye of an observer located far from city lights. It is a Delta Scuti variable star, ranging between magnitude 5.37 and 5.58 over a period of about 3.5 hours.





















